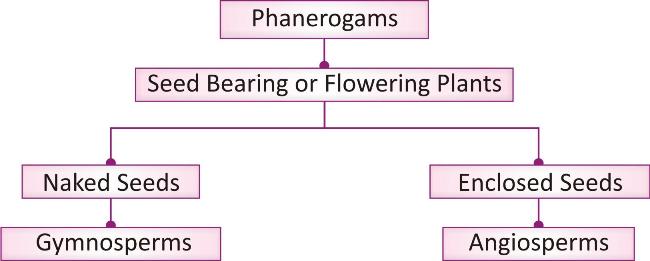
SUB-KINGDOM: PHANEROGAMAE (PHANERO-VISIBLE, GAMOUS-GAMETES/ REPRODUCTIVE PARTS)
-
This subkingdom includes plants that bear external flowers and able to produce seeds.
-
The reproductive parts are well developed in these plants.
-
They reproduce through the formation of seeds which consist of embryo.
-
The further classification depends upon the presence of naked seeds or seeds enclosed in fruits.
-
The plant body is well-differentiated into root, stem and leaves.
-
Vascular system (xylem and phloem) is well developed.
-
An embryo develops from fertilized egg.
Division Gymnosperm: (Gymno-Naked, Sperm-Seed)
-
They are most primitive and simple seed bearing plants.
-
The seeds produced by these plants are naked, i.e., not enclosed within fruits.
-
Plants of this group are woody, perennial and evergreen.
-
Vascular system is well developed but xylem tissue lacks vessels and phloem tissue lacks companion cells.
-
Sporophylls (spore bearing leaves) aggregate to form cones. There are separate male and female cones.
Examples:
-
cycas, deodar, pinus etc.

Division Angiosperm: (Angio-Case/Covered, Sperm-Seed):
-
Angiosperms are highly evolved plants having well differentiated body with developed vascular system.
-
They produce seeds that are enclosed within the fruit. Seeds are comprised of embryo that has precursor tissues for the development of plant.
-
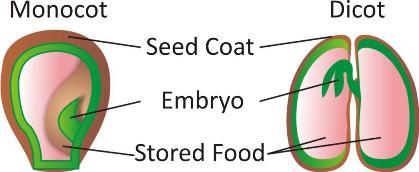
Plant embryos in seeds are covered with structures called cotyledons.
-
Cotyledons are also known as seed leaves as they emerge as green leaves when the seeds germinate.
-
Angiosperms are further classified on the basis of number of seeds.
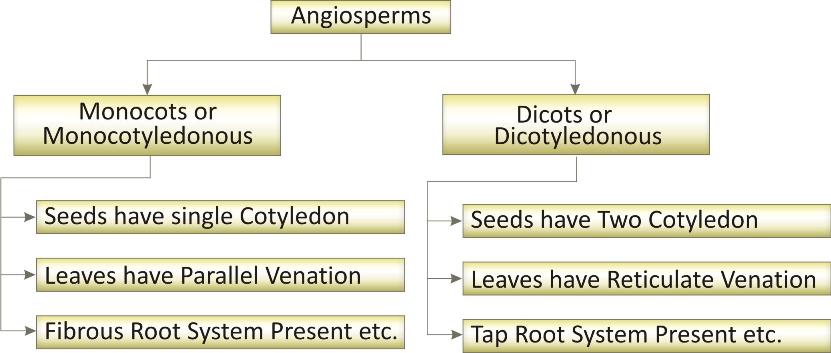
Monocotyledous (Monocot):
-
The seeds of these plants have only one cotyledon.
-
Their leaves have parallel venation.
-
The root system consists of similar fibrous roots.
-
The flowers are trimerous, i.e., have there or multiple of three petals.
Example:
-
Maize, wheat, rice, barley, bamboo, coconut, banana, sugarcane etc.

Dicotyledonous (Dicots)
-
The seeds produced by these plants have embryos with two fleshy leaves, i.e., the cotyledons.
-
Their leaves have reticulate venation, with a network of veins.
-
The root system has a prominent tap root.
Examples:
-
Pea, potato, sunflower, banyan, margosa (neem), apple, mango, beans, gram, oak etc.

Comparison of monocots and dicots







