Force and laws of motion Worksheet-4
A. 22.5 m/s B. 225 m/s
C. 82.5 m/s D. None of these
A. 4.4 m/s B. 44 m/s C. 20 m/s D. 5.6 m/s
A. mass B. Energy C. Momentum D. Velocity
A. 32 N B. 0 N C. 2 N D. 8 N
A. Always act on the same body but in opposite direction
B. Always on different bodies in opposite directions
C. Have same magnitudes and directions
D. Act on either body at normal to each other
A. m s–1 B. kg.ms–1 C. kg.ms–2 D. Nm2kg–2
A. 50 N B. 2500 N C. 10 N D. 500 N
A. A B. B C. C D. D
A. 4 B. 100 C. 0.25 D. 2.5
A. A force can stop a lighter vehicle as a heavier vehicle which are moving
B. A force can accelerate a lighter vehicle more easily than a heavier vehicle which are moving
C. A force exerted by a lighter vehicle on collision with a heavier vehicle results in both the vehicles coming to a standstill
D. A force exerted by the escaping air from a balloon in the downward direction makes the balloon to go upwards
A. Exert larger force on the ball
B. Reduce the force exerted by the ball
C. Increase the rate of change of momentum
D. Keep the ball in hands firmly
Answer:
Explanation: First let’s calculate the total momentum of both the cars, before and after the collision.
(a) 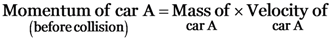
= 1500 × 25
= 37500 kg.m/s
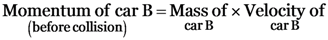
= 1000 × 15
= 15000 kg.m/s
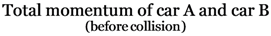 = 37500 + 15000
= 37500 + 15000
= 52500 kg.m/s ……….(1)
(b) After collision, the velocity of car A is 20 m/s.
Momentum of car A = 1500 × 20
(after collision) = 30000 kg.m/s
After collision, suppose the velocity of car B is v m/s
Momentum of car B = 1000 × v
(after collision) = 1000 v kg.m/s
Total momentum of car A and car B
= 30000 + 1000 v ……….(2)
(after collision)
According to the law of conservation of momentum :
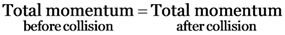
52500 = 30000 + 1000 v
1000 v= 52500 – 30000
1000 v = 22500
v = 22.5 m/s
hence the velocity of car B after the collision will be 22.5 m/s.
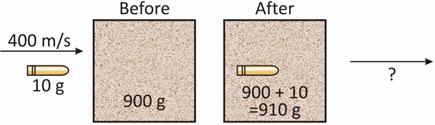
Explanation: Mass of the bullet, m1 = 10 g
= (10/1000)kg
= 0.01 kg
velocity of the bullet, v1 = 400 m/s
Momentum of the bullet = m1 × v1
= 0.01 × 400 kg.m/s ……..(1)
Now, the bullet gets embedded into a wooden block of mass 900 g. Now the mass of wooden block along with the embedded bullet will be 900 + 10 = 910 g.
Mass of wooden block + Bullet, m2 = 900 + 10
= 0.91 kg
Velocity of wooden block + bullet, v2 = ?
Momentum of wooden block + bullet = m2 × v2
= 0.91 × v2 kg.m/s ……….(2)
According to the law of conservation of momentum, the two momenta as given by equations (1) and (2) should be equal.
m1 × v1 = m2 × v2
0.01 × 400 = 0.91 × v2
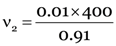 = 4.4 m/s
= 4.4 m/s
Hence the velocity acquired by the wooden block (having the bullet embedded in it) is 4.4 metres per second.
Explanation: Acceleration is inversely proportional to mass if force is constant.
Explanation: Using relation F = ma where m is mass and a is acceleration.