Point:
A point is that which has no part. A point is represented by a fine dot made by a sharp pencil on a sheet of paper.
Plane:
The surface of a smooth wall or the surface of a sheet of paper or the surface of a smooth black board is close examples of a plane.

Line:
A line is breadth less length e.g., the edge of a ruler, the edge of the top of a table, the meeting place of two walls of a room is also examples of a geometrical straight line.

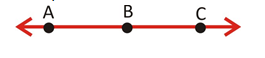
Collinear Points:
Three or more points are said to be collinear, if there is a line that contains all of them.
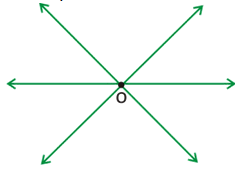
Concurrent Lines:
Three or more lines are said to be concurrent, if all of them pass through a common point.
Two distinct lines cannot have more than one point in common.
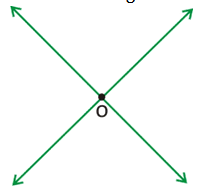
Intersecting Lines:
Two lines who meet at one point are said to be intersecting lines. The common point is called the ‘point of intersection’.
Parallel Lines:
Two lines l and m in a plane are said to be parallel lines, if l ⋂ m = ∅. If l and m are parallel lines in a plane then denote as l || m.

Two lines which are both parallel to the other line then all lines are parallel to each other.
If l, m, n are lines in the same plane such that l intersects m and n || m, then l intersects n also.
If l and m are intersecting line, l || p and q || m, then p and q also intersect.
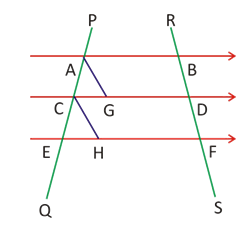
Intercept Theorem:
If a transversal makes equal intercepts on three or more parallel lines, any other line cutting them will also make equal intercepts.
Hence, AC/CE = BD/DF