Carbon and its compounds Worksheet-9
Fill in the blanks:
The various physical forms in which an element can exist are called ______ of the element.
Graphite is a good conductor of electricity but diamond is not because graphite has _____.
Carbon compounds are non-conductors of electricity as they are _____.
______ is the name of second member of homologous series of compounds of general formula CnH2nO.
The compound which comes before pentanone in the homologous series of ketone is _____.
The difference in the molecular moss of C3H7OH and C2H5COOH is ______.
Formation of Propyl chloride from propane is an example of ______ reaction.
Multiple-Choice Question:
(A) Diamond
(B) Graphite
(C) Buckminster fullerene
(D) Both Buckminster fullerene and graphite
(A) C7H15OH (B) C6H13CHO (C) C3H7COC3H7 (D) C6H13COOH
(A) C3H7Cl (B) C3H6Cl2 (C) C3H6Cl (D) C3H8Cl
(A) Pentene (B) Hexene (C) Hexyne (D) Hexane
(A) Pentanoic acid (B) Propanoic acid
(C) Butanal (D) Butanoic acid
(A) 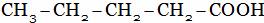
(B) 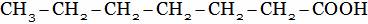
(C) 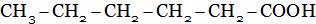
(D) 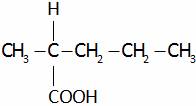
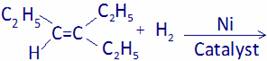
(A) 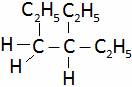 (B)
(B) 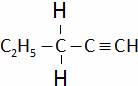
(C) 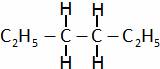 (D) All of these
(D) All of these
(A) NaOH + C2H6 (B) C2H5ONa + H2
(C) CH4 + CH3 ONa (D) H2 gas + CH3 ONa
Answer key:
Allotropes
Free electrons/Free electron
Covalent
Ethanal/Butanone
Butanone
16/ sixteen
Substitution
(C)
(A)
(A)
(D)
(D)
(C)
(C)
(B)