LATENT HEAT
-
When a substance changes phase, that is it goes from either a solid to a liquid or liquid to gas, it requires energy to do so. The potential energy stored in the in the substance needs to be overcome by the kinetic energy of the particles which is due to the motion of the particles before the substance can change phase.
-
The energy required to change the phase of a substance is known as a latent heat. The word latent means hidden.
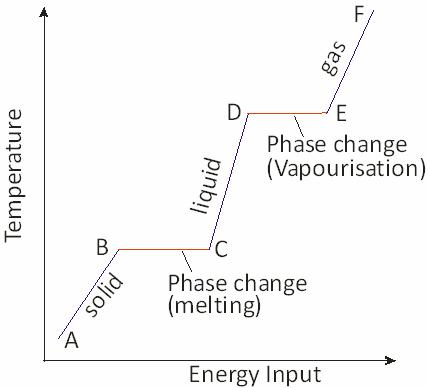
Phase changes are indicated by flat regions where heat energy used to overcome attractive forces between molecules
-
Starting a point A, the substance is in its solid phase, heating it brings the temperature up to its melting point but the material is still a solid at point B.
-
As it is heated further, the energy from the heat source goes into breaking the bonds holding the atoms in place. This takes place from B to C. At point C all of the solid phase has been transformed into the liquid phase. Once again, as energy is added the energy goes into the kinetic energy of the particles raising the temperature, (C to D). At point D the temperature has reached its boiling point but it is still in the liquid phase.
-
From points D to E thermal energy is overcoming the bonds and the particles have enough kinetic energy to escape from the liquid. The substance is entering the gas phase.
-
Beyond E, further heating under pressure can raise the temperature still further is how a pressure cooker works.
