PHYLUM ANNELIDA: [ANNELUS-RING]
-
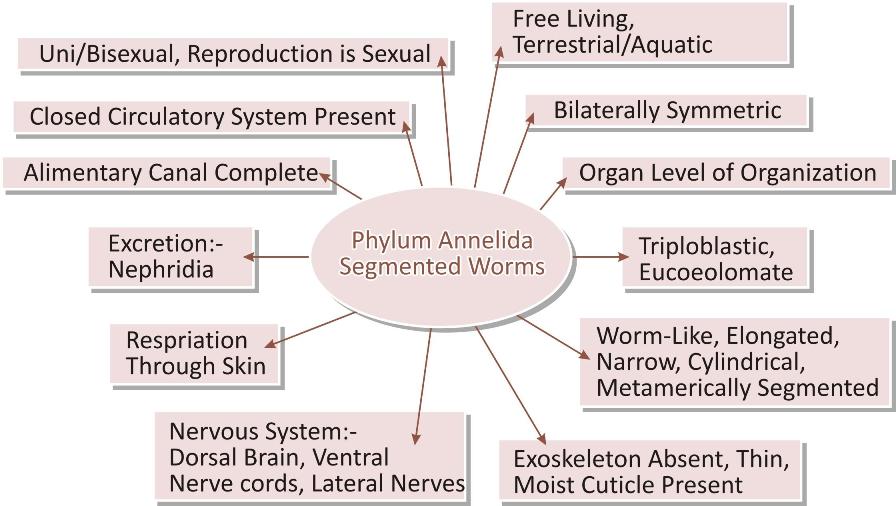
The organisms are commonly known as segmented worms.
-
Habit and Habitat: they are free-living organisms found in different habitat like terrestrial [soil] or water both marine and fresh.
-
Symmetry: they are bilaterally symmetric [left and right side of the body has same design].
-
Body cavity: True coelomic cavity is present so they are known as coelomates or eucoelomates.
-
Body differentiation: They are multicellular, real organs present with extensive diffrentiataion.
-
Germ layer: They are the first triploploblastic animals.
-
Body organization: Body is worm-like, elongated, narrow and cylindrical. Body is metamerically segmented by external grooves and internal septa.
-
Skeleton: Exoskeleton is absent; body is covered with thin moist cuticle.
-
Alimentary canal/ digestive tract is complete and straight having two openings- mouth and anus.
-
Close blood circulatory system is present. It is the first group to have developed circulatory system.
-
Respiration occurs through skin.
-
Excretion takes place through structures called nephridia present in each segment.
-
Nervous system is comprised of dorsal brain, ventral nerve cord and lateral nerves.
-
They are unisexual or bisexual. Reproduction is sexual.
-
Paired locomotory organs are present [setae or parapodia]
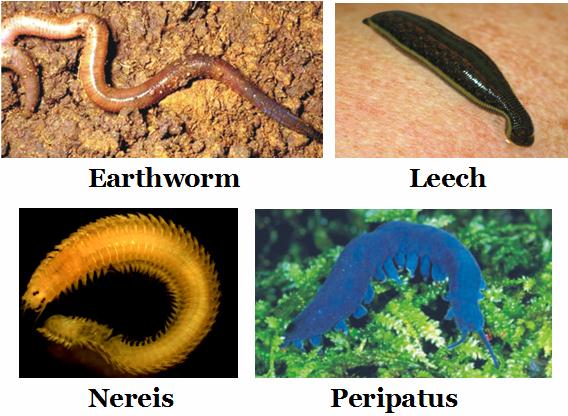
Examples:
Earthworm [Pheretima], leech [Hirudinaria], Neries etc.

Comparison of worms: platyhelminthes, nematode and annelida
|
Feature
|
Platyhelminthes
|
Nematode
|
Annelida
|
|
Habitat
|
Host body or aquatic
|
Host body
|
Soil, water
|
|
Habit
|
Free living or parasitic
|
Parasitic, few are free living
|
Free living
|
|
Symmetry
|
Bilateral
|
Bilateral
|
Bilateral
|
|
Body organisation
|
Tissue
|
Organ
|
Organ
|
|
Body cavity
|
Acoelomate
|
Pseudocoelomate
|
Eucoelomate
|
|
Germ layer
|
Triploblastic
|
Triploblastic
|
Triploblastic
|
|
Exoskeleton
|
Absent
|
absent
|
absent
|

