Light Worksheet-6
Answer:
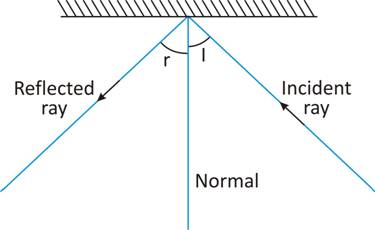
Following are the laws of reflection:
(i) When a ray of light falls on a reflected surface it is reflected in such a way that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, i.e. ∠i = ∠r
(ii) The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
(i) Plane mirror form virtual images.
(ii) Plane mirror form erect images.
(iii) Image is laterally inverted.
(iv) Image formed is of the same size as the object.
(v) The distance of image from the mirror is equal to the distance of object from the mirror.
Remove the mirror. Draw a line making an angle of 90° to the line representing the mirror at the point where the incident ray strikes the mirror. This line is known as the normal.
The angle between the normal and incident ray is called the angle of incidence (∠i).
The angle between the normal and the reflected ray is known as the angle of reflection (∠r). Measure the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection.
Repeat the activity several times by changing the angle of incidence.
Every time the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
This proves that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
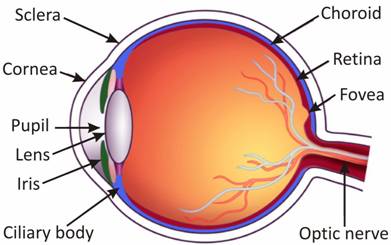
The outer coat of the eye is white. It is tough so that it can protect the interior part of the eyes from any mishap or accident.
Its transparent front part is called cornea.
Behind the cornea, a dark muscular structure called iris.
In the iris, there is a small opening called pupil.
The size of the pupil is controlled by the iris.
The iris controls the amount of light entering the eye.
Behind the pupil of the eye is a lens which is thicker in the centre.
The lens focuses light on the retina.
The retina contains several nerve cells.
Sensations felt by the nerve cells are then transmitted to the brain through the optic nerve. There are two kinds of cells cones and rods.
In this method text is written on a thick paper using special symbols representing the letters of alphabet. Groups of dots are used to write letters.
There is Braille code for common languages, Mathematics and Scientific notation. Braille system has 63 dots patterns.
Each pattern represents a letter, a combination of letters, a common word or a grammatical sign.
Dots are arranged in cells of two vertical rows of three dots each.
Codes of music and mathematics are different. Any language can be read through the codes of Braille.