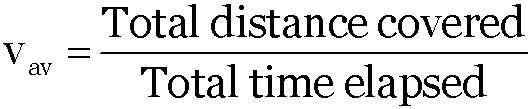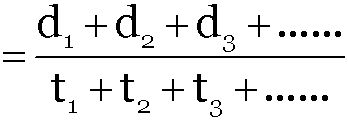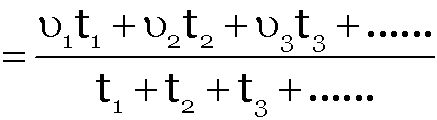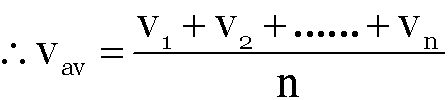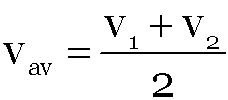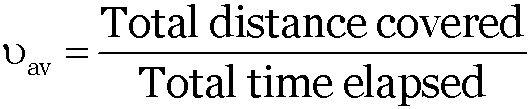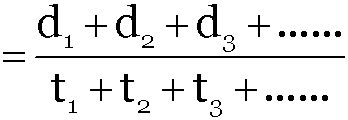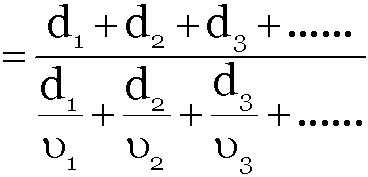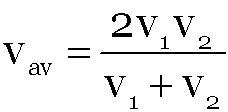UNIFORM MOTION AND NON-UNIFORM MOTION
-
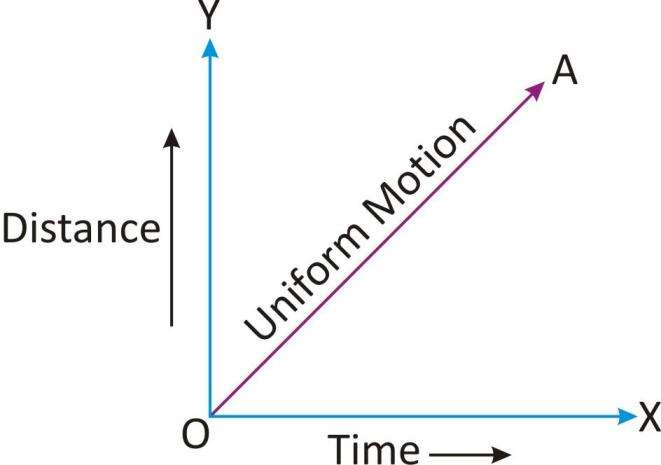
A body has a uniform motion if it travels equal distances in equal interval of time.
-
The distance time graph for uniform motion is a straight line.
-
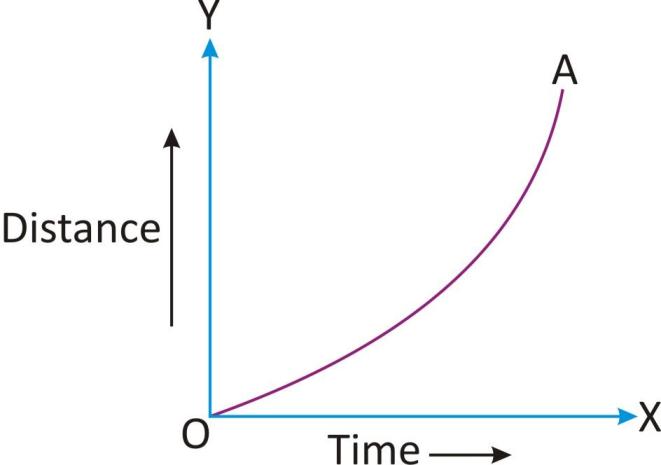
A body has a non-uniform motion if it does not travel equal distance in equal intervals of time. The motion of a freely falling body is an example of non-uniform motion.
-
The distance time graph for a non-uniform motion is a curved line.
-
A non uniform motion is also called an accelerated or retarded motion.
Speed:
-
It is the distance covered in unit time.
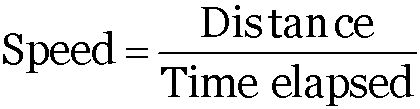
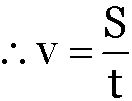
-
Where v is the speed of the body S is the distance travelled in time t.
-
Speed is a scalar quantity as it has only magnitude, but has no specified direction.
-
SI unit of speed is m/s or ms–1.
Uniform speed:
-
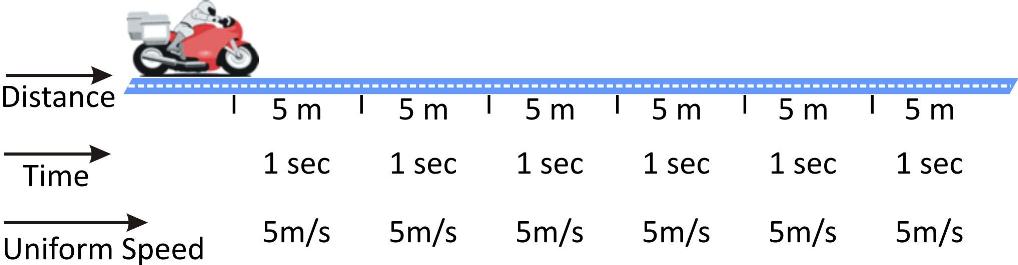
When a particle covers equal distances in equal intervals of time, then it is said to be moving with uniform speed.
-
For example, in illustration given below, motorcyclist travels equal distance (= 5 m) in each second. So we can say that particle is moving with uniform speed of 5 m/s.
Non-uniform (variable) speed:
-
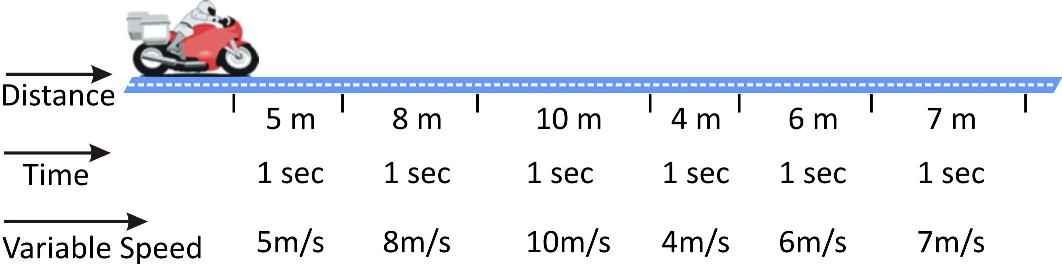
In non-uniform speed particle covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time.
-
For Example, in illustration given below, motorcyclist travels 5m in 1st second, 8m in 2nd second, 10m in 3rd second, 4m in 4th second etc. Therefore its speed is different for every time interval of one second. This means particle is moving with variable speed.
Average speed:
-
It is the ratio of the total distance travelled (path length) by the object to the total time taken.
Average speed = 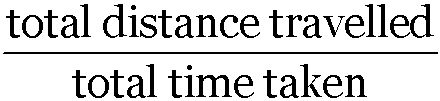
-
The average speed of a particle for a given ‘interval of time’ is defined as the ratio of distance traveled to the time taken.
Average speed = 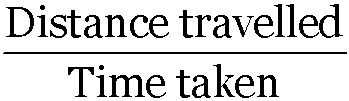
-
Time average speed
-
When particle moves with different uniform speed
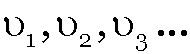 etc in different time intervals t1, t2, t3, ... etc respectively, its average speed over the total time of journey is given as
etc in different time intervals t1, t2, t3, ... etc respectively, its average speed over the total time of journey is given as
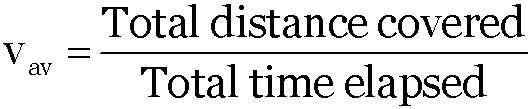
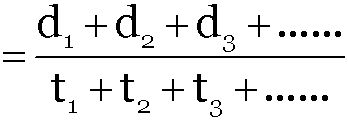
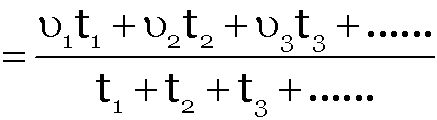
If time intervals are equal then t1 = t2 = t3 ... tn = t
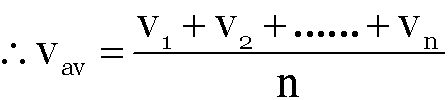
-
It means average speed is equal to arithmetic mean
-
When particle moves with speed v1 up to half time of its total motion and in rest time it is moving with speed v2 then
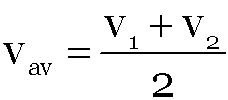
-
When a particle describes different distances d1, d2, d3,... with different time intervals t1, t2, t3, ... with speeds v1, v2, v3 ... respectively then the speed of particle averaged over the total distance can be given as
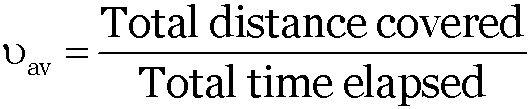
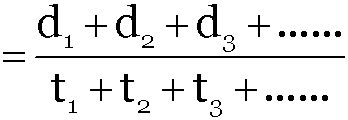
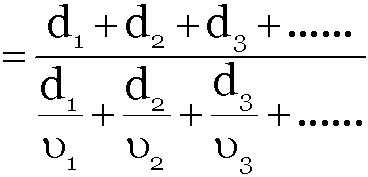
-
When particle moves the first half of a distance at a speed of v1 and second half of the distance at speed v2 then
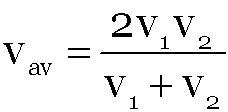


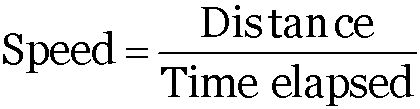
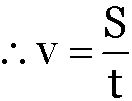


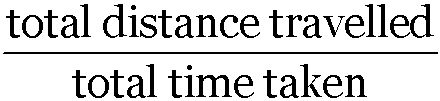
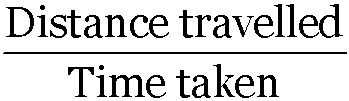
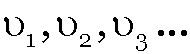 etc in different time intervals t1, t2, t3, ... etc respectively, its average speed over the total time of journey is given as
etc in different time intervals t1, t2, t3, ... etc respectively, its average speed over the total time of journey is given as