WINDS-MOVEMENT OF AIR
-
Beside temperature regulation, air also helps in maintaining the weather-wind, rain, snow etc.
-
Wind is a flow of gases on a large scale. Since air is a mixture of gases so due to variation in temperature and pressure it tends to move from one region to the other resulting in winds.
Generation of wind:
-
The movement of air is the result of changes that take place in our atmosphere due to the heating of air and the formation of water vapor.
-
When solar radiations fall on the earth, some radiations are absorbed while most of it are reflected/ re-radiated by the surface of the land and water bodies.
-
These reflected radiations increase the atmospheric temperature and sets convection current in the air.
-
Since the land gets heated faster than water, the air over the land also gets heated faster than the water bodies. This creates a temperature and pressure difference between land and water body region due to which raised hot air tends to flow from a region of high pressure to the region of lower pressure. Hence generating the Winds.
-
The direction of flow of wind varies during day and night in coastal region.
Wind in Coastal region:
-
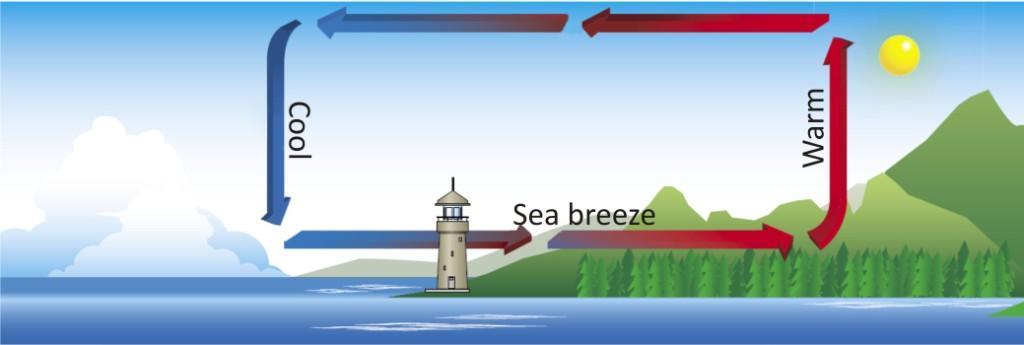
In coastal regions during the day, the air above the land gets heated faster and starts rising.
-
As this air rises, a region of low pressure is created and air over the sea moves into this area of low pressure. The movement of air from one region to the other creates winds. During the day, the direction of the wind would be from the sea to the land which is known as sea breeze.
-
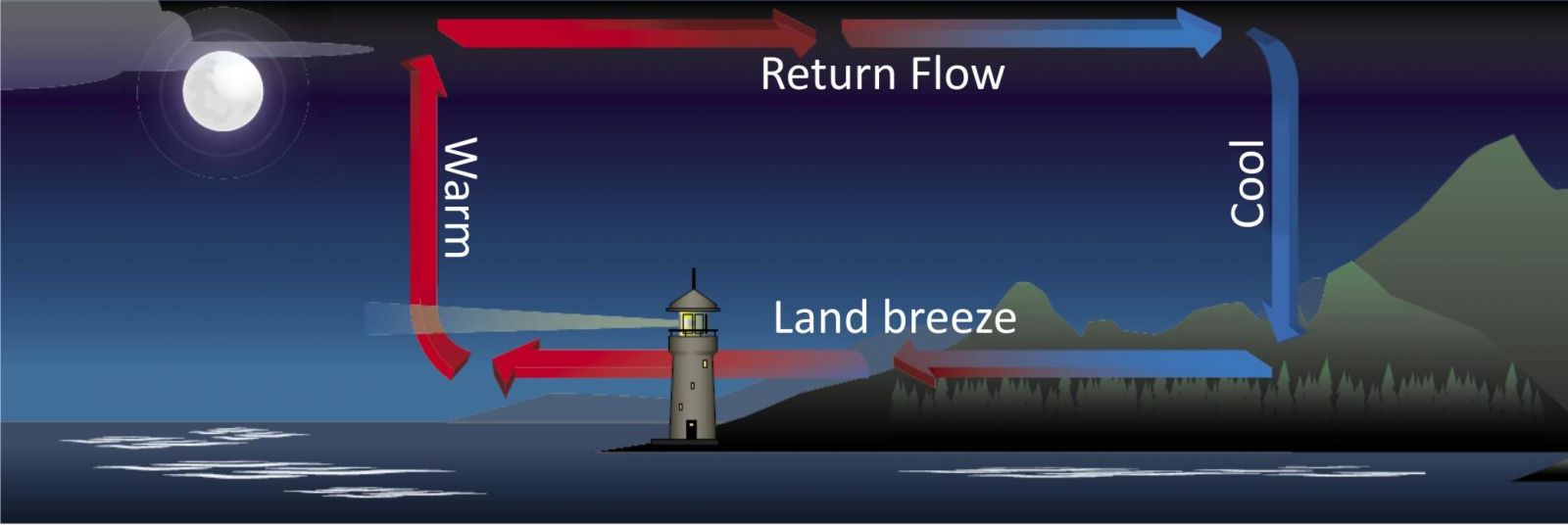
At night, both land and sea starts to cool. Since water cools down slower than the land, the air above water would be warmer than the air above land. So the air from land tends to move towards sea from the land and thus the wind generated is known as land breeze.
Factors affecting direction of wind:
-
Uneven heating of land in different parts of the earth.
-
Differences in heating and cooling properties of land and water bodies.
-
Vaporization and condensation of water and water vapors.
-
Rotation of the earth around the sun.
-
Diversion of wind due to the presence of mountain ranges in its path.

