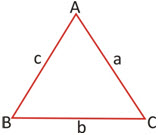
Perimeter of a Triangle:
If a, b and c units be the lengths of the sides of a triangle, perimeter = a + b + c
or 2s = a + b + c, where 2s denotes the perimeter of the triangle.
Heron’s Formula for Area of a Triangle:
If a, b and c are the sides of a triangle and 2s = a + b + c, the area of the triangle is given by:
A = √s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)
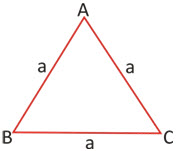
Area of an Equilateral Triangle:
Let ‘a’ be the side of an equilateral triangle. Then,
Hence, A = ((√3)/4)side2
Sine Formula:
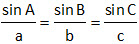
Area of triangle = (1/2) ab sin c = (1/2) bc sin A = (1/2) ac sin B
Cosine formula:
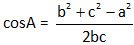
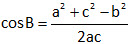
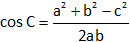
Perimeter and Area of a Rectangle:
P = 2(l + b)
A = l × b

Properties of a Rectangle:
Opposite sides are parallel, i.e., AB || DC and AD || BC.
Opposite sides are equal, i.e., AB = DC and AD = BC.
Each angle is right angle, i.e., ∠A = ∠B = ∠C = ∠D = 90º.
Diagonals are equal, i.e., AC = BD.
Diagonals bisects each other, i.e., AO = OC and BO = OD.
Perimeter and Area of a Square:
P = 4a units
A = a2 square units

Properties of Square:
All the sides are equal.
Each angle is of 90°.
The diagonals are equal.
The diagonals are perpendicular to each other.
Angle between a diagonal and a side is 45°.
Parallelogram:
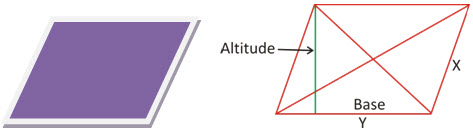
A quadrilateral, which has both pair of opposite parallel sides, is called a parallelogram.
In a parallelogram, opposite sides are equal.
The opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal.
The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
Perimeter P = 2(x + y) units
Area A = Base × Altitude
Rhombus:
If all sides of a parallelogram are equal, then it is a rhombus.
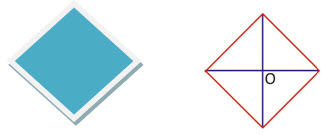
P = 4 × side
Area of rhombus = 1/2 [Product of the diagonals]
Properties of a Rhombus:
Opposite sides are parallel, i.e., AB || DC and AD || BC.
All the sides are equal, i.e., AB = BC = CD = DA.
Opposite angles are equal, i.e., ∠A = ∠C and ∠B = ∠D.
Diagonals bisect each other at right angle, i.e.,
OA = OC = (1/2)AC; OB = OD = (1/2)BD, and
∠AOB = ∠BOC = ∠COD = ∠AOD = 90º.
Diagonals bisect and the angles at the vertices, i.e.,
∠OAB = ∠OAD; ∠OBA = ∠OBC;
∠OCB = ∠OCD; ∠ODC = ∠ODA
Trapezium:
A quadrilateral, which has one pair of opposite parallel sides, is called a trapezium.
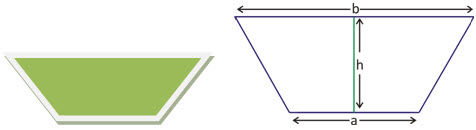
Area of the trapezium is equal to half the altitude multiple by the sum of the parallel sides. Area = (1/2)h[a+b]
Area of a Quadrilateral:
In the given figure, ABCD is a quadrilateral whose diagonal BD divides it into two triangles, i.e., ΔABD and ΔBCD. AE and CF are perpendiculars from A and C to BD.
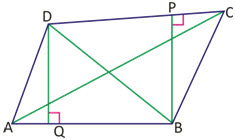
Area of the quadrilateral ABCD
= area of ΔABD + area of ΔBCD
= (1/2)BD.AE+(1/2)BD.CF
= (1/2)BD(AE+CF)sq.unit.