ANIMAL KINGDOM
-
Animals are eukaryotic, multicellular heterotrophic organisms having no cell wall. They are classified on the basis of some basic features.
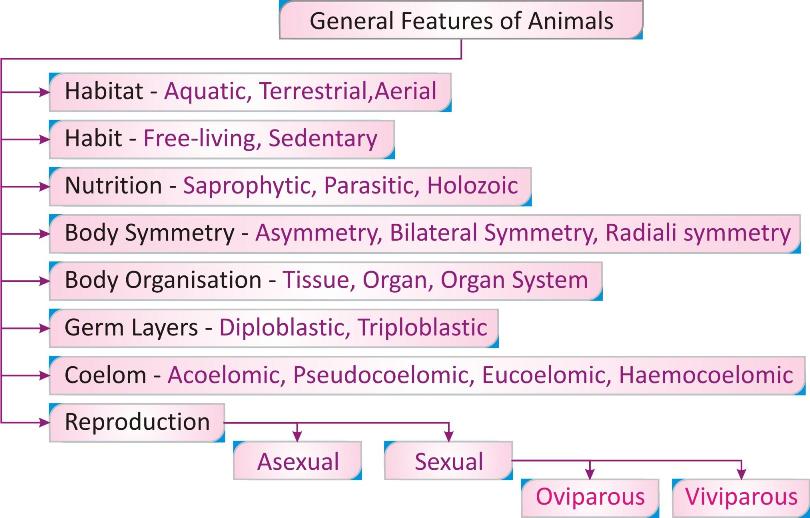
Habitat:
-
On the basis of habitat where organisms live they can be aquatic (water], terrestrial [land] or aerial [flying animals]. There are the organisms that can share more than one habitat.

Habit:
-
Free living: Able to move and lead an independent life.

-
Sedentary: non- motile, remains attached to the substratum.

Nutrition:
-
Saprophytic- feeds on dead and decayed material
-
Parasitic: obtains simplified food material from other living organisms.
-
Holozoic: feeds on complex food material and digests it inside the body.
Body Symmetry:
-
Body symmetry is the similarity of parts in different regions and directions of body. It refers to the arrangement of body parts in a balanced manner through the body axis to maintain the shape of its body. On the basis of symmetry, the animals can be asymmetric, radially symmetric or bilaterally symmetric.
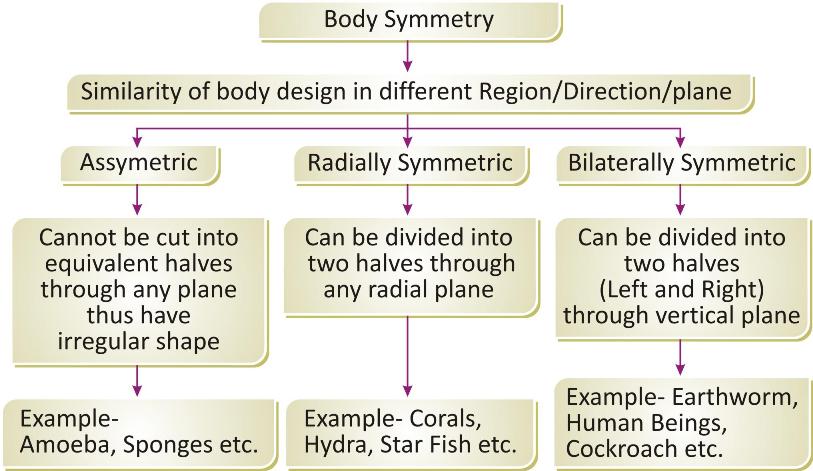
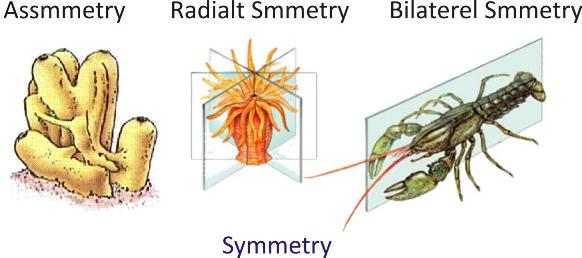
Body Organisation:
-
Animals are sub-classified on the basis of organization of cells into tissue, organ or organ system or further complexity of organ system.
Development From Germ layers:
-
All multicellular organisms develop from the tissue layers known as germ layers during embryonic phase. Depending on this the organisms may be of different types.
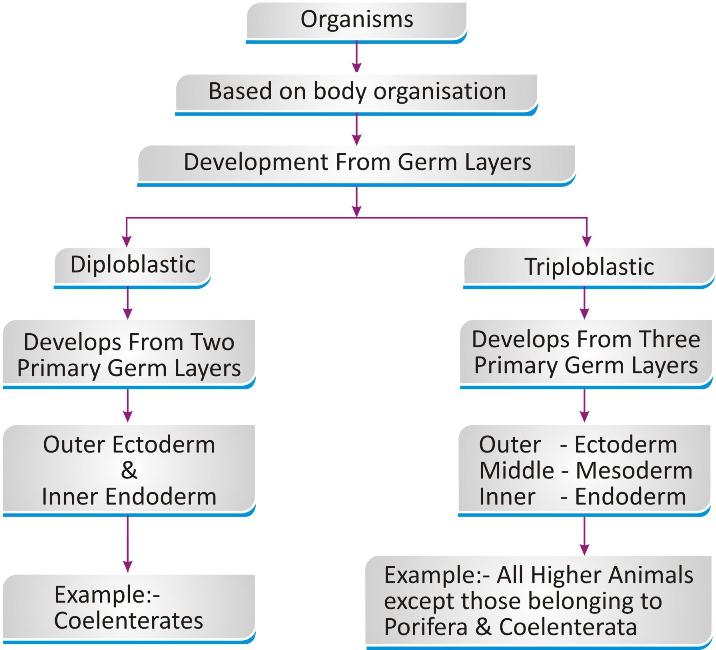
Body Cavity or Coelom:
-
Body cavity/ coelom refer to the space present between the body wall and internal gut which is lined by mesoderm. Body cavity can be of different types depending on its development and complexity.
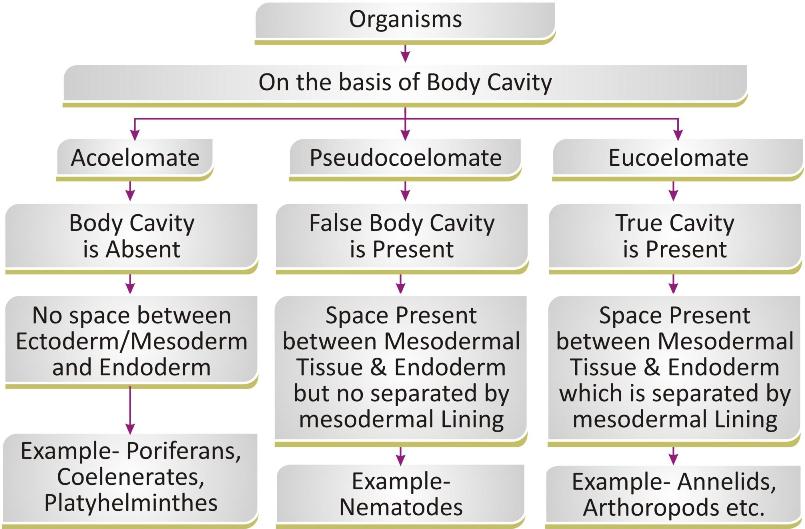
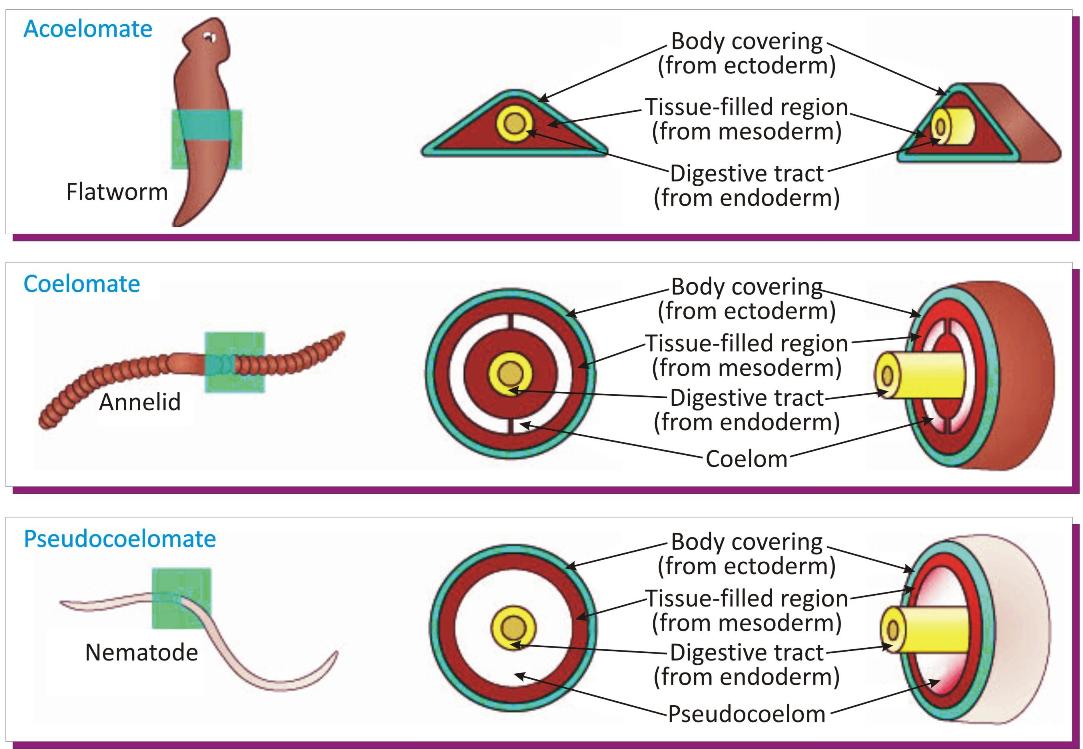
Acoelomate:
-
The animals which do not have coelom are called acoelomate. In these animals, the space between body wall and digestive tract is filled with the special type of connective tissue which leaves no cavity in their body.
Pseudocoelomate:
-
The animals which have body cavity, called pseudocoel the cavity develops from their embryonic blastocoel and not lined by mesoderm.
Coelomate
-
The animals which possess true coelom are called coelomate.
-
They possess usually a spacious cavity between their body wall and digestive tract which is lined by a tissue derived from mesoderm.
-
The coelomic cavity is filled with coelomic fluid.
Haemocoelomate:
-
It is a type of true coelomic cavity which is filled with blood. It is found in organisms having open circulatory system like those belonging to group arthropoda [scorpio] and mollusca [octopus].
Reproduction:
-
Asexual: reproduce by cell division.
-
Sexual: reproduce by fusion of gametes. These organisms can be oviparous [Egg laying] or viviparous [giving birth to young ones].








