KINGDOM FUNGI
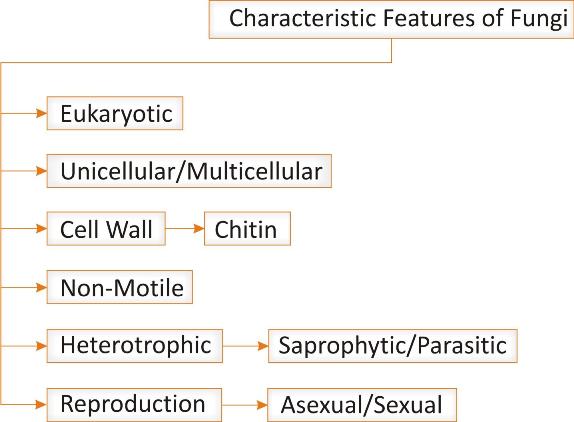
Eukaryotic:
-
They are eukaryotic organisms, i.e., they contain a well defined nucleus and membrane bound organelles.
Cell wall:
-
Fungal cells are covered with cell wall made up of chitin- a complex carbohydrate. Presence of cell wall is a peculiar feature of plant cells and some unicellular organisms also. Unlike fungal cells, plant cell wall is made up of cellulose while in bacteria [unicellular organism] it is made up of peptidoglycan.
Body organization:
-
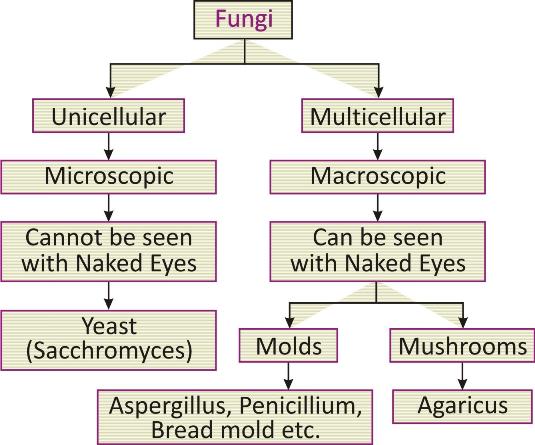
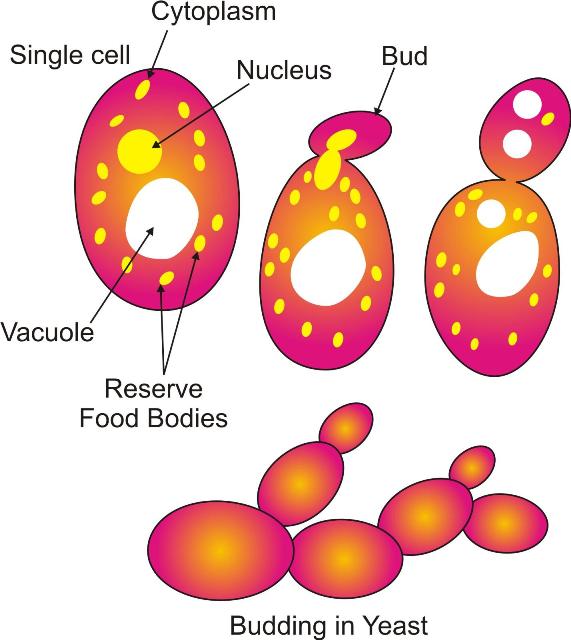
They may be unicellular [yeast] or multicellular [bread mold].
-
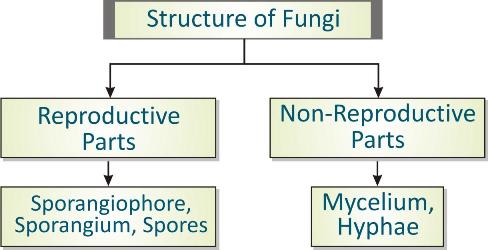
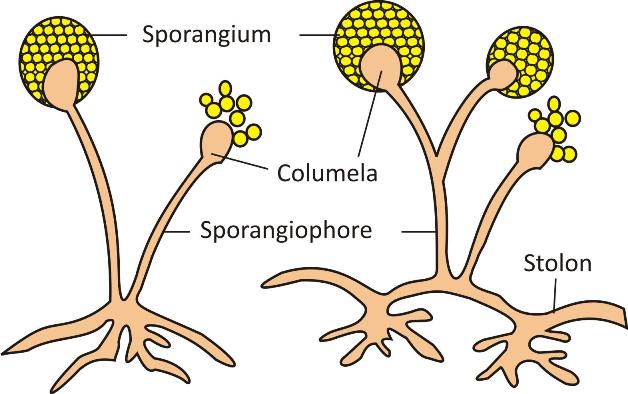
Multicellular organisms live in colony with little body organization, i.e., they have filamentous body sturucture. In such organisms body is composed of several thread-like structures known as hyphae. Hyphae constitute the structure known as mycelium. Some parts are specialized for the process of reproduction and known as sporangium.
Examples:
Yeast : Sacchromyces
Molds: Aspergillum, Penicillium, Mucor, Rhizopus etc.
Mushroom: Agaricus etc.

Locomotion:
-
Organisms of kingdom fungi are non- motile but their spores can spread through different medium.
Mode of nutrition:
-
Fungi is heterotrophic, i. e. it obtains food from outside. They feed on dead and decaying material so known as saprophytic organisms. The reserve food material in these organisms is glycogen like animals.
Reproduction:
-
Fungi can reproduce by asexual mode [budding, fragmentation, spore formation]. It can also reproduce by sexual mode but the mechanism is different from the sexual reproduction that occurs in plants and animals.
Lichens:
-
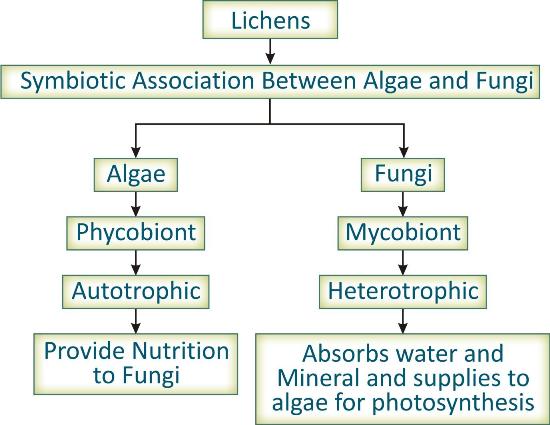
Lichens are the symbiotic association between algal and fungal species where both organisms provide advantage to each other.
-
Symbiotic association is the close interaction between two organisms where each provides advantage to the other.
-
Algae are autotrophic so provide nutrition to fungi while fungi absorb water and mineral from surrounding and supply it to algae. Algae are therefore known as phycobiont and fungi are known as mycobiont.
-
Fungus also provides protection to the algae by growing over it.
-
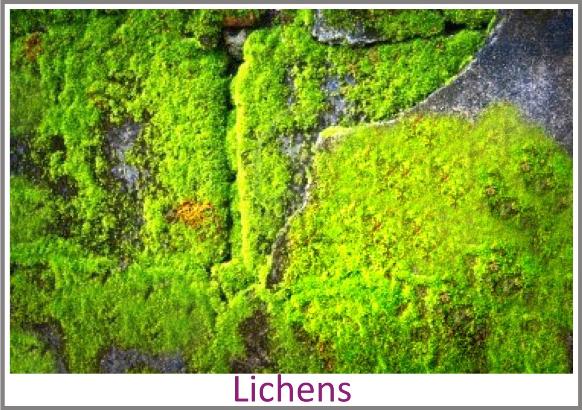
Lichens are observed as slow growing hard and coloured patches on rocks, bark of trees and even on the ground.

Note:
-
Lichens can tolerate prolonged draught and drastic changes in temperature but they are highly sensitive to air pollution.









