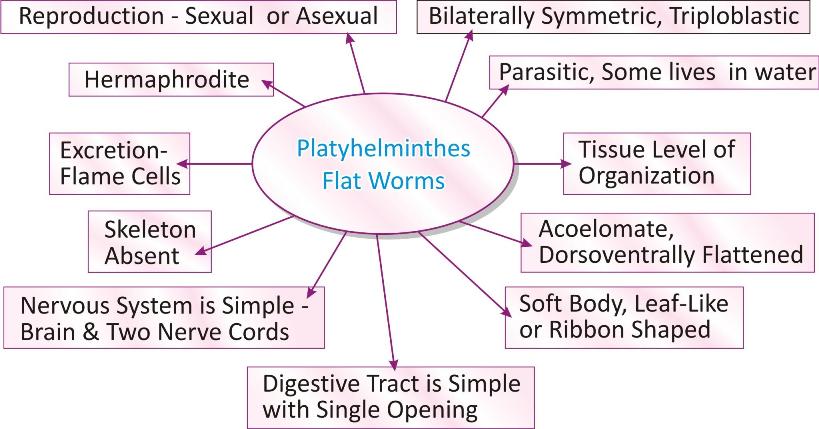
PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES: [PLATY-FLAT, HELMINTHES-WORMS]
-
Habit and Habitat: They are parasitic i.e., they live in other animal’s [host] body; some are free living that lives in fresh or marine water.
-
Symmetry: they are bilaterally symmetric [left and right side of the body has same design].
-
Body cavity: They are acoelomate, i.e., true cavity is absent. Their body is dorsoventrally flattened, i.e., body is flattened from the backside [dorsal] to the abdominal side [ventral].
-
Body differentiation: They are multicellular which possess tissue level of organization with distinct division of labour. More complexity occurs in their tissue differentiation and function.
-
Germ layer: They are the first triploblastic animals where body tissues develop from three layers of cells- Ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. This allows the formation of body lining and some organs. Since they are acoelomate there is no space where well developed organs can be accommodated so they show only tissue grade organization.
-
Body organization: Body is soft, thin, leaf like or ribbon-shaped. They usually have suckers and hook on their body.
-
Skeleton: they lack skeleton.
-
Life processes:
-
Digestive cavity is present with a single opening known as mouth, anus is absent.
-
Respiratory and circulatory systems are absent. Transport of food and oxygen occurs through diffusion.
-
Excretion takes place through special structures known as flame cells.
-
Nervous system is simple, comprised of simple brain and two nerve cord.
-
They are hermaphrodite; both male and female sex organs are located on same body.
-
Reproduction can be asexual [fragmentation and regeneration] or sexual with internal fertilization.
Examples:
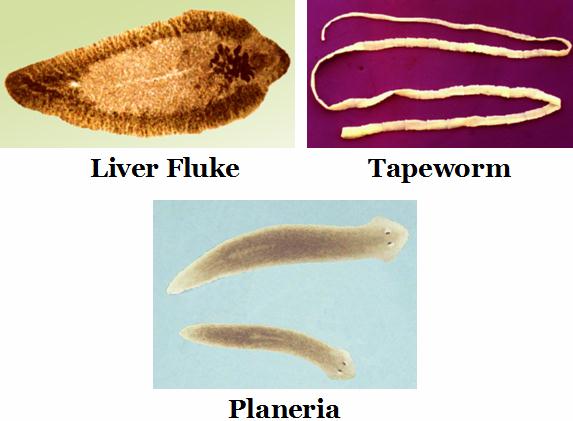
Liver fluke, tapeworm, planaria etc.