SUPERCLASS TETRAPODA
-
It is a superclass of the subphylum Vertebrata of the phylum Chordata.
-
These organisms have jaws with teeth.
-
These animals have two pairs of appendages, i.e., four appendages and hence the name tetrapoda.
-
Each of the appendages has five fingers.
-
The endoskeleton is made up chiefly of bones.
-
Generally, the respiratory organs are lungs.
-
This superclass includes the following four classes:
1. Amphibia
2. Reptilia
3. Aves
4. Mammalia
Class-Amphibia: Amphi-Two, Bios-Life:
-
These organisms lead their life cycle in two habitats thus known as amphibians.
-
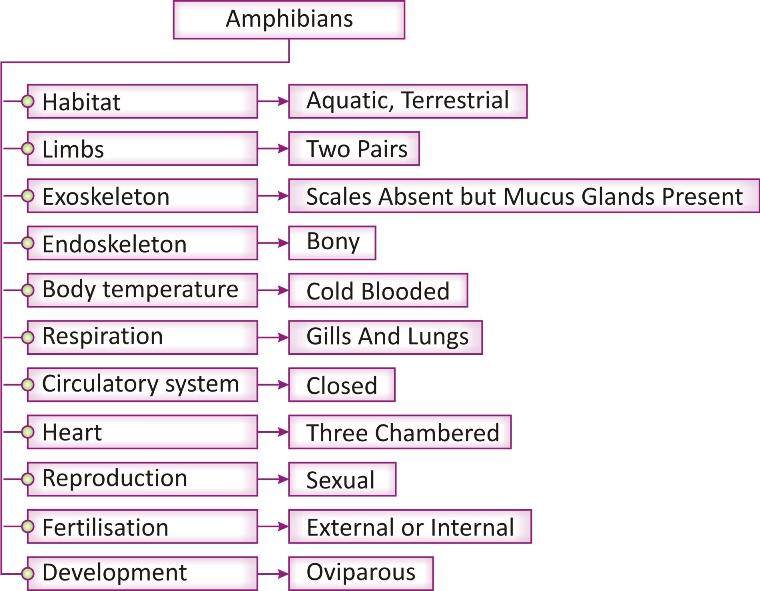
Habitat: Amphibia is the first group among the chordates/ vertebrates that live out of water [on land]. They live on land but lay their eggs in water.
-
Body design: body is divided into head and trunk region but neck is absent, tail may or may not be present. These animals have two pairs of pentadactyl limbs [Exceptions are there].
-
Limbs: They have two pairs of limbs. Limbs are made up of five types of bones.
-
Exoskeleton: Skin is without scales but possess mucus glands that keep the skin most and slimy.
-
Endoskeleton: Internal skeleton is made up of bones.
-
Body temperature: organisms of this group are cold blooded, i.e. their body temperature varies with the change in surrounding/ environmental temperature.
-
Respiration: Respiration occurs by gills, lungs or skin. Their larva usually llive in water and respire through gills. Adults respire through lungs.
-
Circulatory system: Closed circulatory system present with three chambered heart and blood vessels. Heart is comprised of one ventricle and two auricles.
-
Reproduction: they are unisexual organisms that reproduce by sexual mode. Fertilization may be external or internal. They are oviparous organisms.
Examples:
Frogs, toads, salamanders etc.

Class- Reptilia: Repre- To Crawl:
-
These organisms are the first true land animals, have evolved from amphibians, also known as creeping animals.
-
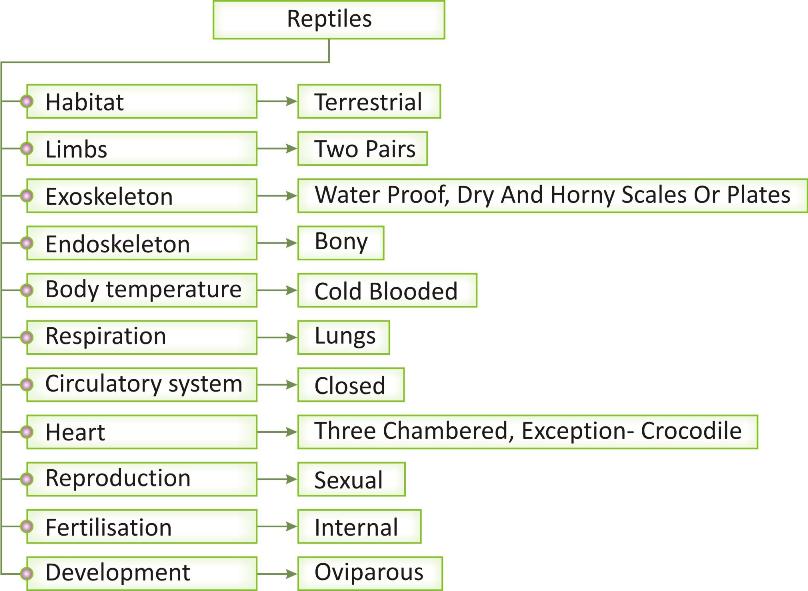
Habitat: They are terrestrial organisms that live on land in warmer regions, may also move to water bodies. Unlike to amphibians, they lay their eggs on land.
-
Body design: body is divided into head, neck and trunk region, tail is well developed in some but reduced in some others.
-
Limbs: They have two pairs of pentadactyl limbs, i.e., Limbs are made up of five types of bones. In some organisms limbs are reduced or vestigial.
-
Exoskeleton: Skin is covered with water proof, dry and horny scales or plates that provide protection to the organism and prevent loss of water from body.
-
Endoskeleton: Internal skeleton is made up of bones.
-
Body temperature: organisms of this group are cold blooded, i.e. their body temperature varies with the change in surrounding/ environmental temperature.
-
Respiration: Respiration occurs through lungs.
-
Circulatory system: Closed circulatory system present with three chambered heart and blood vessels. Heart is comprised of one ventricle and two auricles. Ventricle is partially separated. Exceptionally crocodile has four chambered heart.
-
Reproduction: they are unisexual organisms that reproduce by sexual mode. Fertilization is internal. They are oviparous organisms and lay eggs with hard and thick covering over it on land. Aquatic larval stage is absent.
-
Examples: lizards, turtles, snakes, crocodile etc.

Class- Aves: Avis- Birds:
-
They are commonly known as birds that have evolved from amphibians and have adapted to flying.
-
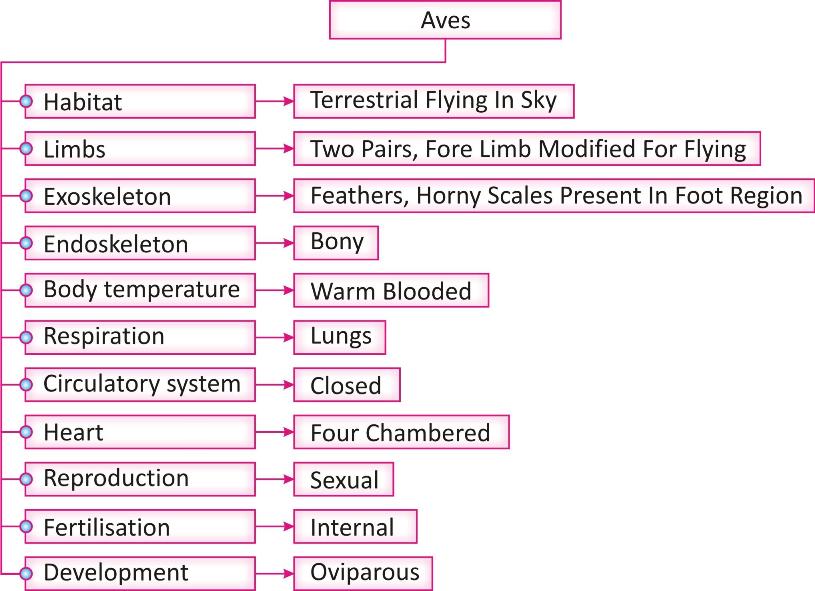
Habitat: They are terrestrial organisms that usually live on trees and are able to fly in the sky, hence also known as aerial organisms.
-
Body design: Body is usually streamlined spindle shaped which is divided into head, neck, trunk, and tail; neck disproportionately long for balancing and food gathering. Their jaws have been modified to beak.
-
Limbs: Two pairs of pentadactyl limbs are present. Front/ Anterior pair is known as fore limbs which is modified into wings for flying; posterior pair/ hind limb is adapted for perching, walking, and swimming; foot has four toes. Wings are vestigial in some birds like penguin [a flightless bird].

-
Exoskeleton: Skin is covered with feathers, horny scales present in foot region, skin glands are absent. Feathers are adapted for flying in to provide warmth to the body.
-
Endoskeleton: Internal skeleton is made up of hollow bones [have air cavities] so as to keep their body weight light and help in flying.
-
Body temperature: organisms of this group are warm blooded, i.e. their body temperature is maintained constant due to metabolism.
-
Respiration: Respiration occurs through lungs.
-
Circulatory system: Closed circulatory system present with four chambered heart and blood vessels. Heart is comprised of two ventricles and two auricles. There is no intermixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. This is required to maintain their high energy needs and constant body temperature.
-
Reproduction: they are unisexual organisms that reproduce by sexual mode. Fertilization is internal. They are oviparous organisms and lay fertilized eggs.
Examples:
pigeon, peacock, parrot, eagle, vulture, ostrich, humming bird etc.

Class- Mammalia: Mammus- Breast:
-
These organisms are unique as they give birth to the young ones and feed them with mammary glands secretion-milk.
-
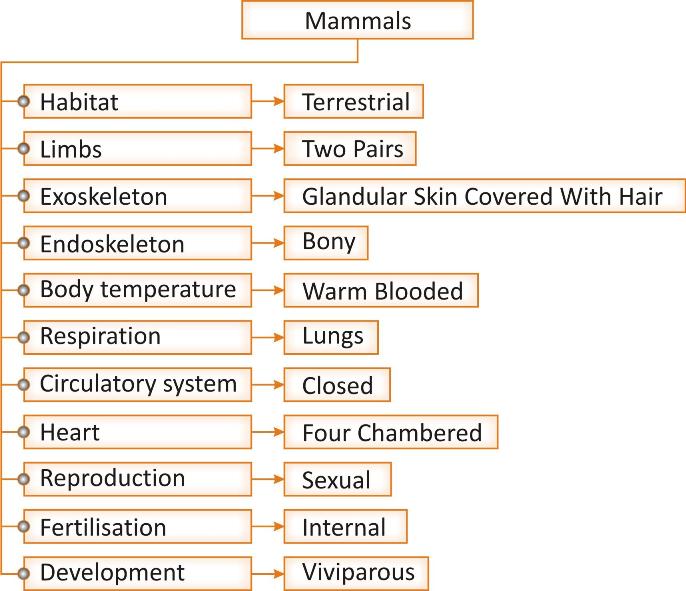
Habitat: They are terrestrial organisms, some may be aquatic. They inhabit in different zones like deserts, polar ice caps, oceans, mountains, forest etc.
-
Body design: Body is divided into head, neck, trunk, and tail. Tail may be absent in some. Movable eyelids and external ear/ pinnae are present. Teeth are embedded in jaws.
-
Limbs: Two pairs of pentadactyl limbs, i.e., fore limbs and hind limbs are present which are modified in different species for different functions.
-
Exoskeleton: Skin has is glandular [sebaceous glands, sweat glands, oil glands etc] and covered with hairs. It also has a fat layer that provides insulation and protection to the body.
-
Endoskeleton: Internal skeleton is made up of bones [osteocytes embedded in hard matrix].
-
Body temperature: organisms of this group are warm blooded, i.e. their body temperature is maintained constant due to metabolism.
-
Respiration: Respiration occurs through lungs.
-
Circulatory system: Closed circulatory system present with four chambered heart and blood vessels. Heart is comprised of two ventricles and two auricles. There is no intermixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. This is required to maintain their high energy needs and constant body temperature.
-
Reproduction: they are unisexual organisms that reproduce by sexual mode. Fertilization is internal. They are viviparous organisms and give birth to the young ones.
Examples:
Human beings, Whale, Apes, elephant, dogs, giraffe, rats etc.

Exceptions:
Platypus and echidna- oviparous mammal

Kangaroo: give birth to weak and immature young one.

Bat: flying mammal

Whale: limbless mammal

|
Feature
|
Pisces
|
Amphibians
|
Reptiles
|
Aves
|
Mammals
|
|
Habitat
|
Aquatic
|
Aquatic, terrestrial
|
Terrestrial
|
Terrestrial
Flying in sky
|
Terrestrial
|
|
Limbs
|
Fins
|
Two pairs
|
Two pairs
|
Two pairs, fore limb modified for flying
|
Two pairs
|
|
Exoskeleton
|
Scales/ plates
|
scales absent but mucus glands present
|
water proof, dry and horny scales or plates
|
feathers, horny scales present in foot region
|
glandular skin covered with hairs
|
|
Endoskeleton
|
Cartilage or cartilage and bones both
|
Bony
|
Bony
|
Bony
|
bony
|
|
Body temperature
|
Cold blooded
|
Cold blooded
|
Cold blooded
|
Warm blooded
|
Warm blooded
|
|
Respiration
|
Gills
|
Gills and lungs
|
Lungs
|
Lungs
|
Lungs
|
|
Circulatory system
|
Closed
|
Closed
|
Closed
|
Closed
|
Closed
|
|
Heart
|
Two chambered
|
Three chambered
|
Three chambered, exception- crocodile
|
Four chambered
|
Four chambered
|
|
Reproduction
|
Sexual
|
Sexual
|
Sexual
|
Sexual
|
Sexual
|
|
Fertilization
|
External
|
External or internal
|
Internal
|
Internal
|
Internal
|
|
Development
|
Oviparous
|
Oviparous
|
Oviparous
|
Oviparous
|
Viviparous
|












