AGRICULTURE: CROP PRODUCTION
-
Plants of same type cultivated at same piece of land at large scale through agricultural practices is known as crop. There are different types of crops that provide different types of nutrients.
|
S.No.
|
Crop
|
Major nutrient
|
Examples
|
|
1
|
Cereals
|
Carbohydrate
|
wheat, rice, maize, millets, sorghum etc.
|
|
2
|
Pulses
|
Protein
|
gram (chana), pea (matar), black gram (urad) green gram (moong), pigeon pea (arhar), lentil (masoor) etc.
|
|
3
|
Oil seeds
|
Lipids
|
Soya bean, ground nut, sesame, castor, mustard linseed, sunflower etc.
|
|
4
|
Vegetables, spices and fruits
|
Vitamins, minerals, proteins, carbohydrates, fats, fiber etc.
|
Spinach, gourd, turmeric, coriander, papaya, apple etc.
|
|
5
|
Fodder
|
fiber
|
Oat, Berseem, Sudan grass etc.
|

Wheat

Pulses

Oilseeds

Vegetables

Fruits

Sorghum
Types of crops:
-
Different crops require different climatic conditions, rainfall [water], temperature and photoperiods [duration of sunlight] for growth and completion of their life cycle.
-
In countries like India, the basic requirements for plant growth are fulfilled by nature in different seasons.
-
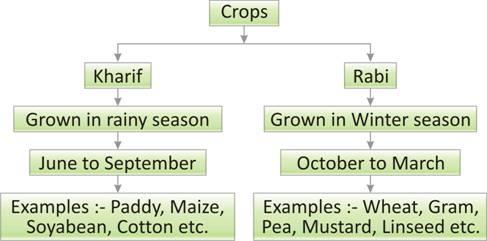
Depending upon the season in which crops grow, they are of two types.
-
Kharif Crops: The crops which are sown in the rainy season are called kharif crops. The rainy season in India is generally from June to September.
-
Examples: Paddy, maize, soya bean, groundnut, cotton, etc.
-
Rabi Crops: The crops grown in the winter season are called rabi crops. Their time period is generally from October to March.
-
Examples: Wheat, gram, pea, mustard, linseed etc.
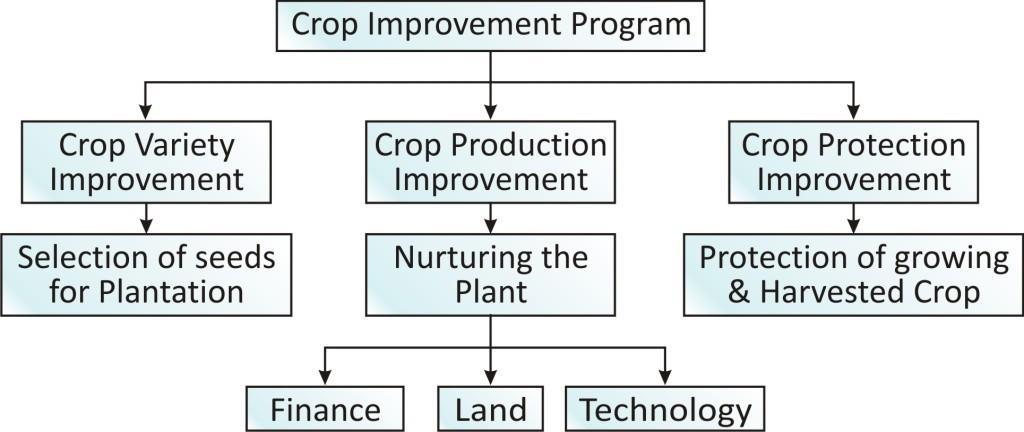
Improvement in Crop Yields:
-
The product yield from agricultural farms can be increased by following different practices which are related to the improvement of variety, production and protection of crops. The major groups of activities for improving crop yields are:
-
Crop variety improvement
-
Crop production improvement
-
Crop protection management