CROP PROTECTION MANAGEMENT
-
Crops can be destroyed due to the pest on field and spoilage during storage. Thus the crop protection management is required to prevent the crop in two ways: pre-harvesting and post harvesting management.
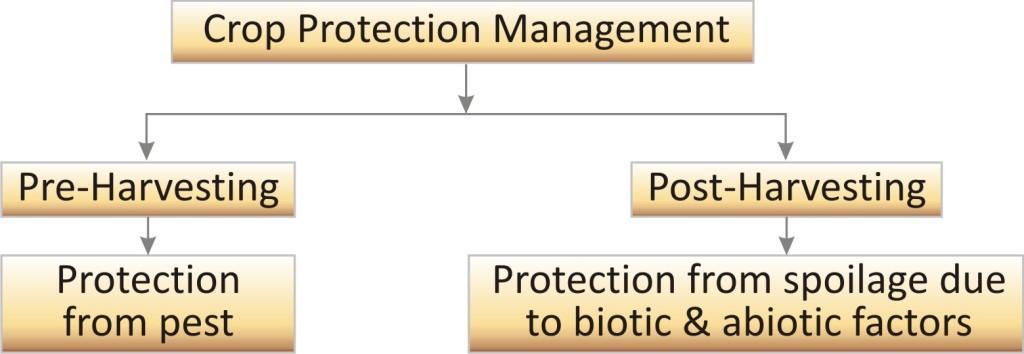
Pre-harvest crop protection:
-
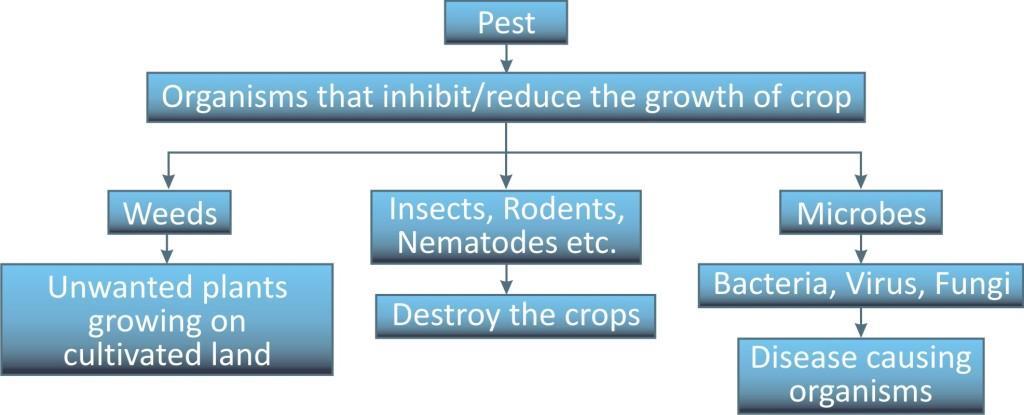
Crops are infested with a variety of pest that affects the product yield. Pests are those organisms that can directly or indirectly inhibit or reduce the growth of crop plants and ultimately result in economic loss.
-
Pests are of different types like weeds, insects, mites, nematodes, rodents, fungi, bacteria, viruses etc and thus protection is required accordingly.
Weeds:
-
Weeds are unwanted plants in the cultivated field, for example, Xanthium (gokhroo), Parthenium (gajar ghas), Cyperinus rotundus (motha).
-
They compete for food, space and light with the crop plant.
-
Weeds take up nutrients and reduce the growth of the crop.
-
Therefore, removal or control of weeds from cultivated fields during the early stages of crop growth is essential for a good harvest.
Weed control:
-
They can be controlled in two ways: mechanical, chemical and biological.
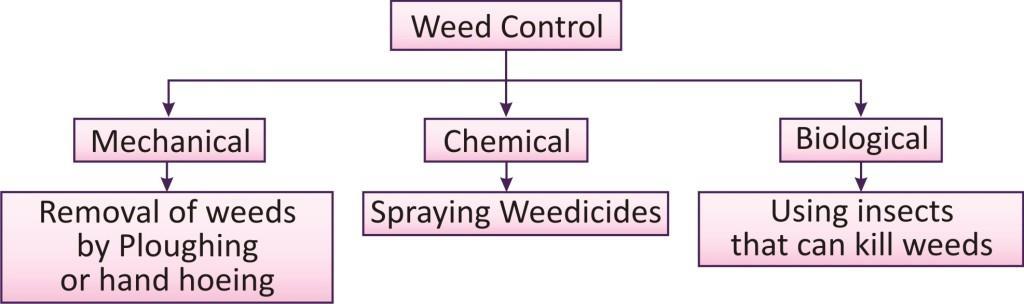
Mechanical:
-
It includes the removal of weeds by ploughing or hand hoeing and timely sowing of crops. Following different cropping patterns can also help in weed control.
Chemical:
-
The chemicals sprayed to control the growth of weeds are known as weedicides.
Examples: 2, 4-D [2, 4- Dichlorophenoxy acetic acid], Atrazine, flucloralin etc.
Biological:
-
It involves the use of insects or other organisms that can destroy the weeds specifically without affecting the growth of crops.
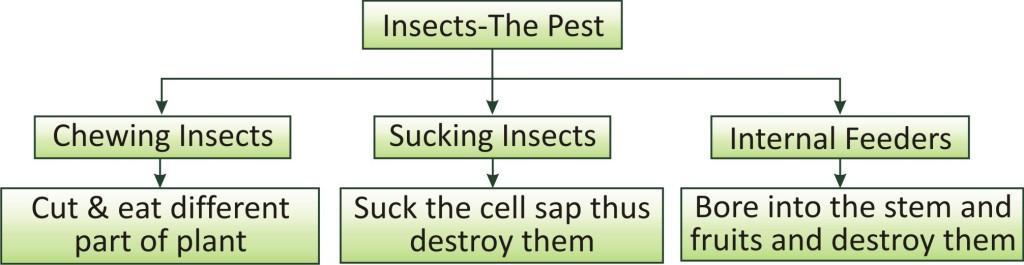
Insects-the pest:
-
Generally insect pests attack the plants in three ways:
-
They cut the root, stem and leaf.
-
They suck the cell sap from various parts of the plant.
-
They bore into stem and fruits thus destroying them.
Pathogenic pests-bacteria, fungi and viruses:
-
Diseases in plants are caused by pathogens such as bacteria, fungi and viruses. These pathogens can be present in or transmitted through the soil, water and air.
Control of pest:
-
They can be controlled by the use of chemicals that can inhibit their growth or kill them. Such chemicals are known as pesticides and of different types.
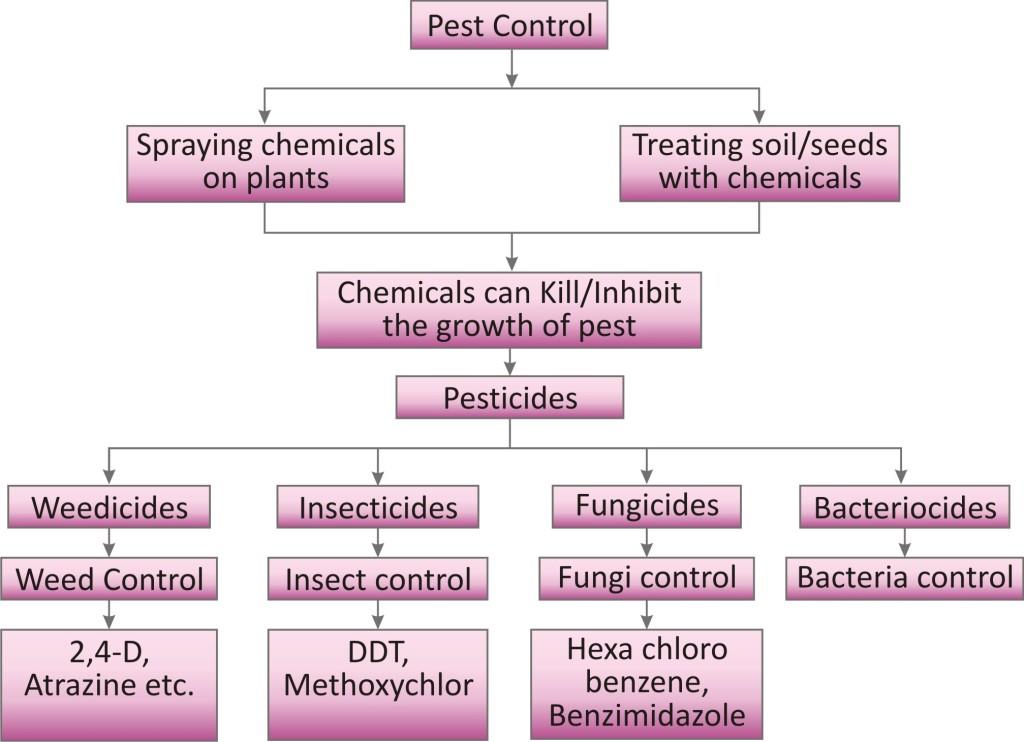
-
These chemicals are sprayed on crop plants or used for treating seed and soil.
-
However excessive use of these chemicals creates problems, since they can be poisonous to many plant and animal species and cause environmental pollution.
Post harvest crop protection management:
-
After the crops are harvested the product has to be stored properly at different levels like producer level, trader’s level and food corporation level.
-
If they are not stored properly they may get spoiled due to various factors: abiotic and biotic.
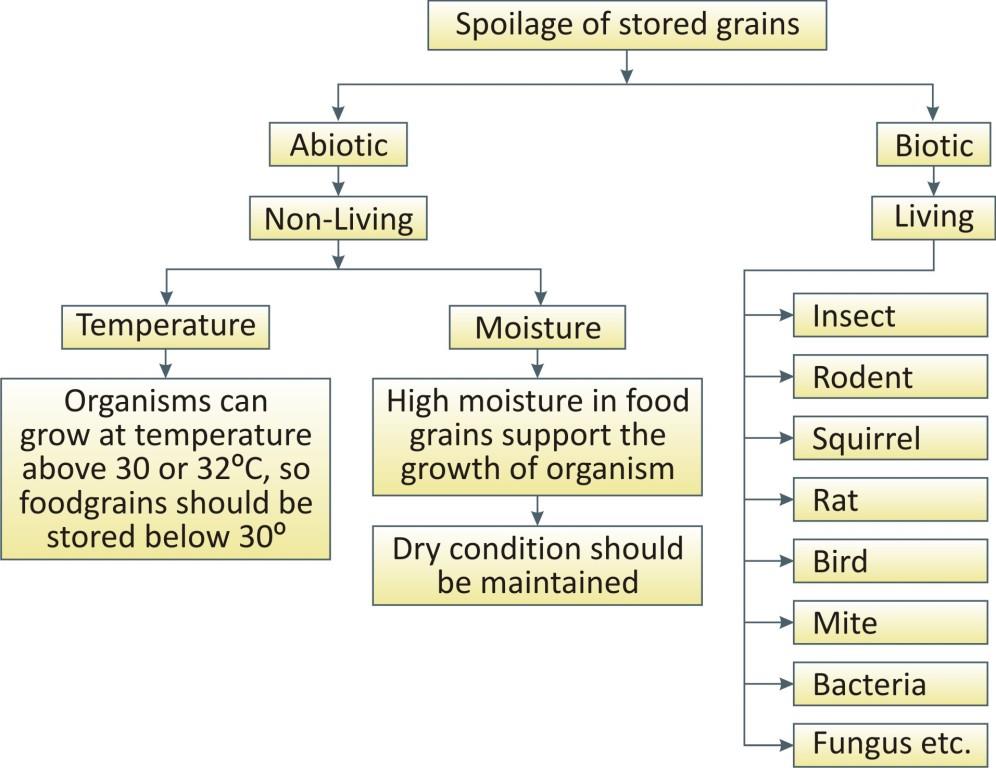
Preventive and control measures for storage:
Drying:
-
Food grains should be dried through different means prior to its storage. Moisture content is more than 14% can support the growth of organism s in the food grains hence damaging it. Drying can be done in done different ways: sun drying, mechanical driers (drier) etc.
Cleaning:
-
Food grains should be cleaned properly and packed in storage bags so as to maintain the quality of product.
Storage conditions:
-
Physical conditions in godowns or stores should be maintained in terms of temperature, humidity, aeration, attack of any organisms etc.
Chemical control:
-
Pesticides like malathion, Benzene hexachloride etc are sprayed over storage bags through mechanical sprayers or manually to prevent the growth of pest. They can be mixed with grains prior to sowing.
Fumigation:
-
The pesticides that results in fumes are known as fumigants and their use is known as fumigation. Such fumigants are used in storehouses so as to inhibit the growth of insects or kill them.
Examples: aluminum phosphate, ethylene chloride, methyl bromide etc.





