BEE-KEEPING/APICULTURE
-
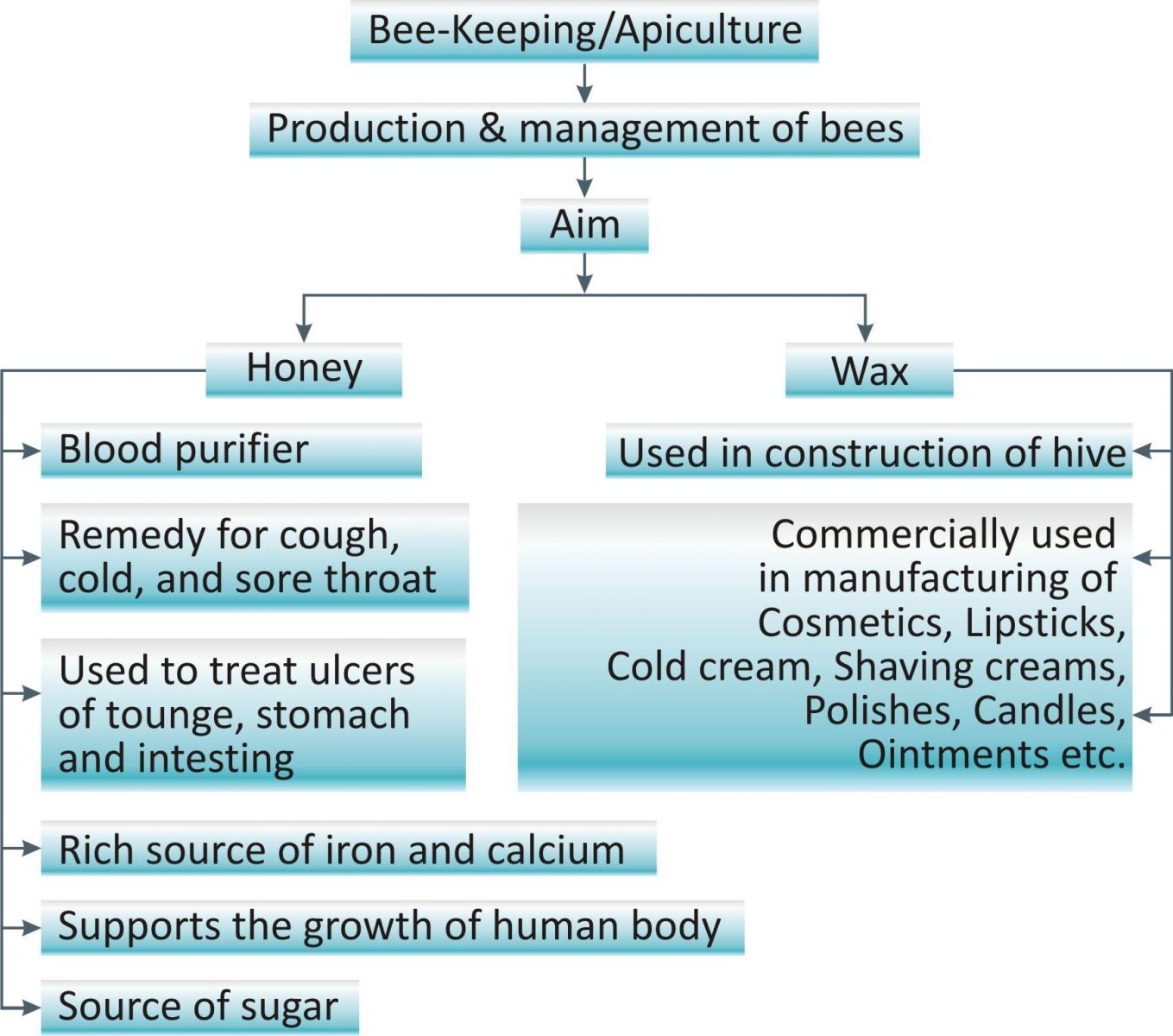
Apiculture/Bee-Keeping s defined as the production and the management of honey bees.
-
It is done for honey and wax that are known to have important medicinal use.
Breeds used in Apiculture:
-
Both Indigenous and exotic breeds are used in apiculture.
Indigenous breeds:
-
Apis cerana indica - Indian bee
-
Apis dorsata - the rock bee
-
Apis Florae - the little bee.
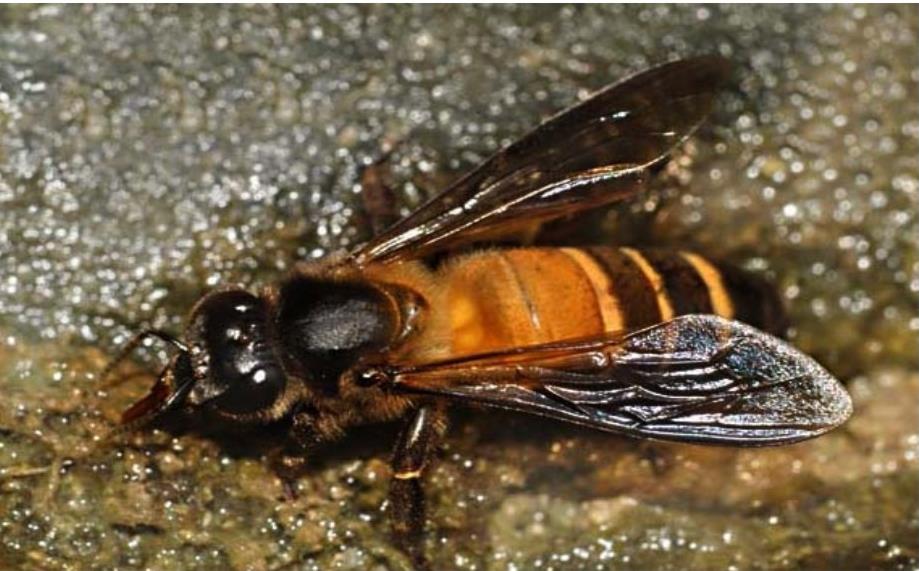

Honey Bee-Apis dorsata

Honey Bee-Apis indica
-
Traditionally Indian breeds were used for the production of honey but the yield is low [4.5kg honey per year per hive approximately] as compared to exotic breeds. Hence exotic breeds were brought in apiculture to increase the yield.
Exotic breeds:
-
Apis mellifera - An Italian bee
-
Apis adamsoni - South African bee
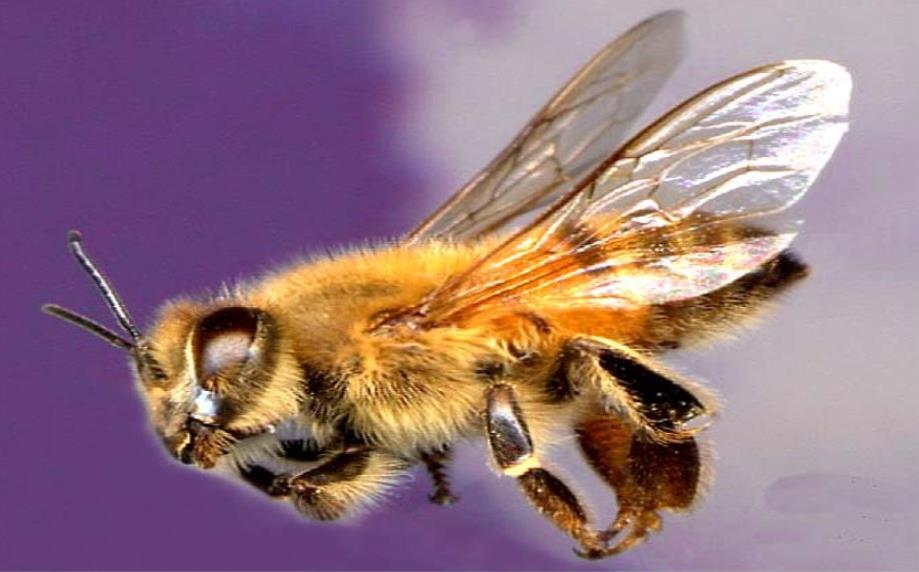

Honey Bee-Apis adansonii
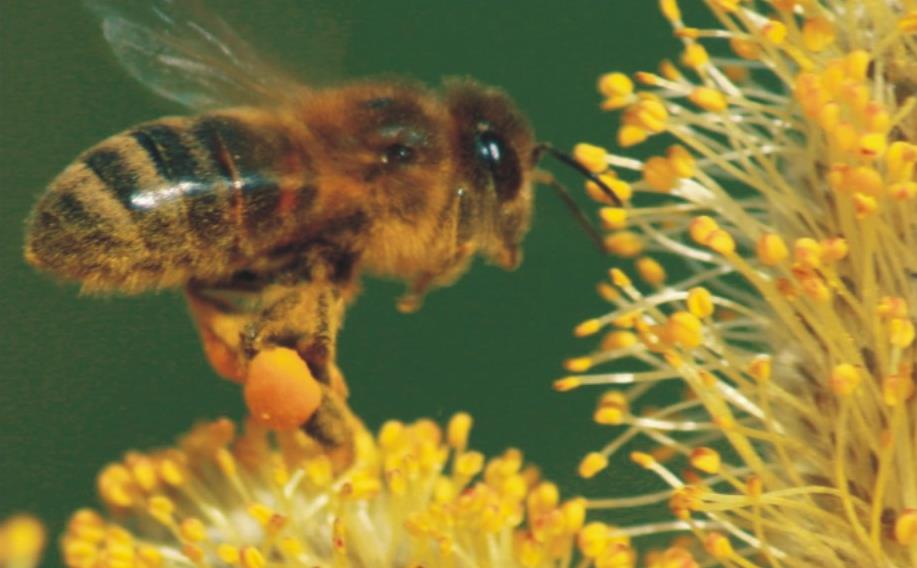

Honey Bee-Apis mellifera
-
Exotic breeds have high honey collection capacity [50 kg to 100 kg honey per year per hive].
-
They sting somewhat less.
-
They stay in a given beehive for long periods and breed very well.
Production of honey:
-
In nature, honey bees produce the honey in the hive from nectar. In a colony of honey bees there are different types of honey bees which have a particular function.
-
Worker bees are small, diploid, sterile, female, active honey bees. They have different roles like bee milk secretion, wax secretion, collection of pollens and nectar from flowers, honey production (due to the secretion of invertase enzyme) and protection of colony due to the presence of sting in them.

-
Quality, taste and quantity of honey depend upon the pasturage or orchards or the type of flowers available for nectar.

Management of honey bees’ production:
-
Commercially Italian species is used for honey production. It is selected because of following features:
-
Gentleness, stingless
-
Good honey collection capacity
-
Prolific development of queen bee
-
Protection of bee hive.
-
The establishment where honey bees are grown for honey production and other products is known as apiaries where bee hives are placed so as to develop them. For good production of honey, several factors are considered.
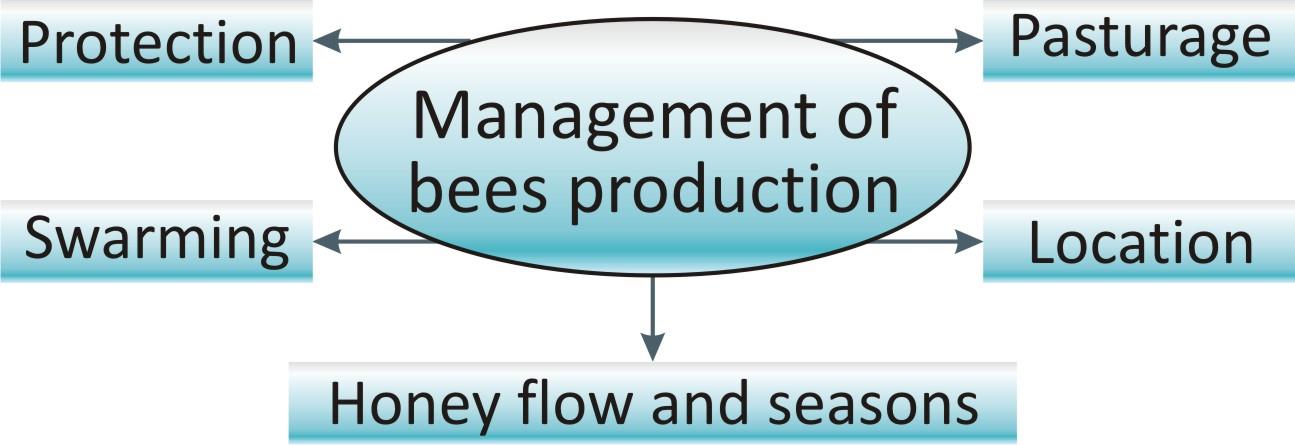
Pasturage/ crop/ Flora:
-
It is the vegetation that provides different types of flowers for nectar and pollen collection. Quality of honey is determined by the variety of flowers to which the honey bees are exposed.
Bee-Hive:
-
Naturally it is produced by worker bees. Here it is made up of special wooden box having chambers for laying eggs, honey collection.
Location:
-
Apiaries are established for setting up of number of bee hives in a systematic manner at a correct location to collect maximum nectar. Proper vegetation in a 1-2km radius is preferable.
-
It should east facing to allow the exposure to sunlight in morning and shade during mid-day or evening.
-
Water should be available nearby.
-
Front side should be open for easy entrance of bees into hive.
Honey flow and seasons:
-
In a season, honey collection depends upon duration for which honey bees are working. To increase the production, apiaries should be established in a region where there is abundance of flowers for long durations.
Swarming:
-
Swarming is a process when honey bees (queen bee, some worker bees and male drones) shift to the new hive for reproduction. This process reduces the production of honey. Hence less swarming breed should be selected in apiaries.
Protection:
-
Bees are needed to be protected from different diseases caused by virus, bacteria, fungi and protozoa and pest like wasps, wax moth mites and birds.







