|
Triangles-Session-1
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
Session: |
|||
A triangle is a three sided closed figure·
A triangle whose all the sides are unequal is called a scalene triangle.
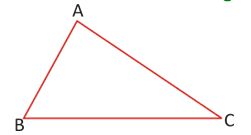
AB ¹ BC ¹ AC
· A triangle, two of whose sides are equal in length is called an isosceles triangle.
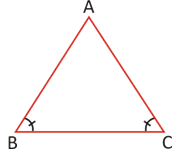
AB = AC ¹ BC
∠B = ∠ C ¹ ∠A
· A triangle, all of whose sides are equal is called an equilateral triangle.
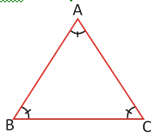
AB = BC = AC
∠A = ∠B = ∠C = 60°
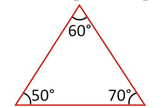
· A triangle, each of whose angles is less than 90°, is called an acute angled triangle.
Acute Angle triangle
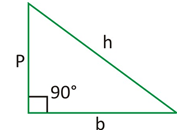
· A triangle with one of its angle 90° is called a right angled triangle.
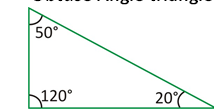
· A triangle with one of its angle greater than 90° is known as an obtuse angled triangle.
Obtuse Angle triangle
If a side of a triangle is produced, the exterior angle so formed is equal to the sum of two interior opposite angles.
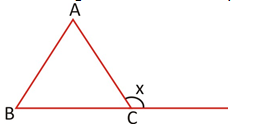
∠x = ∠A + ∠B
∠A + ∠B +∠C = 180° ....(1)
∠C + ∠x = 180° (linear pair) ....(2)
From (1) & (2)
∠x = ∠A + ∠B
Polygons
· If all sides of a polygon are equal, it is called a regular polygon.

· A six-sided figure is called a hexagon.
· A seven-sided figure is called a heptagon.
· An eight-sided figure is called an octagon, etc.
Theorem 1:
· In a convex polygon of n sides, the sum of the interior angles is equal to (2n – 4) right angles.
Theorem 2:
· In a convex polygon of n sides, the sum of the exterior angles, sides produced in order, is equal to 4 right angles.
· If ‘n’ be the number of sides.
Each interior angle = (2n-4)/n right angles.
· Sum of all the interior angles of a polygon of n sides = (n – 2) x 180° where (n ³ 3)
For n = 3 (Triangle) Þ 180°
n = 4 (Rectangle) Þ 2 x 180° = 360°
n = 5 (Pentagon) Þ 3 x 180° = 540°
n = 6 (Hexagon) Þ 4 x 180° = 720°
· Each interior angle of a regular polygon having n sides = (n – 2) x 180°/n
For n = 3 (Triangle) Þ 60°
n = 4 (Rectangle) Þ 90°
n = 5 (Pentagon) Þ 108°
n = 6 (Hexagon) Þ 120°
·
Sum of all the exterior angles formed by producing the sides of polygon = 360°
a + b + c + d + e + f = 360°
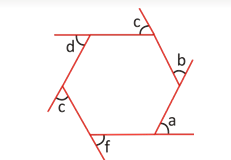
· Number of sides of polygon = 360°/ ( 180°- each interior angle)