RAIN
-
Atmosphere plays an important role in cloud formation and bringing rain.
-
Rain is liquid water in the form of droplets that have produced by the condensation and precipitation of atmospheric water vapors. It falls on earth due to force of gravity.
Formation of clouds and Generation of rain:
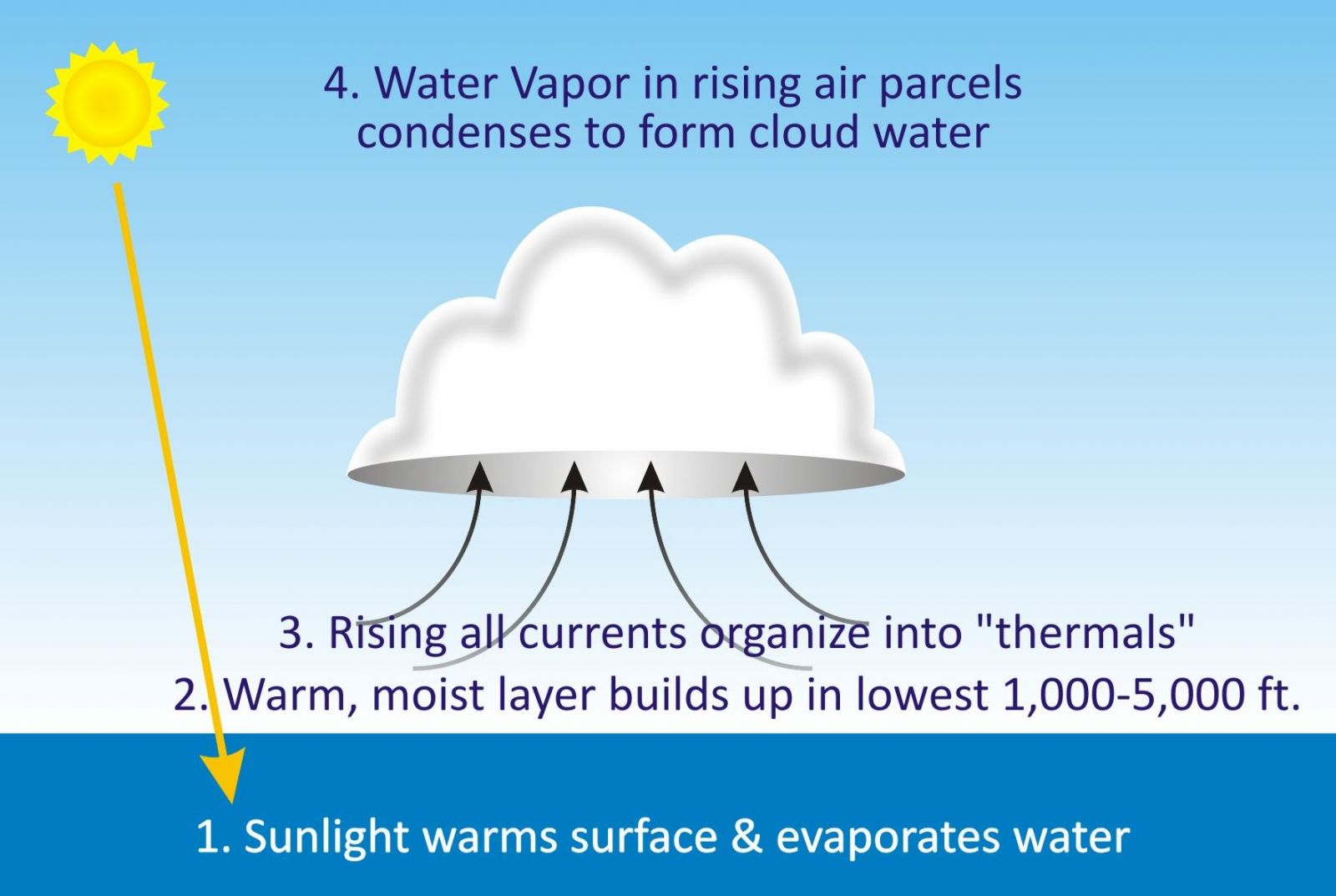
Evaporation:
-
Water bodies are heated during the day; a large amount of water evaporates and goes into the air. Some amount of water vapor also accumulates due to various biological activities into the atmosphere.
-
This air also gets heated. The hot air rises up carrying the water vapors with it. As the air rises, it expands and cools.
Condensation:
-
Cooling in upper region causes the water vapors in the air to convert into tiny droplets. This process is known as condensation which is facilitated by the presence of some particles in the atmosphere. Such particles like dust serve as the ‘nucleus’ for these drops to form around.
Precipitation:
-
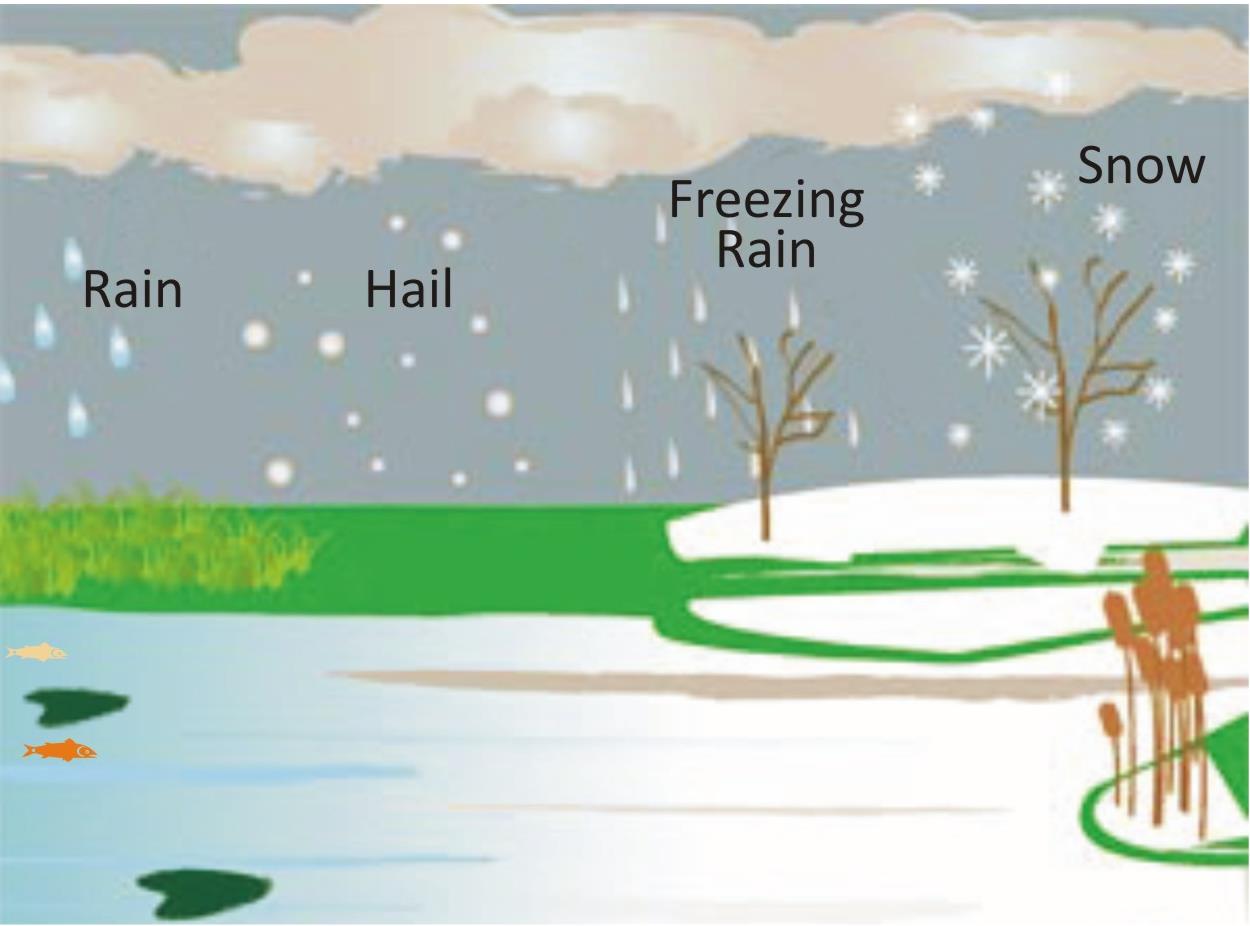
Once the water droplets are formed they grow bigger by the condensation of water droplets when the drops have grown big and heavy, they fall down in the form of rain. Sometimes, when the temperature of air is low enough, precipitation may occur in the form of snow, sleet or hail.
-
Rainfall patterns are decided by the prevailing wind patterns. In large parts of India, rains are mostly brought by the southwest or north-east monsoons.

