Light Worksheet-10
-
(a) What is spectrum?
(b) What is the meaning of VIBGYOR?
-
How is a rainbow formed?
-
Why does white light disperse when it passes through a glass prism?
-
(a) Which part of the human eye makes a person 'blue eyed'?
(b) What role is played by ciliary muscles?
(c) What is the importance of retina in the eye?
-
What is the difference between the eyes of the night birds and day birds?
-
What is cataract of the eye?
-
What are the causes of blindness?
-
Explain how a screen reader can help visually impaired people?
-
(a) What is myopia?
(b) How is it caused?
(c) How can it be corrected?
(d) Draw diagrams to show myopic eye and its correction.
-
(a) What is Hypermetropia ?
(b) How is it caused ?
(c) How can it be corrected ?
(d) Draw diagram to show defective eye and its correction.
True / False:
-
Cones and rods are the light sensitive cells.
-
Kaleiodoscope is based on the bases of spectrum.
-
Rods are sensitive to bright light.
-
The image formed by plane mirror is laterally inverted.
-
Angle of incidence is greater than angle of reflection.
Answer:
-
(a) Spectrum is the band of seven colours obtained on the screen when white light splits on passing through a prism.
(b) VIBGYOR represents the seven colours of the spectrum, i.e. violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red.
-
The water droplets suspended in the air after the rain act as prisms. When the sun is towards the horizon the inclined rays pass through the water drops to disperse into the seven colours of the spectrum.
-
The splitting of light into its different components (ROYGBIV) is called dispersion of light.
White light consists of a collection of component colors. These colors are often observed as light passes through a triangular prism. Upon passage through the prism, the white light is separated into its component colors - red, orange, yellow, green, blue and violet. The separation of visible light into its different colors is known as dispersion. Each color is characteristic of a distinct wave frequency; and different frequencies of light waves will bend varying amounts upon passage through a prism, different frequencies of light bend or refract different amounts when passing through the prism. Therefore, dispersion of light into a spectrum takes place.
-
(a) Iris is responsible for making the person blue eyed.
(b) Ciliary muscles help to adjust the focal length of the lens to view all objects clearly.
(c) The image of the object is formed on the retina of the eye.
-
The day birds can see clearly during the day but not at night. The day birds have more cones and less rods. The cones are sensitive to bright light and can sense colours. Night birds can see clearly at night but not during the day. Their eyes have a large cornea and pupil to allow more light to pass. Also their retina has mostly rods and few cones. Rods are more sensitive to dim light.
-
Cataract is a condition in which the lens becomes milky. Light does not pass through such a lens to reach the retina. It can be corrected by replacing the lens with a synthetic lens.
-
Blindness may be caused due to damage to :
(a) the lens
(b) the cornea
(c) the complete eye.
-
A screen reader is a software programme that provides access to computer software applications and the internet by using a speech synthesizer to read the information on the monitor loudly.
-
(a) When a person can see nearby object clearly, but not far away objects, he is suffering from myopia.
(b) It is caused by the flattening of the eyeball and the lens becomes thick and rigid.
(c) It can be corrected by using spectacles with concave lenses.
(d) 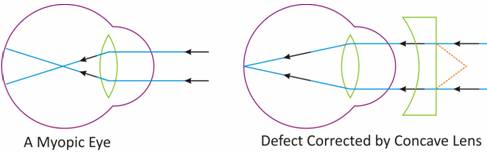
-
(a) A person suffering from Hypermetropia can clearly see distant objects but finds difficulty in reading, writing and viewing different objects.
(b) It is caused by the elongation of the eyeball and the lens becomes flat.
(c) It can be corrected by using a convex lens.
(d) 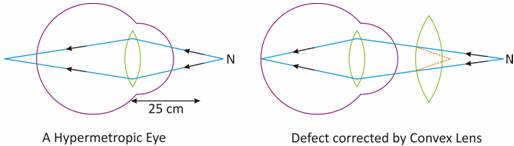
True / False:
-
True
-
False
-
False
-
True
-
False

