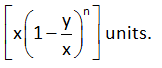The ratio of two quantities ‘a’ and ‘b’ in the same unit, is the fraction a/b and it is denoted as a: b.
The multiplication or division of each term of a ratio by the same non-zero number does not affect the ratio.
Example: 4: 5 = 8: 10 = 12: 15 etc.
Proportion:
The equality of two ratios is called proportion.
If a : b = c : d, also write as a : b : : c : d . ‘a’ and ‘d’ are called extremes, while ‘b’ and ‘c’ are called mean terms.
Product of means = Product of extremes.
Thus, a : b : : c : d Û (b × c) = (a × d).
Points to remember:
Variation:
Chain Rule
Example-1: Cost is directly proportional to the number of articles. (More articles, More Cost).
Example-2: Work done is directly proportional to the number of men working on it. (More Men, More work).
Example-1: The time taken by a car in covering a certain distance is inversely proportional to the speed of the car.
Example-2: Time taken to finish a work is inversely proportional to the number of person working at it. (More persons, Less is the time taken to finish a job).
Remark: In solving question by chain rule, we compare every with the term to be found out.
Alligation and Mixture :
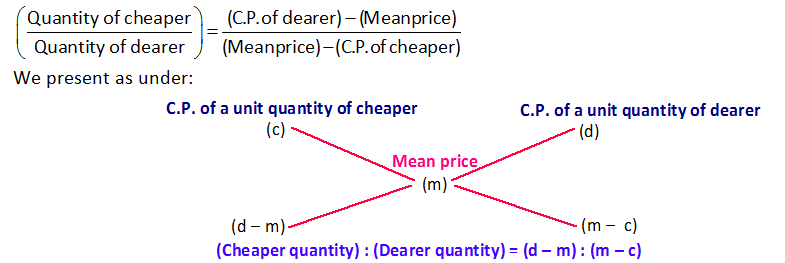
Suppose a container contains x units of liquid from which y units are taken out and replaced by water. After n operations, the quantity of pure liquid =