CHARACTERISTIC FEATURES OF FIVE KINGDOM SYSTEM
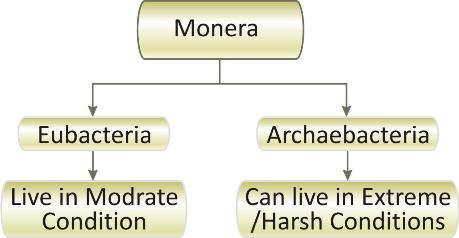
Monera: Also known as Prokaryotae
-
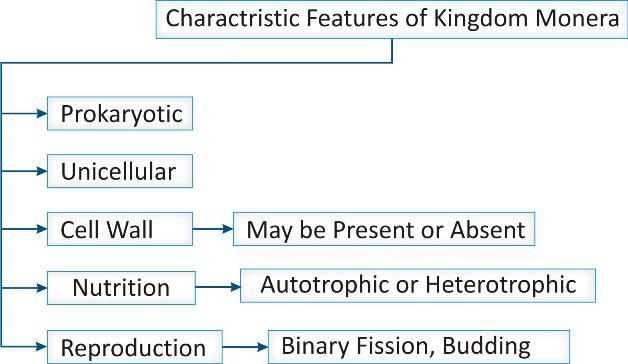
Prokaryotic: This phylum includes all organisms made up of prokaryotic cells, i.e., the cell in which well defined nucleus and membrane bound organelles are absent.
-
Unicellular: These simple organisms are always unicellular, i.e., a single cell performs all life sustaining functions and able to live as an independent organism.
-
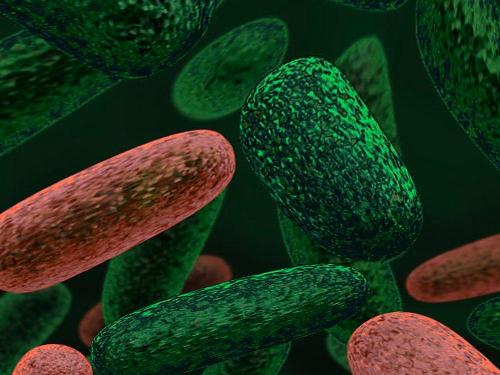
Mode of nutrition: These organisms can be autotrophic or heterotrophic, i.e., either they can synthesize their own food or obtain their food from other organisms.
Example:
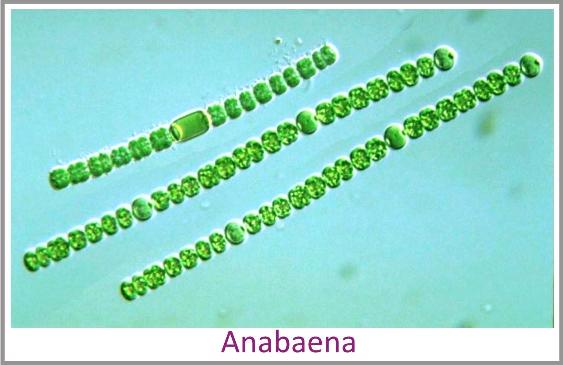
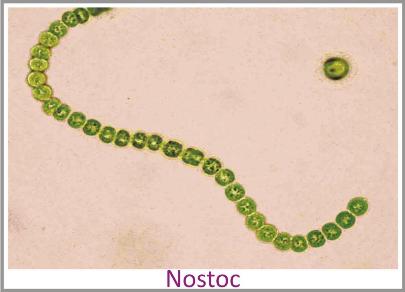
Autotrophic: Cyanobacteria or blue-green algae
Heterotrophic: Most bacteria, Mycoplasma
-
Cell wall: They may or may not have cell wall.
Cell wall present: Bacteria, Cyanobacteria
Cell wall absent: Mycoplasma
-
Size: size is in the range of 0.15 micron to 2 microns.
-
Reproduction: these organisms reproduce by asexual mode usually by binary fission or budding.
Sub-Classification of Phylum Monera
-
Monera was further classified into two sub-kingdoms by Carl Woese in 1977.

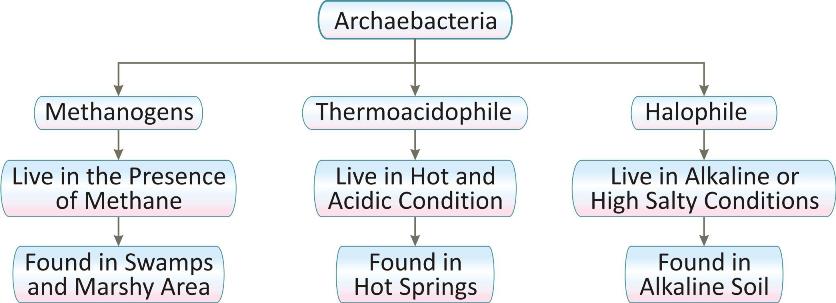
Archaebacteria:
-
Most archaebacteria are autotrophic. The source of energy used for synthesis can be chemical like methane, ammonia, hydrogen sulphide etc or light energy.

Eubacteria:
-
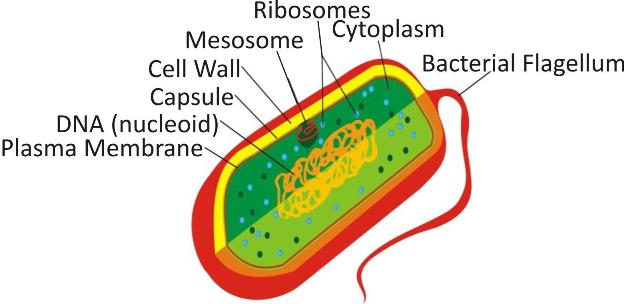
Bacteria have an outer cell wall the plasma membrane & cytoplasm with ribosomes.
-
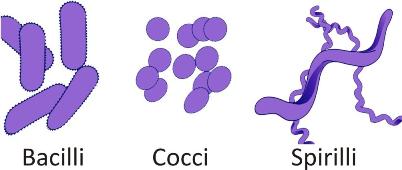
A circular strand of DNA, usually coiled into one region of the cell, the nucleoid, serves as the single chromosome. They differ in their shape:
1. Bacilli: Rod-like
2. Coccus: Spherical
3. Spirilla: Spiral etc.
Bacilli- E. Coli:
Cocci- Staphylococcus aureus:
Spirilli- Clostridium: