DIFFUSION
-
Diffusion refers to the process by which molecules intermingle as a result of kinetic energy of random motion. The molecules of gases are in constant motion and make numerous collisions with each other.
-
Effusion is the escape of gas molecules through a tiny hole such as pinhole in a balloon.
-
All gases spontaneously diffuse into one another when they are brought into contact.
-
Diffusion into a vacuum will take place much more rapidly than diffusion into another place.
-
Both the rate of diffusion of a gas and its rate of effusion depend on its molar mass. Lighter gases diffuse faster than heavier gases. The gas with highest rate of diffusion is hydrogen.
Experiment
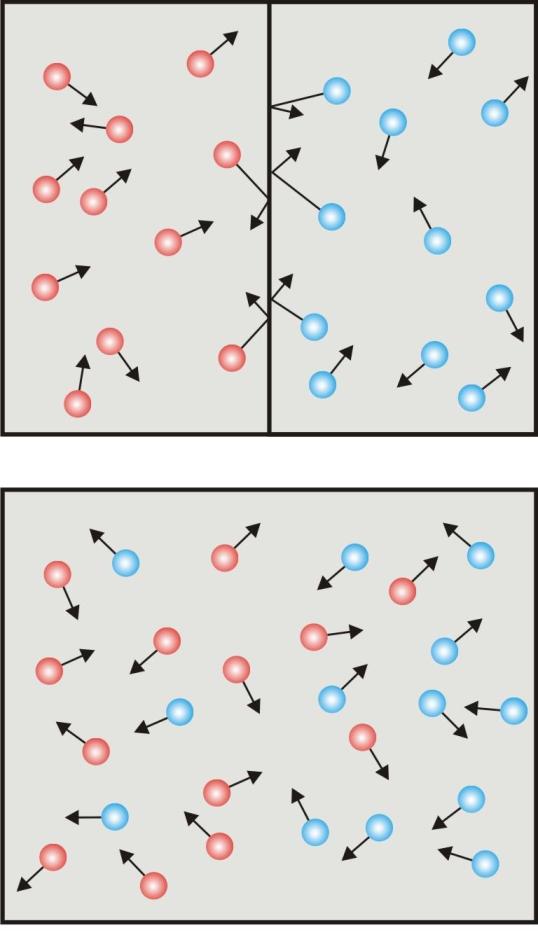
Diffusion
-
Gas particles collide with each other and with the wall of the container as well as partition.
-
If the partition is removed the gases will mix because of their random motion of their molecules.
-
The rate of diffusion is very strong even at room temperature because of the high molecular velocities due to the thermal energy of the particles.
Characteristics of Particles of Matter:
-
The important characteristics of particles of matter are :
-
The particles of matter are very, very small.
-
The particles have spaces between them.
-
The particles of matter are in constant motion.
-
The particles of matter attract each other.
-
The particles of matter are very small:
It can be shown by dissolving potassium permanganate in water.
-
The colour of a liter of water will change even if 3-4 tiny crystals of potassium permanganate are dissolved in it. Crystals of potassium permanganate are made up of very tiny particles which imparts colour to large volume of water particles by taking up space between water particles.
-
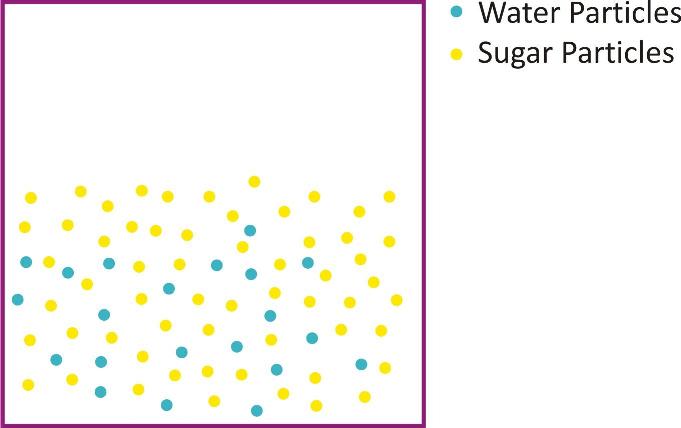
The particles of matter have spaces between them:
-
If 50 gram of sugar is dissolved in 100 ml taken in a beaker it is observed that there is no increase in volume of water on dissolving sugar in it.
-
It can be concluded that there is space between particles of water which is occupied by sugar particles.
-
The particles of matter are constantly moving:
-
When we light (or burn) an incense stick (agarbatti) in one corner of room, its fragrance (pleasant smell) spreads in the whole room quickly.
-
The particles of gases produced by the burning of incense stick move rapidly in all directions, mix with the moving particles of air in the room, and reach every part of the room quickly.
-
When the gaseous particles from the incense stick reach our nose with air, we can smell the fragrance.
-
The particles of matter attract each other:
-
There are some forces of attraction between the particles of matter which bind them together.
-
The force of attraction between the particles of the same substance is known as cohesion.
-
There is intermolecular force of attraction between the particles of matter which is maximum in solids.
-
The magnitude of force of attraction differs in different types of solids.
For example:
-
It is more in iron nail as compared to wooden block which is further more than in a chalk.
-
Classification of matter on the basis of physical properties:
-
Solids
-
Liquids
-
Gases

