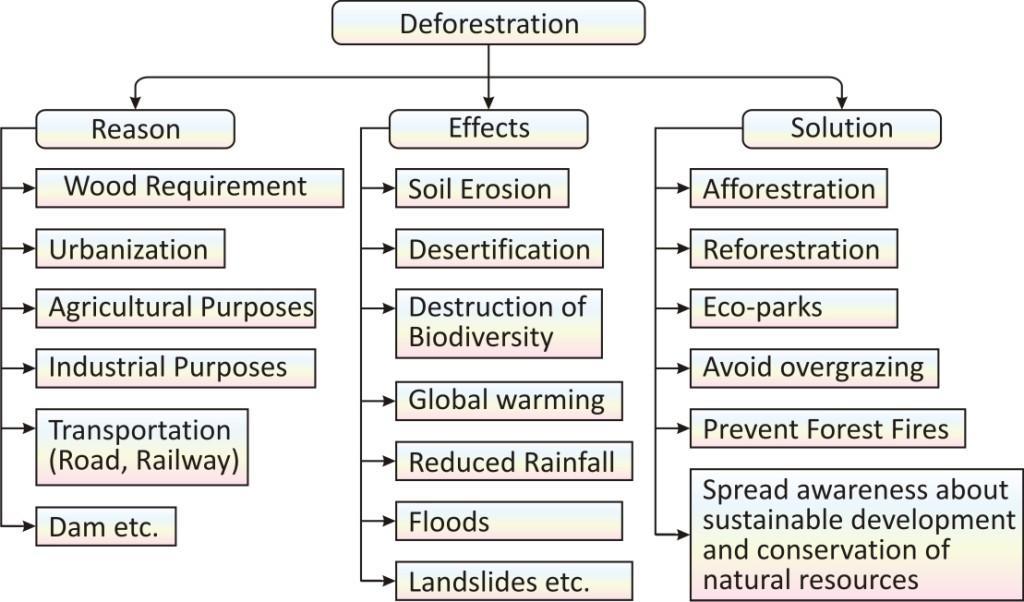
SOIL EROSION
-
Soil erosion is defined as the removal of top soil due to running water and wind reducing the productivity of the soil in that area.
-
Generally, the rate of removal of fine particles from the surface is the same as the rate of formation of soil.
-
But sometimes disturbance in this balance, usually man-made, lead to a greater rate of removal of soil.
Causes of soil erosion:
Deforestation:
-
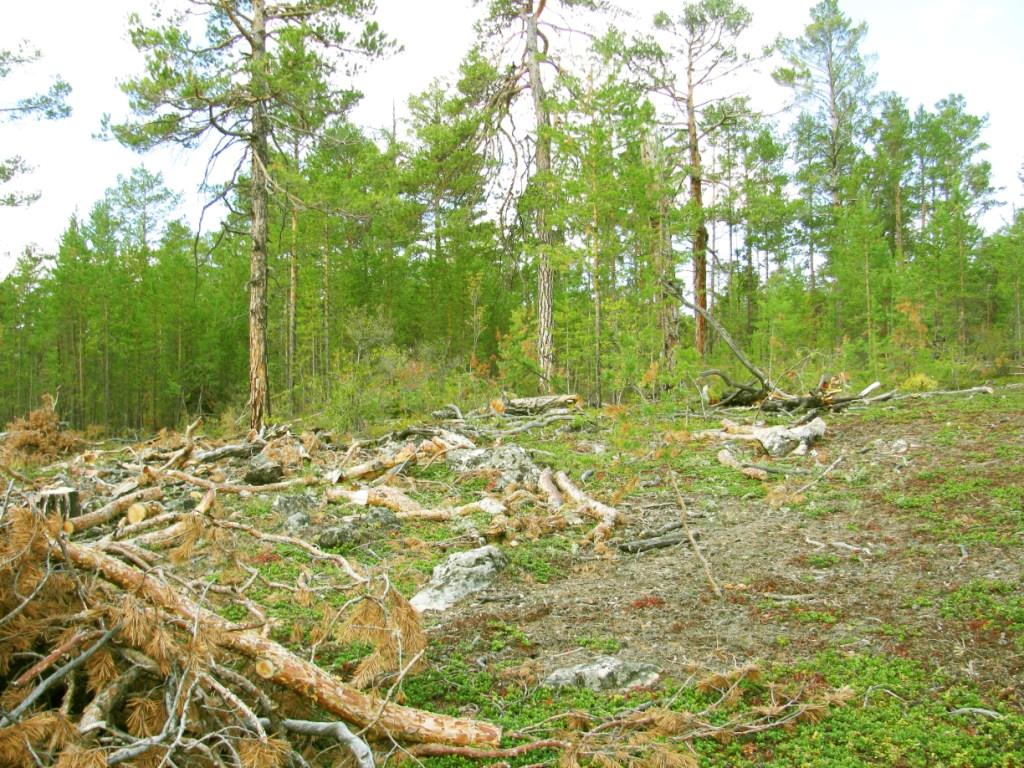
The excessive cutting of trees on a large scale is known as deforestation.

-
When trees are removed, soil particles are left loose and can be easily carried away by running water and wind.
Overgrazing:

-
Repeated grazing by animals on the same patch of land without sufficient recovery periods, leads to the removal of grass on a large scale.
Floods and heavy rainfall:
-
Floods and heavy rainfall wash off soil, especially when there are no trees and the land is lying bare.
Improper farming:
-
Improper farming on hills makes it easy for wind and water to erode soil.
Prevention of soil erosion:
-
Reduction or prevention of soil erosion is called soil conservation. It can be done in different ways:
-
Planting of trees in large numbers on deforested land (afforestation).
-
Grasses and herbs can be used to cover large patches of loose soil.
-
Overgrazing of a single patch by animals should be avoided.
-
Animals should be moved to a different area after some time.
-
Floods can be controlled to a large extent by building dams.
-
Embankment or mud walls should be constructed around hill slopes or fields to stop the flow of water.
-
Terrace farming should be adopted in hilly areas.

-
In terrace farming, suitable crops are grown on sloping ground which is cut into large steps called terraces. This reduces the speed with which water flows down, thereby reducing soil erosion.



