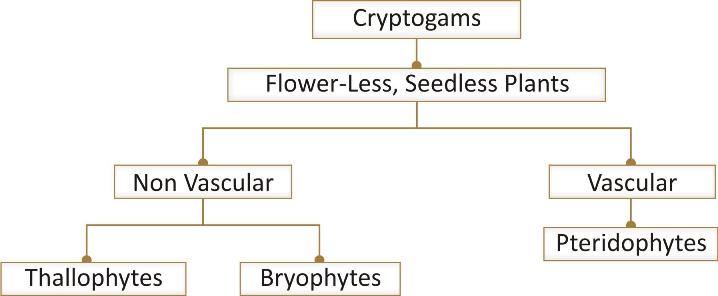
SUB-KINGDOM: CRYPTOGAMAE (CRYPTO-HIDDEN, GAMOUS-GAMETES/ REPRODUCTIVE PARTS)
-
This subkingdom includes plants that do not produce external flowers and seeds. The reproductive parts are hidden or inconspicuous in these plants. They reproduce through spores. The variation is observed in terms of body differentiation and vascular system.
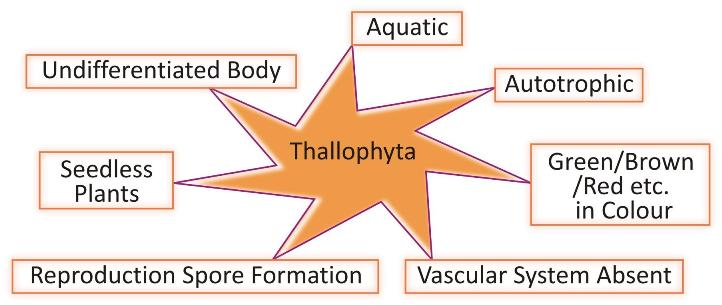
Division Thallophyta: (Thallus-Undifferentiated, Phyta-plant):
-
Plants of this group are most primitive and simplest one. They are commonly known as algae.
-
Cells are not differentiated into stem, root and leaves.
-
Generally they are aquatic, i.e. they grow in water bodies- both fresh and marine. Some may be grow in moist terrestrial region.
-
They are autotrophic, reserve food is generally starch.
-
They are of different colors due to different types of pigments present in their chloroplast.
-
They have a cellulose cell wall around their cells.
-
Vascular system is absent.
-
They reproduce through spore formation. Sex organs are not well differentiated, present as single cell.
Example:
Spirogyra, Ulothrix, Ulva , Chara etc.

Division Bryophyta: (Bryos- moss, phyta- plant)

-
Bryophytes are small multicellular terrestrial green plants. They are just few centimeters tall.
-
They are also called amphibians of the plant kingdom as they grow in wet conditions.
-
Body is differentiated into thallus (undiffrentiated stem) and leaves. Roots are not well developed, present as delicate fibres and known as rhizoids.
-
Vascular system is absent, i.e., xylem and phloem tissues are absent. Thus transport of material occurs through diffusion.
-
They do not bear seeds and the sex organs are multicellular, less differentiated and hidden or inconspicuous.
-
Reproduction occurs through spore formation. An embryo is produced after fertilization.
-
They are of two types: moss and liverworts.
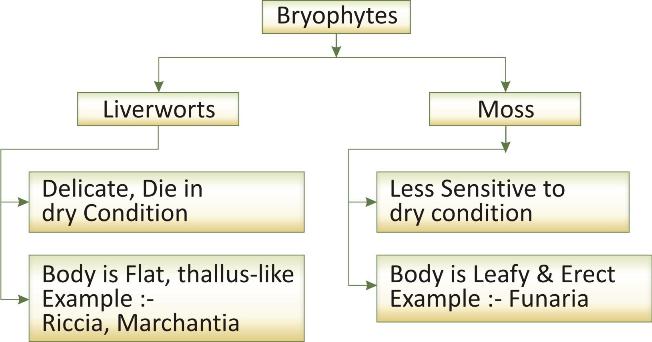
Examples:

Division Pteridophyta:

-
They are terrestrial plants which grow mainly in shady or damp places.
-
The plant body is well differentiated into root, stem and leaves.
-
They have well developed vascular system (xylem and phloem) that helps in the conduction of water, minerals, food etc.
-
These plants are non flowering and do not produce seeds. They bear naked embryos.
-
Sex organs/ reproductive parts are multicellular and inconspicuous.
-
Reproduction occurs through spore formation. The fertilized egg develops into embryo
Examples:
-
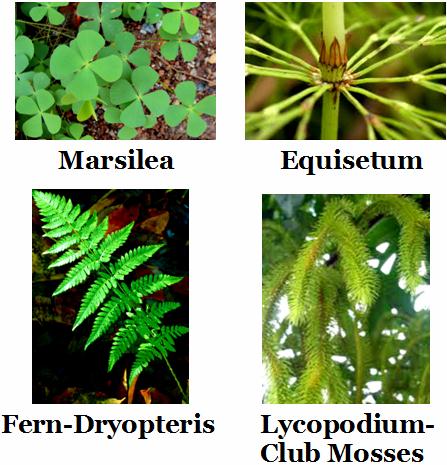
Club mosses (Selaginella, Lycopodium), horsetails- (equisetum), ferns (dryopteris) etc.

Comparison of thallophytes, bryophytes and pteridophytes:
|
Features
|
Thallophyta
|
Bryophyte
|
Pteridophyta
|
|
Habitat
|
Aquatic
|
Terrestrial- wet conditions
|
Terrestrial- shady area
|
|
Body differentiation
|
Undifferentiated
|
Thallus (stem), leaves, rhizoids
|
Stem, leaves, roots
|
|
Vascular system
|
Absent
|
Absent
|
Absent
|
|
Reproductive parts
|
Hidden, sex organs are unicellular
|
Hidden, sex organs multicellular, spores develop into embryo
|
Hidden, sex organs multicellular, spores develop into embryo
|
|
Seed
|
Absent
|
Absent
|
Absent
|
|
Example:
|

Spirogyra
|

Liverworts-Marchantia
|

Fern-Dryopetris
|







