ADAPTATIONS FOR AQUATIC HABITAT
Animals:
-
Animals which live in water must have special adaptations to help them survive in an aquatic habitat.
-
The more time an animal spends in the water, the more adaptations the animal will have for an aquatic life.
-
Aquatic animals show a variety of adaptations to stay in water.
-
Ducks have webbed feet that help them in swimming.

Duck
-
They also have hollow bones that help them to stay afloat.
-
Oil produced from under their tails makes their feathers waterproof.
-
Fish have the following modifications to live underwater.
-
Gills are special organs that help fish to breathe underwater.

-
Fins help them in swimming and keeping the body balanced.
-
Their streamlined body shape allows them to swim fast by reducing resistance due to flowing water.
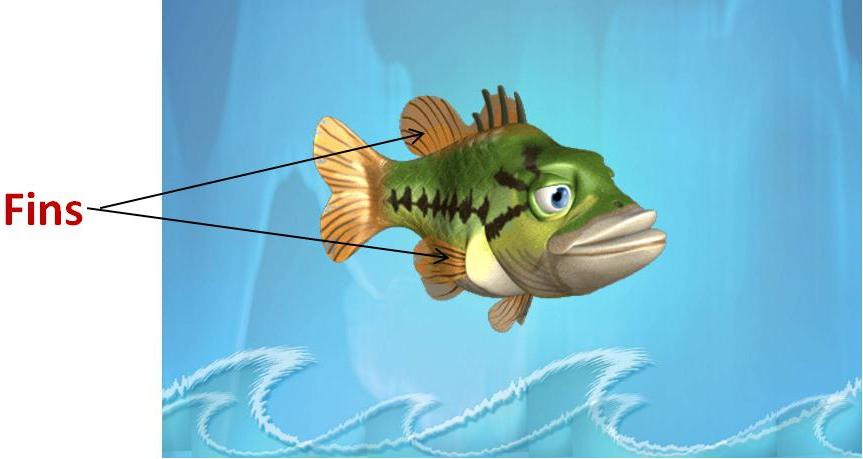

-
Some sea animals such as octopus and squid do not have streamlined shape.
-
However, while they move in water, they make their body streamlined.

-
Animals such as dolphins and whales do not have gills to breathe in water.
-
They have blowholes located at the upper parts of their heads.
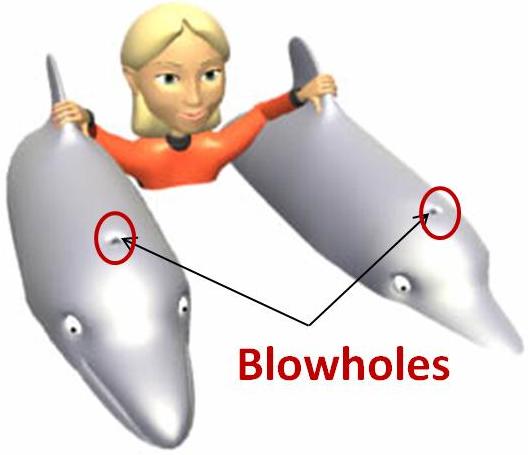
-
They come to the water surface and breathe in air through the blowholes from time to time.
-
This allows them to stay under water for a long time.

Plants:
-
Freshwater plants show the following adaptations.
-
Plants that live in moving water have long, narrow stems.
-
This prevents the plants from being carried away with water currents.
-
Stems have air chambers that allow the aquatic plants to float in water.
-
Leaves of plants like lotus and water lily have a waxy covering that prevents them from rotting.







