CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS
Structural Organization:
-
Living things have a definite structural organization.
-
Their bodies are made of cells, which are the building blocks of the body.
-
A cell is the smallest living structure that is able to function independently.
-
A group of similar cells that perform a particular function form a tissue .
-
A group of tissues performing a particular function in the body form an organ .
-
A group of organs interacting with one another to perform a particular process form an organ system.
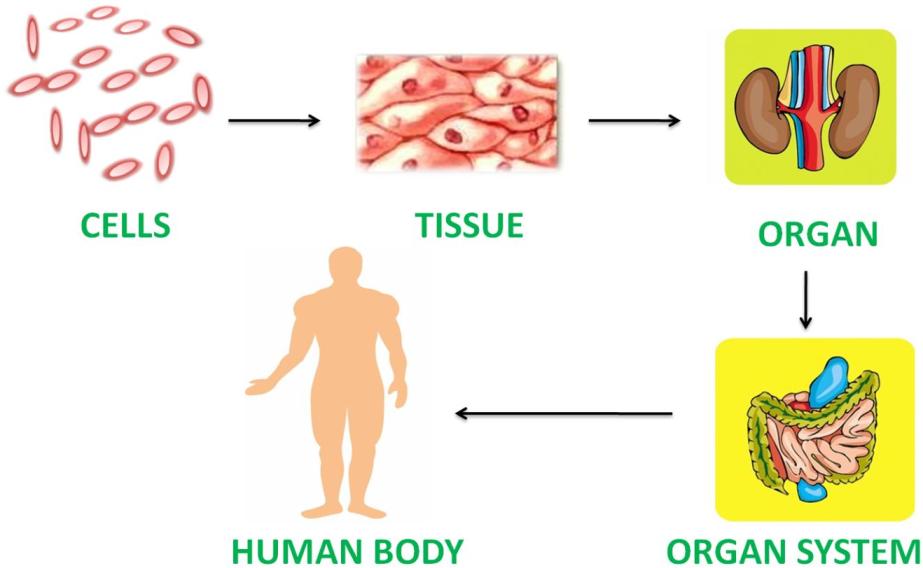
Structural organization of living things
-
An organism can be made of one cell or more than one cell.
-
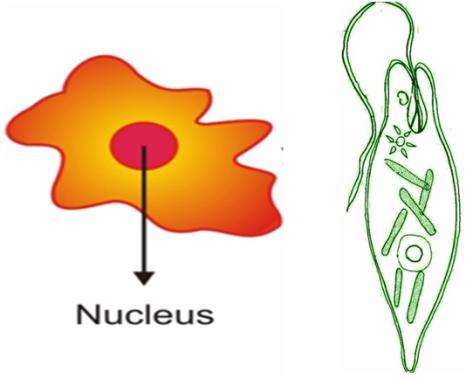
An organism consisting of a single cell which performs all its functions is called a unicellular organism.
-
In a unicellular organism, all life processes are carried out by a single cell. ( Life process: Different processes that help an organism to stay alive, e.g. Digestion, Respiration, etc.)
-
E.g. Amoeba, Euglena, Paramoecium, etc
-
An organism consisting of several cells is called a multicellular organism.
-
E.g. Human beings, plants, animals
Movement and response to stimuli:
-
Most living things are capable of moving on their own.
-
Animals move from place to place in search of food and water, to escape from danger, and for various other reasons.
-
Plants cannot move from one place to another on their own.
-
However, they exhibit movement of certain parts, such as leaves and roots, in response to changes in their immediate environment.

-
A change in the immediate environment of an organism, which produces change in the activities of the organism, is called a stimulus (plural: stimuli).
-
An organism's reaction to a stimulus is called a response. Leaves of touch-me-not (lajwanti) curl up when touched.
-
Here, touch is the stimulus and curling up of leaves is the response.
-
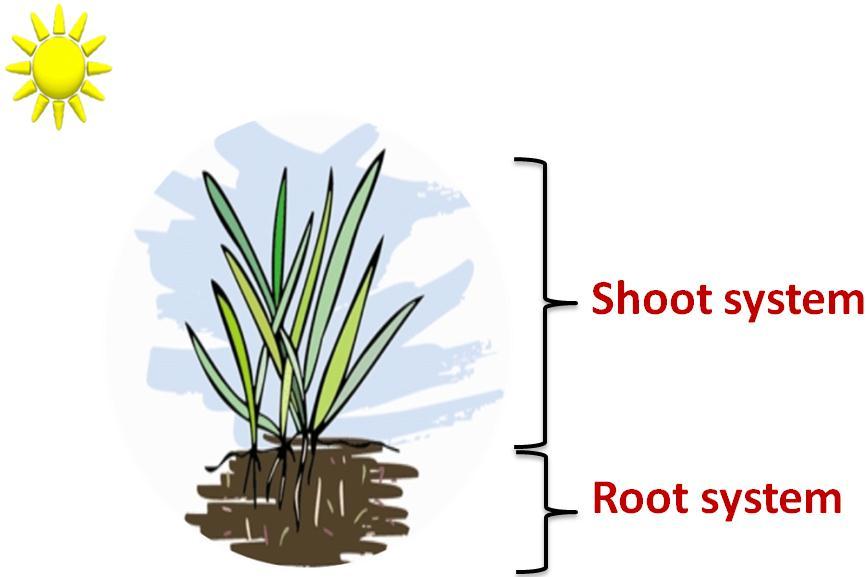
The movement of leaves, roots, etc., of a plant in response to external stimuli such as light and gravity is called tropism.
-
Shoot of a plant grows towards the light and the root grows towards gravity.
Growth:
-
Living things grow.
-
For example, a child grows into an adult and a seedling grows into a tree.
-
Growth in living things is irreversible.
-
We cannot get the seedling back from a tree. We cannot become a baby again.

Excretion:
-
Excretion is the process of removal of wastes from the body of a living organism.
-
Living things remove waste from their body through excretion.
-
Most animals excrete solid wastes in the form of faeces, liquid wastes in the form of urine, and gaseous wastes in the form of carbon dioxide.
-
Plants get rid of wastes in the form of gum, resins, latex, etc.
Respiration:
-
The process by which living things utilize the oxygen to release energy stored in the food they eat is called respiration.
-
Breathing is a part of respiration.
-
By breathing, we inhale air which contains oxygen.
-
It is through respiration that this oxygen is used by the body to obtain energy from food.
-
Plants also respire to obtain energy from the food they make by photosynthesis. Thus, respiration is a vital process for all living organisms.
Reproduction:
-
Living things have the ability to produce more of their kind through reproduction.
-
Different organisms have different means of reproduction.
-
Plants reproduce mostly through seeds.
-
Animals reproduce by either laying eggs or giving birth to young ones.
Feeding:
-
All living things need food.
-
Green plants manufacture their own food in their green leaves by photosynthesis. So, they are called autotrophs {auto, self; trophe, food).
-
Animals cannot manufacture their own food. So, they are called heterotrophs (hetero, different; trophe, food). They depend on plants and other animals for food.
Life span and death:
-
All living things follow a cycle of growth and development, in which an organism takes birth, grows into an adult, grows old, and dies.
-
This is known as the life cycle of an organism.
Differences between living and non-living things:
|
Living things
|
Non-living things
|
-
Living things are made of cells.
|
-
Non-living things are not made of cells.
|
-
Living things follow a cycle of growth and they finally die.
|
-
Non-living things do not grow or die.
|
|
|
-
Non-living things do not reproduce.
|
-
Living things excrete and get rid of wastes.
|
-
Non-living things do not get rid of wastes.
|
-
Living things need food and air to stay alive.
|
-
Non-living things do not need food or air to stay alive.
|




