Microorganisms Friends and Foe Worksheet-6
(a) E.coli (b) Amoeba
(c) Bacillus bacteria (d) Salmonella typhi
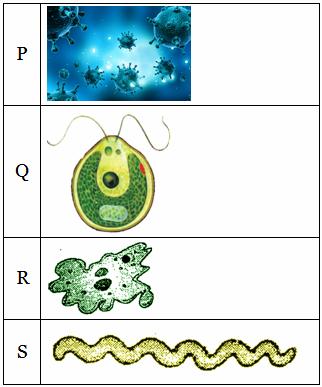
(a) P-Bacteria, Q-Protozoa, R-Viruses, S-Algae
(b) P-Protozoa, Q-Viruses, R-Algae, S-Bacteria
(c) P-Viruses, Q-Algae, R-Protozoa, S-Bacteria
(d) P-Algae, Q-Protozoa, R-Bacteria, S-Viruses
(a) Shape (b) Nutrition (c) Size (d) Habitat
(a) The production of chemical fertilizers
(b) The production of fireworks
(c) The production of soft drinks
(d) The production of antibiotics
(a) Cheese (b) Vinegar (c) Wine (d) Yoghurt

What is the importance of the presence of bacteria in the root nodules of legumes?
(a) The nitrate salts produced are used by the plants to produce proteins
(b) The ammonium compounds make the soil more fertile
(c) The nitrate salts produced help the plants to grow faster
(d) The nitrogen produced is required by the plants to accelerate the process of photosynthesis
I – Drying
II – Using common salt
III – Freezing
(a) I and II only (b) I and III only
(c) II and III only (d) I, II and III
(a) Fermentation of glucose (b) Food poisoning in humans
(c) Heart diseases in humans (d) Production of antibiotics
I – body contact
II – the air
III – a vector
(a) I and II only (b) I and III only
(c) II and III only (d) I, II and III
I – By producing toxic substances that will destroy the cells or tissues of the host.
II – By destroying red blood cells of the host
III – By releasing a lot of heat to raise the body temperature of the host
(a) I and II only (b) I and III only
(c) Il and III only (d) I, II and III
Answer Key:
(1)-(a); (2)-(c); (3)-(d); (4)-(d); (5)-(c); (6)-(a); (7)-(d); (8)-(b); (9)-(d); (10)-(a)