PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
-
The differences in properties help us in grouping materials into different categories.
-
Materials can be grouped on the basis of properties such as roughness, lustre, transparency, solubility, flotation, attraction towards a magnet, conduction of heat, and conduction of electricity.
Appearance/Lustre:
-
The surface of some objects shine when light falls on them. Lustre is the shine of a material.
-
These materials are said to have lustre and are called lustrous materials.
-
Metallic surfaces generally show this property.
-
All metals in pure state are shiny and said possess lustre.
-
This property of metals is widely used for making jewellery and other decorative articles.
-
Materials such as gold, silver, and bronze have lustre.

-
Dull-looking materials like paper, wood, plastic, cotton, rubber etc. which do not have shine are called non-lustrous materials.

Hardness:
-
Shape of objects like wood, steel or stone, etc. cannot be changed by pressing.
-
All these materials and objects are said to be hard.
-
Shape of objects like foam, cotton, wool etc.; can be changed by pressing them.
-
All such materials and objects are said to be soft.
-
It is easier to cut soft materials but difficult to cut hard materials.
Texture:
-
The feel of an object on touching is called its texture.
-
Some of them are smooth whereas others are rough to touch.
Example:
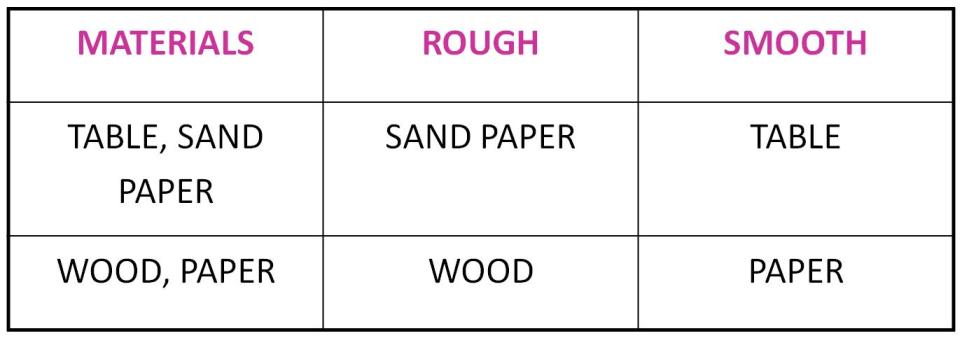
Transparency:
-
Transparency is the property of a material by the virtue of which we can see through it as they allow light to pass through them.
-
The materials through which light can pass are called transparent materials.
-
Window panes are made of glass these days as it allows us to see the things outside but we would not be able to see through a window made of wood or iron.
-
Glass, Water, Acrylic sheet, and Cellophane paper are some examples.
-
Shopkeepers generally prefer to keep items like cold drinks, soft drinks, etc. in transparent glass refrigerator so that we can easily see them.
Transparent materials
-
The materials like wood, metal, cardboard etc. through which light cannot pass are called opaque materials.
Example:
-
Wood, metals, leaf, stone, and cardboard are opaque materials.

Opaque materials
-
The materials through which light can pass partially are called translucent materials.
Example:
-
thin cloth, misty glass, oil-spreads paper

Translucent materials
Solubility:
-
The ability of a substance to dissolve in another substance is called solubility.
-
Some materials are soluble in water whereas some are insoluble.
Example:
-
Common salt and sugar are soluble in water whereas sand is insoluble.
-
Alcohol is soluble in water but oil is insoluble.
-
Solids like sugar, common salt, and potassium permanganate are examples of solids that are soluble in water.
-
Some solids are insoluble in water, e.g., wood, stone, sand, chalk powder, and wax.
-
Liquids such as alcohol, vinegar, lemon juice, honey, and glycerin dissolve in water whereas kerosene, coconut oil, and diesel are insoluble in water.
Soluble or miscible:
-
Materials which dissolve in or disappear in water are called soluble or miscible (in case of liquids).Salt and sugar are soluble in water.
-
Water is the solvent and sugar or salt is solute.
-
Water is called as universal solvent as most of the substances are soluble in water.
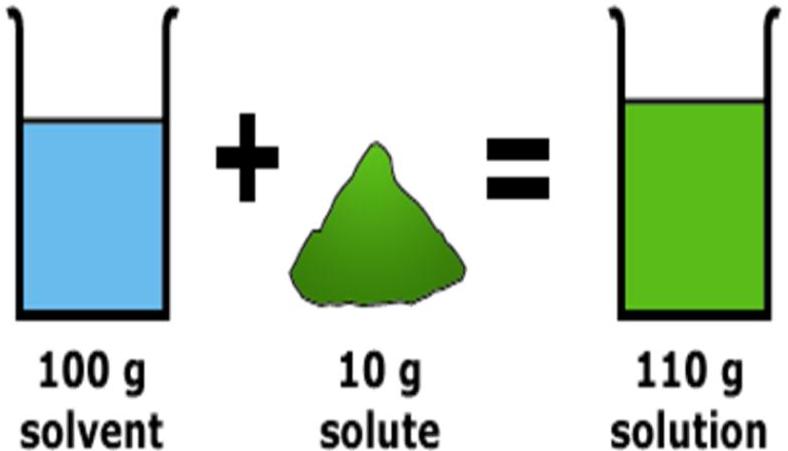
Solvent:
-
Water is not the only solvent used for dissolving other substances.
-
Kerosene oil, petrol, ether etc. are some other liquids which are also used as solvents.
-
There are some liquids which mix with water completely.
-
They are said to be miscible with water e.g., milk or lemon juice.
-
Other liquids like mustard oil, petrol, hair oil etc. do not mix with water and are said to be immiscible with water.
Sinking and floating:
-
If the density of an object is greater than that of density of water, the object sinks.
-
Certain materials float on water whereas others sink. This property is called flotation.
-
Generally, materials such as wood, leaves, and feathers float on water whereas rocks and metals sink.

Floating objects
-
If the density of water is greater than the density of object, the object floats.
Sinking objects
Magnetic property:
-
The substances which get attracted towards magnet are called magnetic substances.
-
E.g. iron, nickel, and cobalt
Magnetic objects
-
The substances which are not attracted towards magnet are called non-magnetic substances.
-
E.g. plastic, glass, rubber, liquids and gases

Non-magnetic objects
Conduction of electricity:
-
Some substances like most of the metals, which allow electricity to pass through them are called conductors of electricity. This property is called conductivity.
-
The materials which do not allow electricity to pass through them are called insulators.
-
Our body can also conduct electricity as salts dissolved in the blood are good conductors of electricity.
-
We get electricity in our homes through cables and wires made up of metal like copper.
-
An electric cable consists of a number of metal wires with or without a plastic covering.
-
The substances that conduct electricity are called good conductors of electricity or conductors whereas substances that do not conduct electricity are called bad conductors of electricity or insulators.
-
For example, metals are good conductors of electricity; wood, air, and plastic are insulators.
Conduction of heat:
-
Some materials are good conductors of heat while others are bad.
-
So we can group the materials into two classes on the basis of conduction of heat through them.
-
Most of the utensils kept in our kitchen, are made of metals, where as their handles are made of wood or hard plastic because metals get heated whereas materials such as plastic and wood do not.
-
It would be difficult to hold metal utensils after cooking if the handles were made of metal.
-
Mercury is a good conductor of heat and thus it is used in thermometers.
Thermometer
Good and bad conductors:
-
Substances which allow heat to pass through them, like most of the metals; are called good conductors of heat.
-
Silver is the best conductor of heat.
-
Substances which do not allow heat to pass through them, like plastic, wood, rubber, etc. are called bad conductors of heat.











