ARTIFICIAL METHODS
-
Plants can also be produced vegetatively by artificial means.
-
These methods include cutting, grafting, and layering.
Cutting:
-
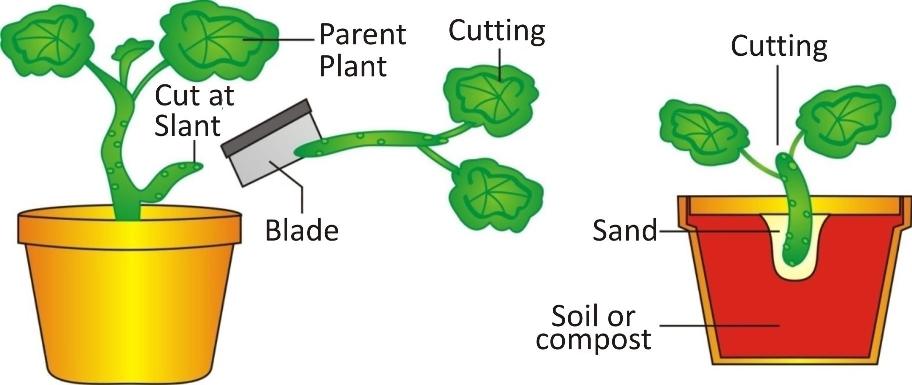
It involves cutting off part of a stem, leaf, or root and placing it in moist soil.
Cutting method
-
After some time, these stems strike roots at the base and grow into a new plant.
-
This method is generally used for sugarcane, rose, Bougainvillea, hibiscus, etc.
Grafting:
-
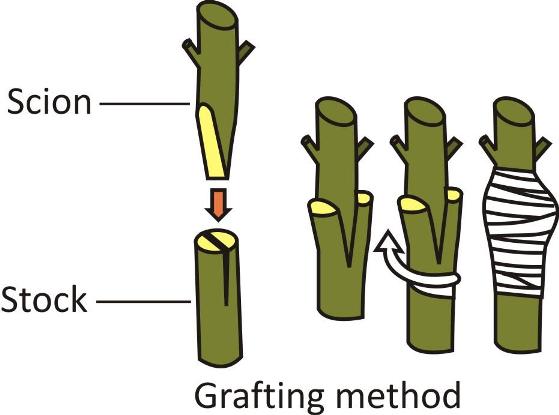
This is a very common method used in ornamental and fruit plants to develop new varieties called hybrid varieties.
-
A bud, or a cutting that has several buds, called the scion, of one plant is placed over the cut stem with roots of another plant called the stock.
-
The scion and the stock are then firmly tied together.
-
The stock supplies water and minerals to the scion.
Layering:
-
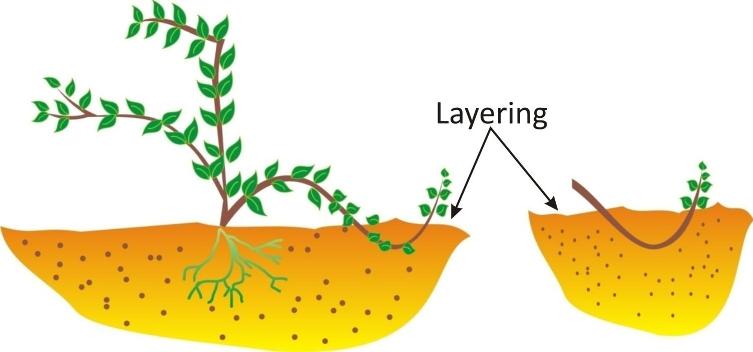
This is a method most commonly used in grapes, jasmine, and Bougainvillea.
Layering method
-
In this process, a young branch is lowered down and bent towards the ground and covered by moist soil forming a layer.
Process of layering
-
After some time, roots arise from the branch and grow downwards.
-
The branch can then be cut off from the parent plant and allowed to grow into a new plant.
Advantages of Vegetative Reproduction:
-
The advantages of vegetative reproduction are listed below:
-
It is a faster and more certain method of reproduction. Sometimes the seed may not germinate due to unfavourable conditions.
-
But in this case, new plant directly grows from a part of the parent plant.
-
New plants exactly resembling the parent plant are formed. Thus, it helps in conserving characteristic features of the parent plant.
-
Plants which do not flower or have seeds can reproduce with this method.



