CONSERVATION OF FOREST AND WILDLIFE
-
Conservation refers to the preservation and careful management of plant and animal species in order to prevent their extinction.
-
India is sixth on a list of 12 mega-biodiversity countries in the world. It contains two of the 13 biodiversity hot spots of the world – North-East India and the Western Ghats. These areas are very rich in biodiversity.
-
India has more than half of the world’s wild tigers, 65% of the Asian elephants, 85% of the great one-horned rhinoceros and 100% of the Asian lions.
-
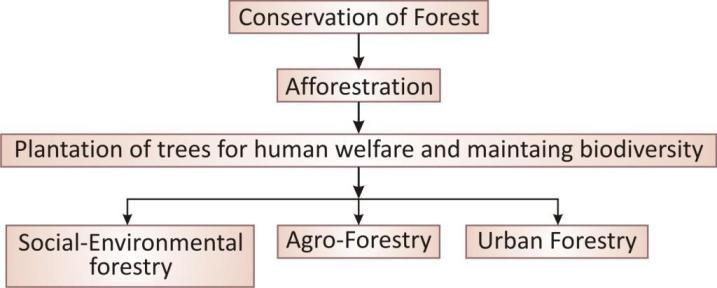
Social and Environmental Forestry- It involves growing of trees for firewood, fodder, agricultural implements for the benefits of rural and tribal community.
-
Agro- Forestry- It is an absolute commercial forestry developed to fulfill the need of various forest based industries. It is done on the fallow land or free-grazing lands.
-
Urban Forestry- It involves growing of ornamental trees along roads, vacant lands and common parts of urban areas.
-
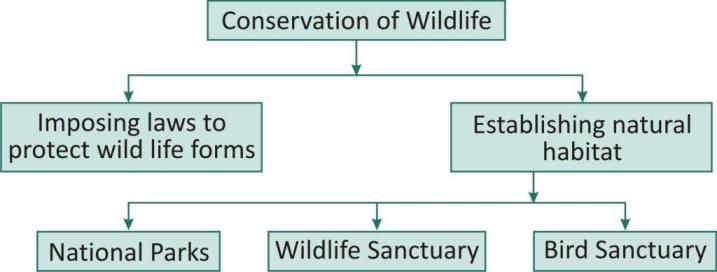
The government has laid down rules, methods and policies to protect and conserve animals and plants.
-
To protect our flora and fauna and their habitats, protected areas called sanctuaries, national parks and biosphere reserves.
Biosphere Reserve:
-
Large areas of protected land for conservation of wild life, plant, animal resources and traditional life of the tribal living in the area. These are the areas meant for conservation of biodiversity.
-
The biosphere reserves help to maintain the biodiversity and culture of that area.
-
The Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve consists of one national park named Satpura and two wildlife sanctuaries named Bori and Pachmarhi.
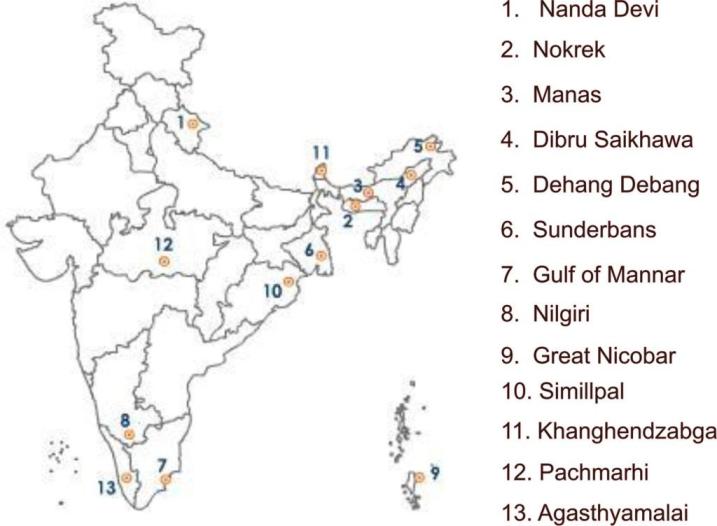
Biosphere Reserves of India
Wildlife Sanctuary:
-
Wild life sanctuaries are protected forests all across the world to preserve certain plants and animal species.
-
Wildlife sanctuaries provide protection and suitable living conditions to wild animals.
-
These sanctuaries are places where killing (poaching) or capturing of animals is strictly prohibited.
National Park:
-
These reserves are large and diverse enough to protect whole sets of ecosystems. An ecosystem is made up of all the plants, animals and microorganisms in an area along with non-living components such as climate, soil.
-
They preserve flora, fauna, landscape and historic objects of an area.
-
Satpura National Park is the first Reserve Forest of India. The finest Indian teak is found in this forest. Rock shelters are also found inside the Satpura National Park. These are evidences of prehistoric human life in these jungles. These give us an idea of the like of primitive people. Rock paintings are found in these shelters.
-
A total of 55 rock shelters have been identified in Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve. Figures of animals and men fighting, hunting, dancing and playing musical instruments are depicted in these paintings. Many tribals still live in the area.
-
Project Tiger was launched by the government to protect the tigers in the country. The objective of this project was to ensure the survival and maintenance of the tiger population in the country.



