SAPROPHYTIC PLANTS
-
Saprophytic plants are plants that do not have chlorophyll. (sapros-rotting; phyton-plant)
-
Saprophytic plants are usually whitish, but can have brightly coloured flowers.
-
These plants have no green leaves; often they even have no leaves at all.
-
They grow in places with lots of rotting dead leaves, often in deep shade in tropical forests.
-
They get all their nutrients from dead and decaying organic matter rather than making their own food as most plants do.
-
Saprophytes include mainly fungi.
-
Fungi are capable of digesting dead and decaying matter.
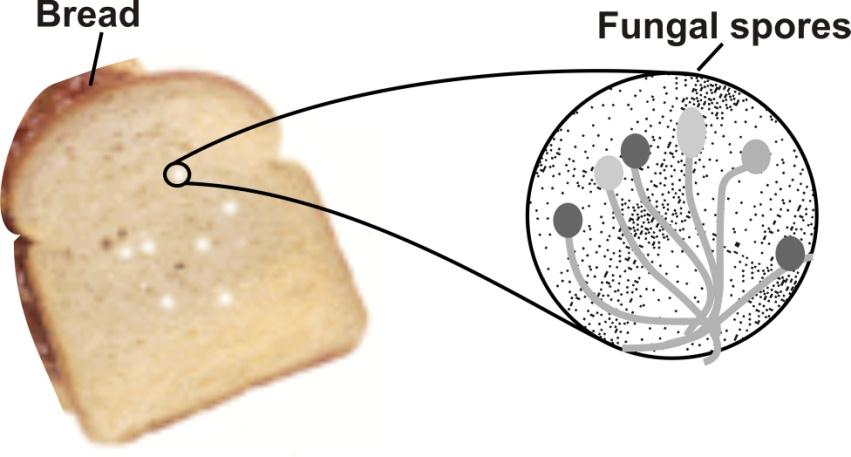
In the above given picture, there is a piece of moistened bread in which white coloured fungi grows when kept in a closed box for some days
-
The fungi produce digestive juices which converts the dead and decaying matter into sugar which can be then used as food by these plants.
-
Fungi are also called saprotrophs.
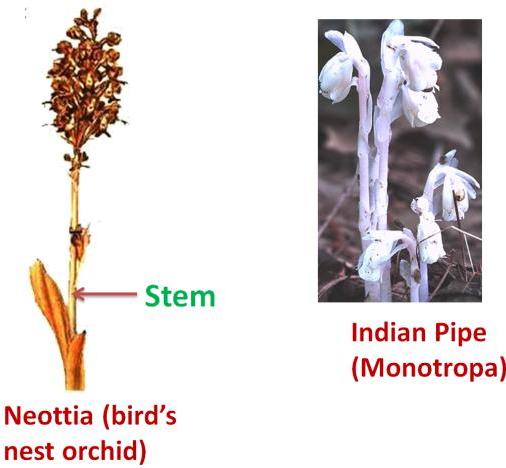
Few Examples:

-
Neottia (Bird's nest plant) and Indian pipe (Monotropa) are flowering plants whose roots constitute a mycorrhizal association with fungal hyphae, which help in absorption.

-
The roots of saprophytes contain living organisms called fungi.


