FRUIT AND SEED FORMATION
-
After fertilization, the ovary enlarges to form the fruit.
-
The wall of the ovary becomes the fruit wall.
-
The ovules become the seeds.
-
A fruit may have one or more seeds.

Pomegranates
-
Petals, sepals, and other parts of the flower dry up and fall off.
-
The fruit is the seed-bearing structure of a flowering plant. It is the ripened ovary of the plant.
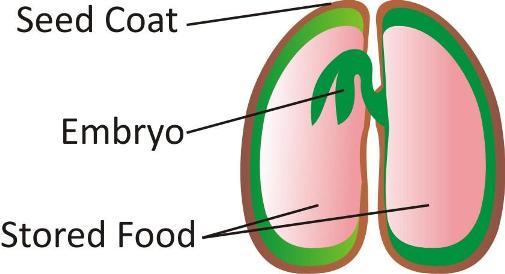
Structure of a seed
-
The seed is the ripened ovule which contains an embryo and its food source is covered by a protective coat.
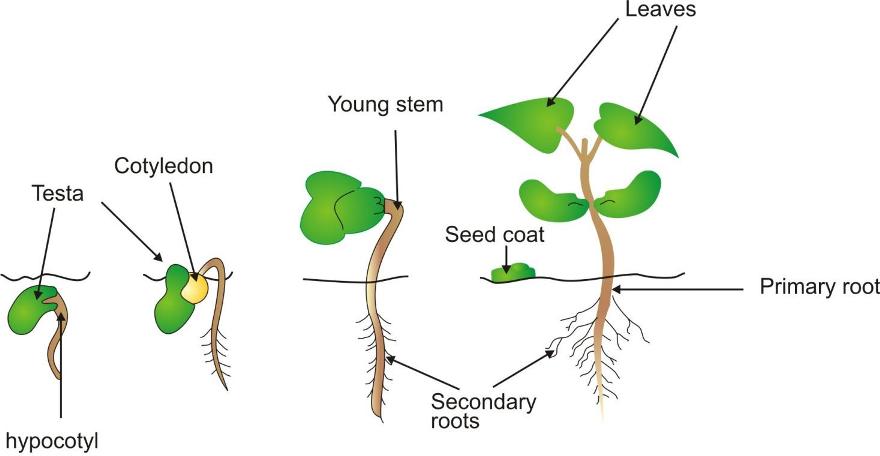
Epigeal Gemination in Bean Seed
-
When a seed has matured, it germinates when suitable conditions of air, water, temperature are available.
-
Otherwise, it lies inactive till conditions for germination become more favourable.
-
The process by which the embryo in the seed becomes active and begins to grow into a new plant is called germination.
-
The seed absorbs water and swells. The young root grows down into the soil.
-
Root hairs develop. This enables the seed to take in more water and minerals.
-
The young shoot grows through the soil and develops leaves.
-
If all plants were to grow at the same place, there would be huge competition for survival.
-
They would not be able to get enough space, sunlight, and water to grow.
-
Scattering helps in reducing this competition and also plants get distributed to distant places to make new habitats. Seeds or fruits get scattered to different places.
-
The process by which seeds or fruits are scattered is called dispersal.


