HETEROTROPHIC NUTRITION
-
Organisms which are incapable of photosynthesising, obtain certain organic compounds from other autotrophs and these organisms are called heterotrophs.
-
The type of nutrition carried out by heterotrophs is termed as heterotrophic nutrition.
-
Organisms which have heterotrophic mode of nutrition are called heterotrophs (heteron-(an)other; trophe-nutrition).
-
Some plants are heterotrophs.
-
Most plants on Earth are green plants but there are certain plants which do not contain chlorophyll, neither in their leaves nor in any other part. Such plants, called non-green plants, are unable to manufacture their own food.
-
Such plants depend on green plants or on other living bodies for their nutrition.
-
According to the mode of nutrition, heterotrophic plants are of the following types:

Parasitic Plants:
-
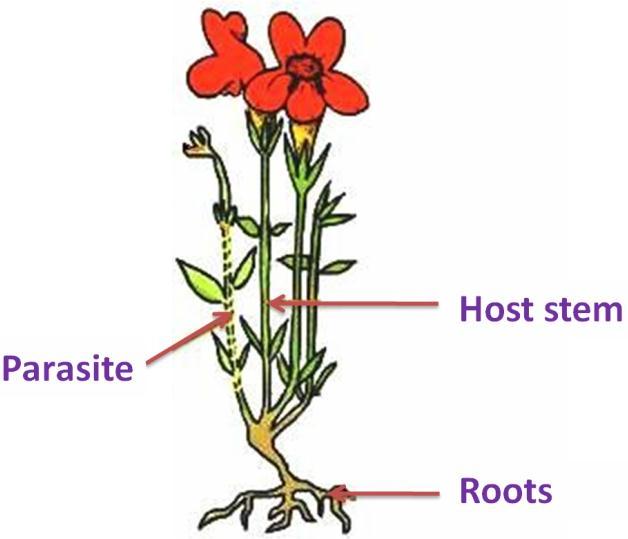
Parasitic plants are those which absorb food from another growing green plant, called the host.
-
Usually, parasitic plants develop special roots called haustoria which penetrate into the tissues of the host plant.
-
The prepared food is generally absorbed from the root or the stem of the host plant.
Example:
-
Stem parasite like Cuscuta (also called as Amarbel) and root like Orobanche are non-green and consequently they have no power to prepare their own food.
-
They get all their food supply from the host plants.
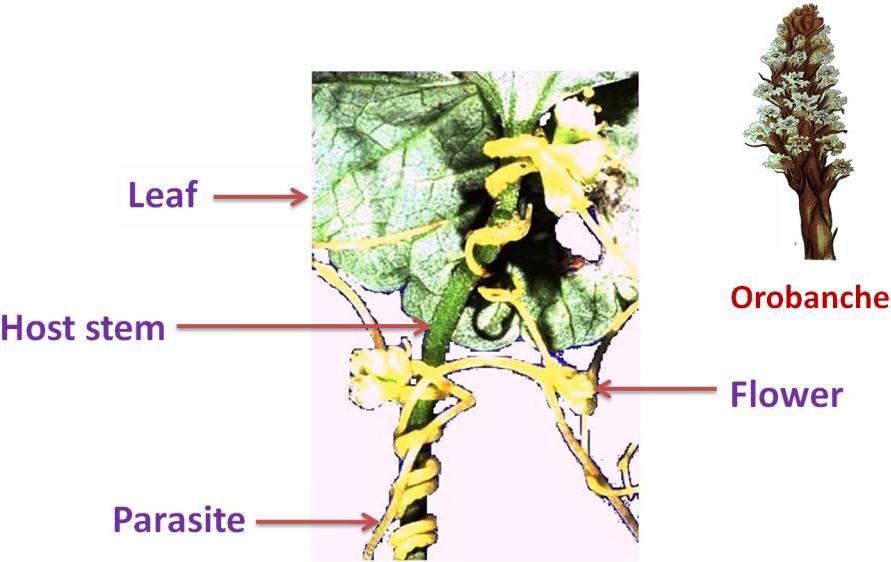
Cuscuta (Dodder) - A STEM PARASITE
-
These parasites maintain physical contacts with the host plant through haustoria (parasitic roots).
-
These haustoria penetrate into host tissue and make connections with the conducting elements of host and draw nourishment.
Cuscuta (Dodder) - Portion of parasite attached to the stem of host

Rafflesia- A parasitic plant (it bears the world’s largest flower)
-
In a parasitic relationship, only the parasitic plant benefits.
-
Parasitic plants harm the host plant.

-
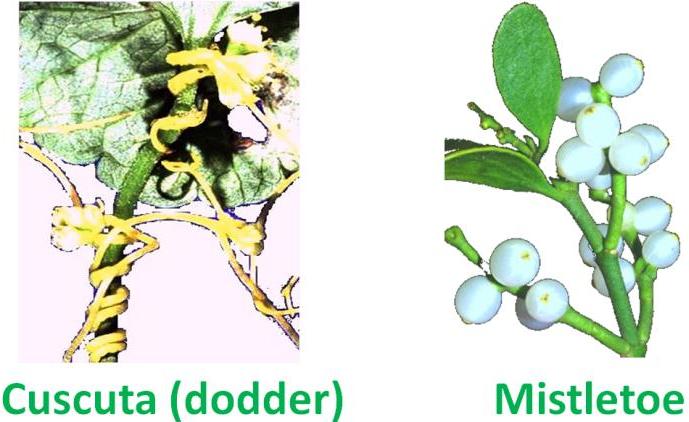
Like Cuscuta and Mistletoe are serious problems for plants.
-
Dodder can cover woody plants and cause heavy damage to certain economically important crops.
-
Mistletoe can become so abundant on a tree that most of the foliage is of the parasite and not of the host.
-
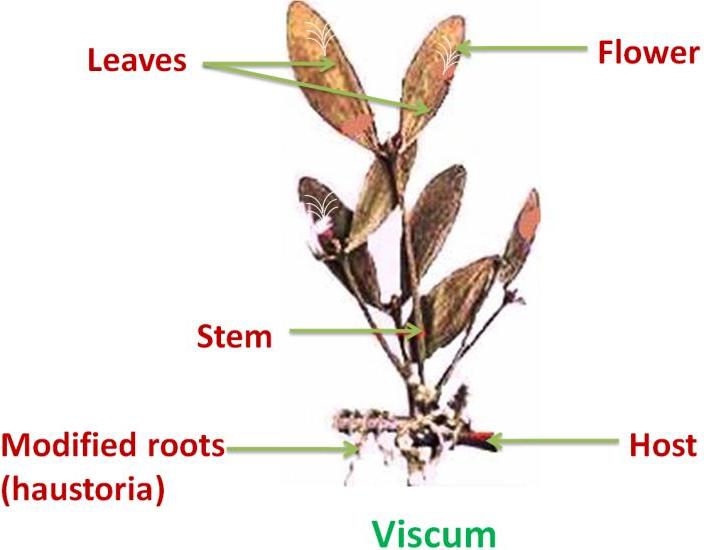
Viscum, a stem parasite has green leaves and thus is capable of manufacturing food, but is dependent on host plant for water supply.





