PARTS OF THE CELL
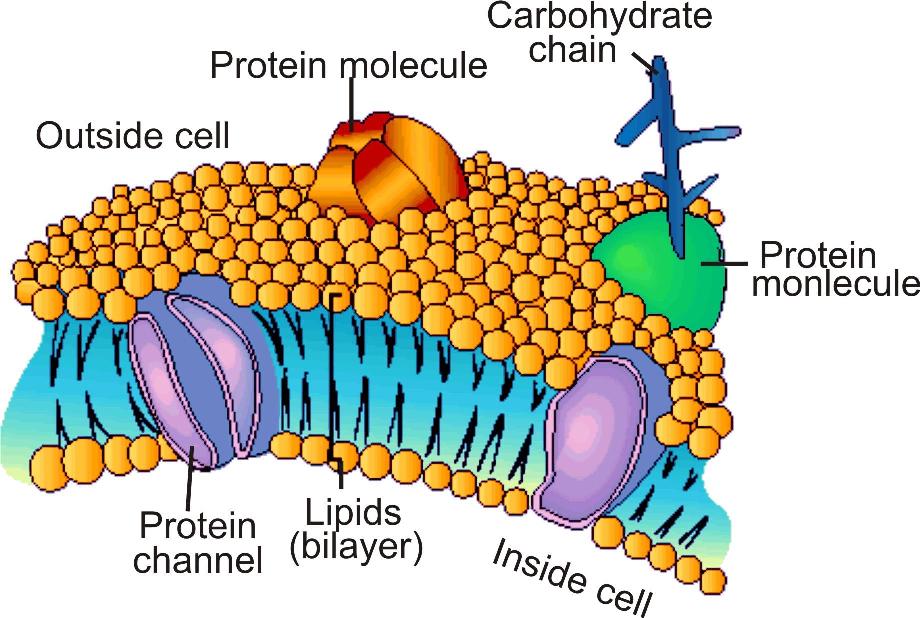
Cell Membrane:
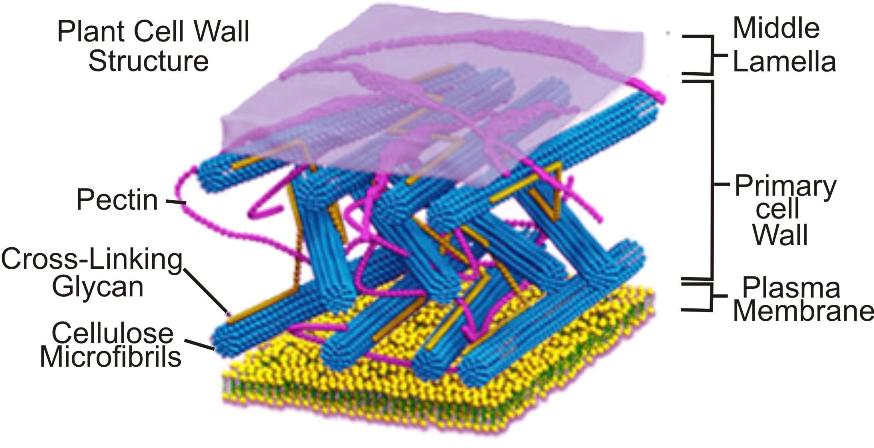
Cell Wall:
Cytoplasm:
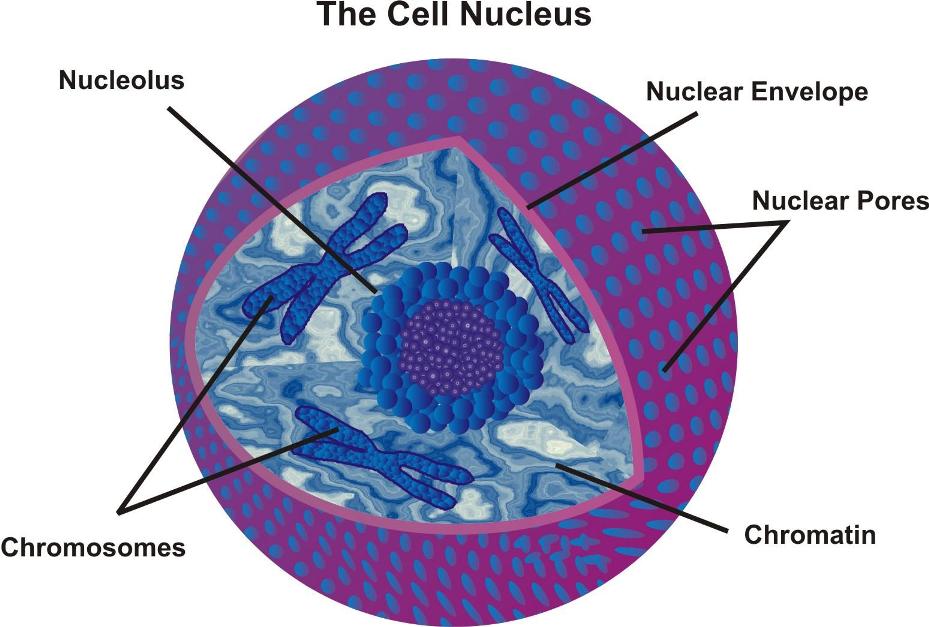
Nucleus:
Vacuoles:
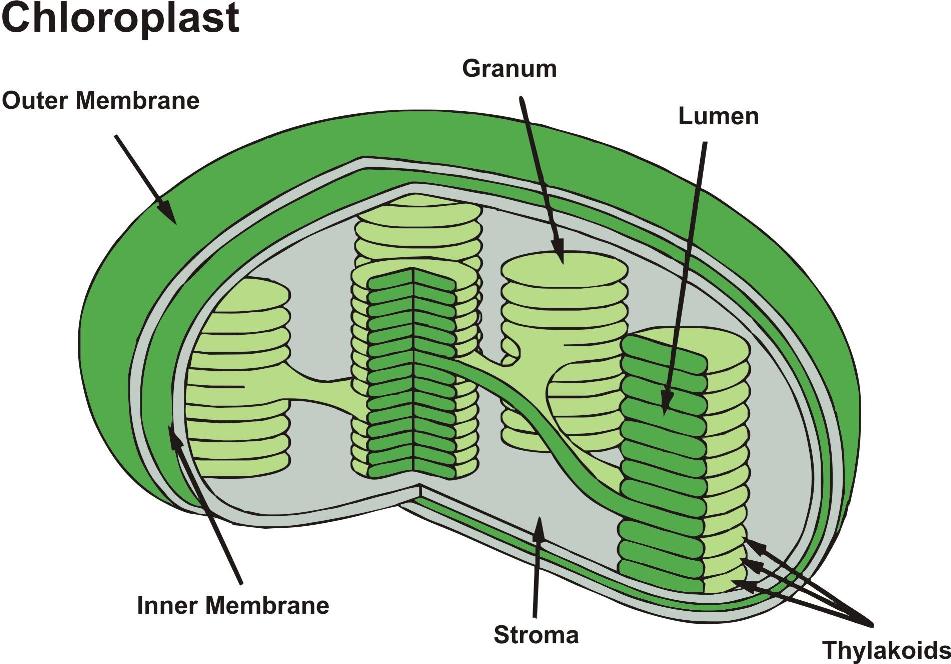
Plastid:
Other Organelles:
|
S. No. |
Organelle |
Function |
Important information |
|
1. |
Endoplasmic reticulum |
1. protein synthesis 2. steroid secretion |
Two types: a. Rough E.R- ribosome are present on their membrane. b. Smooth E.R- ribosome are absent on their membrane. |
|
2. |
Ribosome |
Play an important role in protein synthesis. |
Located on rough endoplasmic reticulum. |
|
3. |
Golgi body |
a. Modification, storage, package and transport of proteins and lipids synthesized by ER b. Secretion of various material like steroids etc. |
Formed from endoplasmic reticulum |
|
4. |
Lysosome |
Intracellular digestion |
Known as suicide bags |
|
5. |
Mitochondria |
Produces and stores energy rich molecule |
Powerhouse of the cell |
|
6. |
Centriole |
helps in cell division |
absent in plant |