Cell - Structure and Functions Worksheet-1
(a) Nerve cells (b) Muscle cells
(c) Bone cells (d) Gland cells
(a) Epithelial tissue (b) Muscle tissue
(c) Connective tissue (d) Nervous tissue
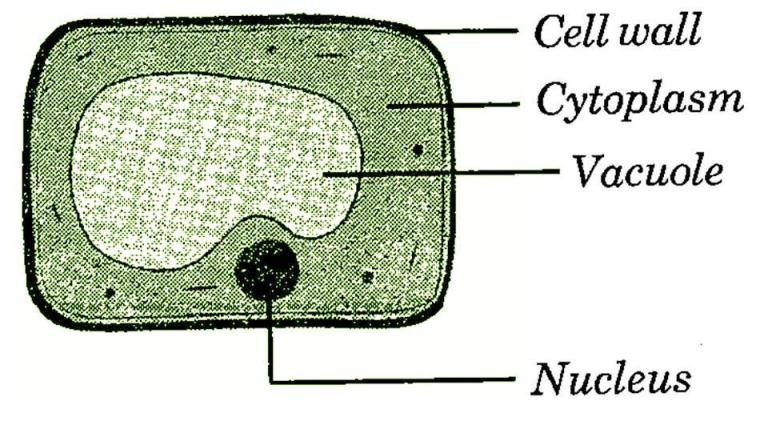
I – Cytoplasm
II – A nucleus
III – A cell wall
IV – A large vacuole
(a) I and II only (b) I and III only
(c) II and IV only (d) III and IV only
(a) To absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis
(b) To break up water into hydrogen and oxygen during photosynthesis
(c) It has chlorophyll for absorbing light energy
(d) To form starch and glucose in sunlight
(a) The cells of a whale are much larger than that of an ant
(b) The cells in our body continue to grow and divide to replace the old and damaged ones
(c) The nucleus controls most of the cellular activities within the cell
(d) The cell wall gives plant cells a regular shape
(a) Iris of eye only (b) Uterus only
(c) Bronchi only (d) All of these
(a) Brain (b) Spinal cord
(c) Cranial and spinal nerves (d) All of these
(a) Epithelial (b) Connective
(c) Nervous (d) Muscular
(a) Nervous tissue (b) Muscle tissue
(c) Epithelial tissue (d) Connective tissue
(a) Muscle tissue (b) Nervous tissue
(c) Epithelial tissue (d) Connective tissue
(a) Transporting proteins that are to be released from the cell only
(b) Packaging proteins into vesicles only
(c) Altering or modifying proteins only
(d) all of these
(a) Passive transport (b) Active transport
(c) Cell adhesion (d) Cellular recognition
(a) The largest part of a living being
(b) The part that can be seen only under microscope
(c) The starting point in the life of all organisms
(d) The structural and functional unit of life
(a) Cell wall (b) Nuclear membrane
(c) Cell membrane (d) Tonoplast
(a) Cytoplasm (b) Tonoplasm
(c) Karyoplasm (d) Cellsap
Answer Key:
(1)-(a); (2)-(c); (3)-(d); (4)-(c); (5)-(a); (6)-(d); (7)-(d); (8)-(b); (9)-(c); (10)-(b); (11)-(d); (12)-(d); (13)-(d); (14)-(c); (15)-(a)