CHARACTERISTICS OF FUELS
-
All the combustible substances can not be used as fuels for all applications because although all the fuels produce heat and light on burning, some produce more energy than others.
-
The choice of fuel depends upon -
-
its cost
-
its efficiency
-
its availability
-
extent of pollution it causes
-
Two important characteristics of fuel are:
-
Calorific value
-
Efficiency of fuel
-
Calorific value of a fuel is defined as the amount of heat produced in kilojoules when one gram of a fuel is completely burned.
-
The unit for representing calorific value is kilojoule (kj). Calorific value is expressed in kJ/g.
-
The higher is the calorific value of a fuel the better is the fuel.
Calorific values of some fuels:
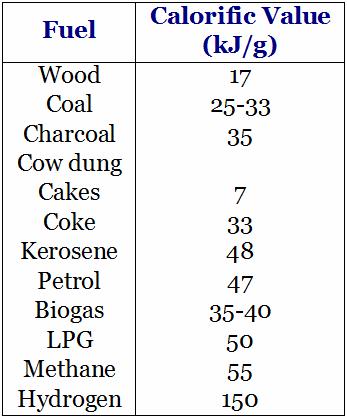
-
When a fuel is burnt, some of the energy produced is given off as waste heat, which cannot be utilized for cooking or other purposes. This is what affects the efficiency of a fuel.
-
Till date, no fuel-burning device is known to exhibit 100% efficiency.
Important characteristics of an ideal fuel:
-
It should have a high calorific value.
-
Its ignition temperature should be low but well above the room temperature. If the ignition temperature is too low, the fuel will catch fire very easily (which could be dangerous) and if it is very high, the fuel has to be heated for a long time before it can catch fire.
-
It should have a moderate rate of combustion and should release heat in a controlled manner.
-
It should be fairly cheap and easily available. A fuel may have a very high calorific value but if it is expensive and not easily available, it cannot be used on a day-today basis.
-
It should be safe to handle, store, and transport.
-
It should not cause pollution on burning.
Examples of some fuels:
Hydrogen as fuel:
-
Hydrogen has the highest calorific value so it may be considered as the best fuel.
-
As it is highly inflammable, its transport, storage and handling are difficult.
-
It is, therefore, used as a fuel only where it is absolutely necessary (e.g., as rocket fuel).
Methane and LPG as fuels:
-
Both Methane and LPG have fairly high calorific values.
-
They burn with a smokeless fire and, therefore, do not cause pollution.
-
They are ideal for use as domestic fuels.
Petrol and diesel as fuels:
-
Both petrol and diesel are mainly used in automobiles.
-
Their main disadvantage is their limited availability.
-
Another disadvantage is that their combustion releases harmful gases into the atmosphere.
Harmful effects on the environment due to burning of fuels:
-
Fuels like wood, coal, petroleum release unburnt carbon particles which cause respiratory diseases like asthma.
-
Incomplete combustion of fuels release carbon monoxide gas which is a poisonous gas which even can cause death in large amounts.
-
Burning of most fuels release carbon dioxide which is a green house gas thus causes rise in the temperature of the atmosphere. This is called global warming. It causes melting of polar ice caps, rise in sea level and flooding of coastal areas.
-
Oxides of sulphur and nitrogen are released on burning of coal and petroleum. These gases dissolve in water forming acid rain. It is harmful for crops, soil and damages buildings.
