CATTLE FARMING
-
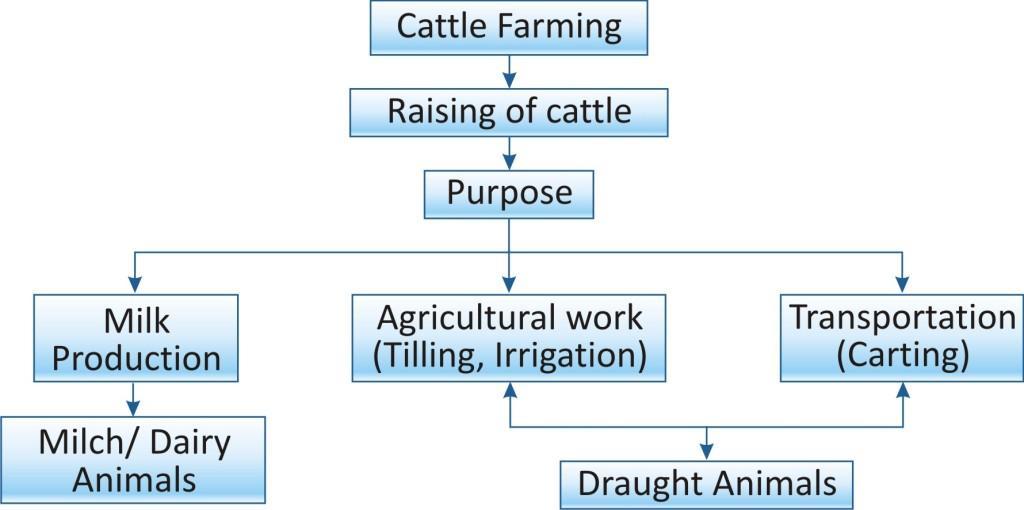
Cattle farming or cattle husbandry is related to the raising of cattle for different purposes.
Dairy/Milch Animals:
-
Animals that are raised in cattle husbandry for the production of milk are known as milch or dairy animals. These include the female organisms.
Examples: Cows, Buffaloes, Camel, Goat, Sheep etc.
-
Organisms chosen for such purposes should have long lactation period and resistance towards diseases.
-
Indian breeds are more resistant towards diseases but have short lactation period. Such breeds are also known as indigineous or locale breeds.
Examples: Cows: Sahiwal, Red Sindhi, Gir etc.

Indian Breed-Sahiwal

Indian Breed-Red Sindhi Cow

Indian Cow-Gir
-
Buffaloes: murrah, surti etc.

Indian Breed-Mehasana Buffalo

Indian Breed-Murrah Buffalo
-
Foreign or exotic breeds have long lactation period but less resistance towards diseases.
Examples: Cows-Holstein-Friesian, Brown Swiss, Jersey etc.

Exotic Breed-Holstein-Friesian Cow

Exotic Breed-Brown Swiss

Exotic breed-jersey
Draught Animals:
-
Cattle husbandry is also done for producing draught animals which are used for agricultural work such as tilling, irrigation and carting.
-
Draught animals are generally the male partners of milch organisms.
Improvement of Indian/ indigenous breeds:
-
Characters desired in improved species are:
-
Tolerance to climatic conditions
-
Lactation period
-
High yield of the produce(milk/ meat, leather etc)
-
Resistance to diseases
-
Age of reproduction
-
Good health
-
Physical appearance
-
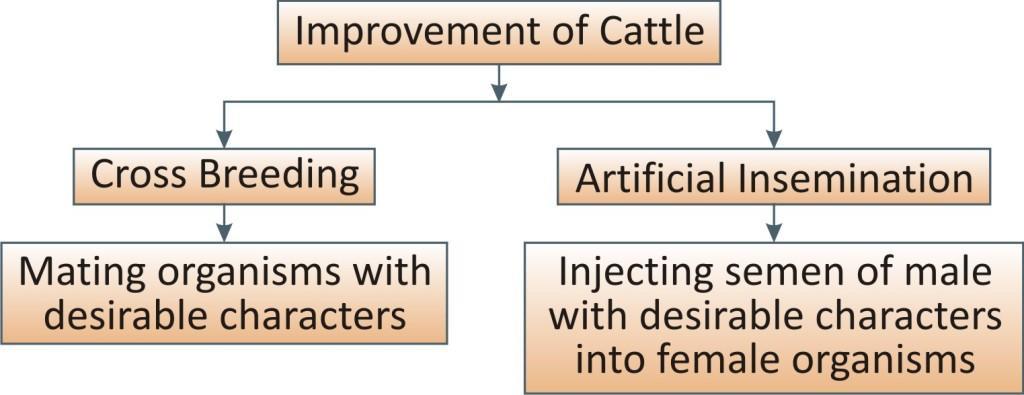
Milk production in Indian disease resistant breeds can be increased by cross breeding them with foreign breeds.
-
Cross breeding refers to the breeding of two different animals with different characteristics with an aim to obtain offspring with desirable characteristic features of both parent organisms.
-
This can be done by artificial insemination, i.e., injecting the semen of males having desirable characters into the female organism.
-
Characters desirable in milch farming is to develop hybrid species having long lactation period and high resistance towards diseases.
-
Examples: Indian cows crossed with foreign breed produces hybrid species.
|
Indian cows
|
Foreign cows
|
Improved hybrids
|
|
Sahiwal
|
Brown Swiss
|
Karan Swiss
|
|
Thaparkar
|
Holstein- Friesian
|
Karan- Fries
|
|
Sahiwal
|
Holstein- Friesian
|
Frieswal
|
Management of cattle husbandry:
-
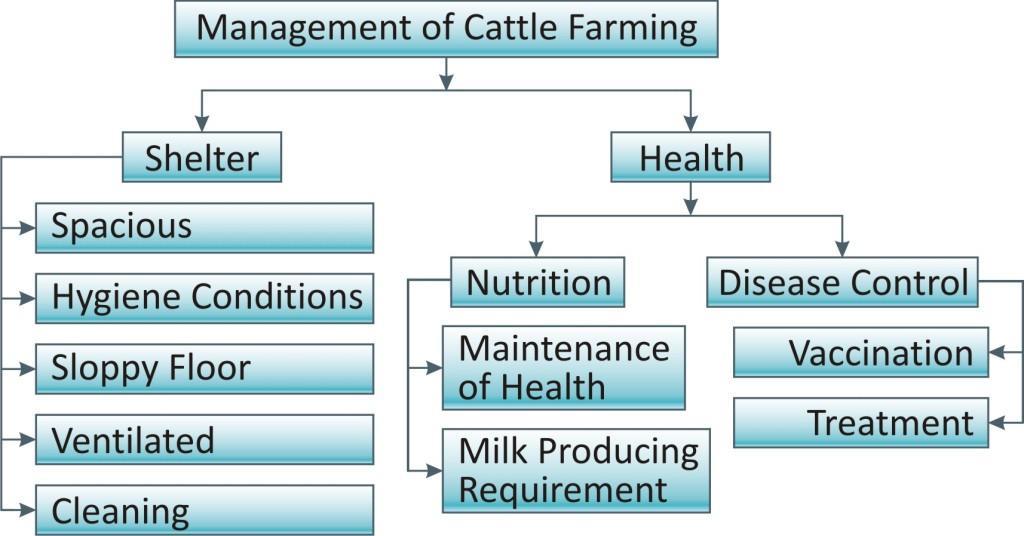
Management is related to the maintenance of shelter of cattle and their health. The surroundings should be kept clean for the good health of cattle and good health is essential for production of milk.
Shelter management:
-
The place designed for the cattle should well ventilated and clean. It should be maintained with conditions favorable for the survival of these species in different seasons. Also the animals should be kept clean.
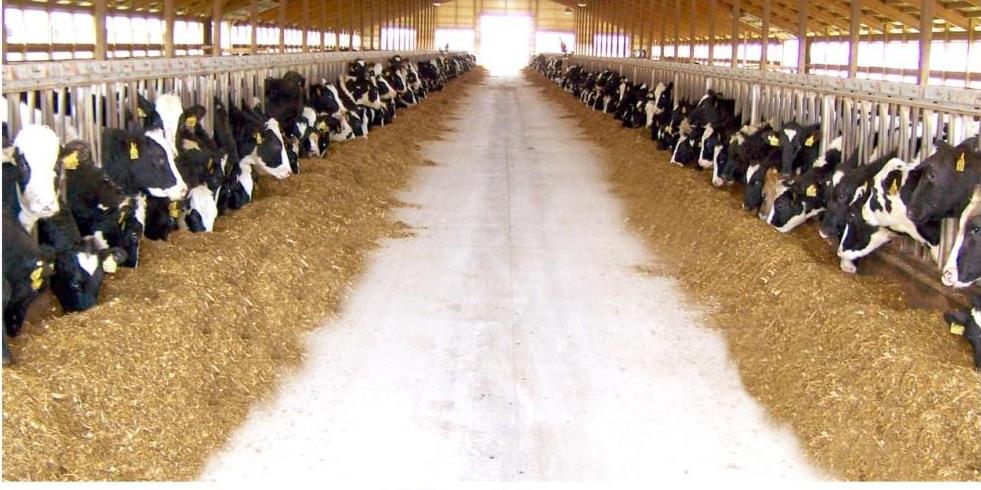

Shelter
-
Important points of consideration are:
-
Shelter should be spacious. Minimum 6m2 is required for cow and little more for buffaloes.
-
It should be covered with shed so as to protect the cattle from, heat, cold and rain.
-
The floor is brick lined and sloppy to facilitate the flow of waste and keeping the area dry. The floor should be washed and cleaned regularly to keep the area clean.
-
A proper arrangement should be there for hygienic disposal of animal excreta. Such waste could be used for the biogas/ manure production.
-
Shelter should be kept neat and clean. Animals require regular brushing for the removal of dirt and loose hair so facilities should be there for regular cleaning of animals as well as cattle.
-
Cross ventilation should be maintained well enough.
-
Proper feeding passage and feeding trough should be there in the shelter.
Nutrition Management:
-
Nutritional requirements of dairy animals are of two types:
-
For health Maintenance: The food required to support the animal to live a healthy life.
-
For Milk production: the type of food required during the lactation period to increase the milk production and its quality.
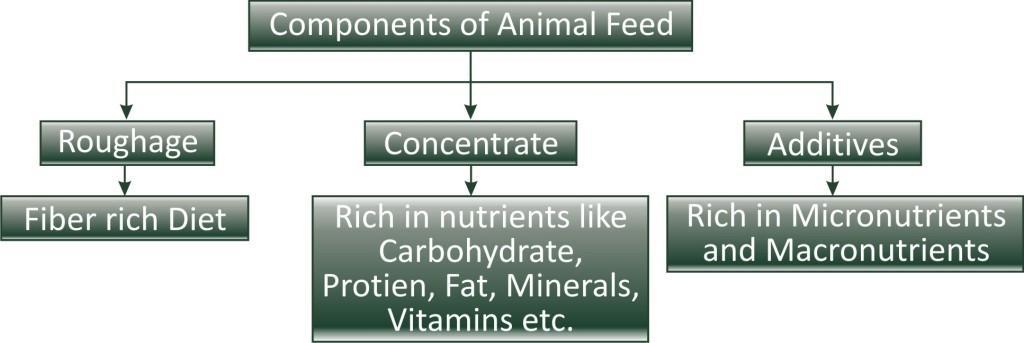
Components of animal feed:
-
Roughage: It contains fibers such as green fodder, hay, straw, legumes (berseem, cow pea) etc. roughage is rich in cellulose and hemicelluloses which provides energy and basic raw materials for different metabolic activities in cattle.
-
Concentrate: It is the diet which is rich in one or more nutrients like carbohydrates, fats, protein, minerals, vitamins etc. it includes cotton seeds, oats, barley, sorghum, rice bran etc. however it has low content of fibers. These materials provide basic raw material for maintenance of good health.
-
Additives: Certain macronutrients and micronutrients are added in regular diet of animals for the better production of milk, both qualitatively and quantitatively. Example: Calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium etc.
Disease control:
-
Cattle suffer from a number of diseases: Parasitic and infectious.
-
Parasitic: fleas, mites, ascaris etc.
-
The external parasites live on the skin and mainly cause skin diseases.
-
The internal parasites like worms, affect stomach and intestine while flukes damage the liver.
-
Infectious: Bacterial (Anthrax), Viral (foot and mouth disease) etc.

Foot and Mouth Disease-Cattle
-
The diseases, besides causing death, reduce milk production. A healthy animal feeds regularly and has a normal posture.
-
To maintain the health of these animals vaccinations are given to farm animals against many major viral and bacterial diseases. This can prevent the disease in individual animals as well as prevent its spread in other organisms.













