INTERDEPENDENCE OF PLANTS AND ANIMALS
-
Living organisms depend on each other for survival and form a biotic community or biota.
-
Forests help to preserve the diverse life forms or living organisms around the world.
-
All animals depend on plants for food, directly or indirectly. For example, a rat eats grains and plants, a snake eats a rat, which is in turn eaten by an eagle.
-
It is like a chain that exists in nature. Such a chain is called a food chain.
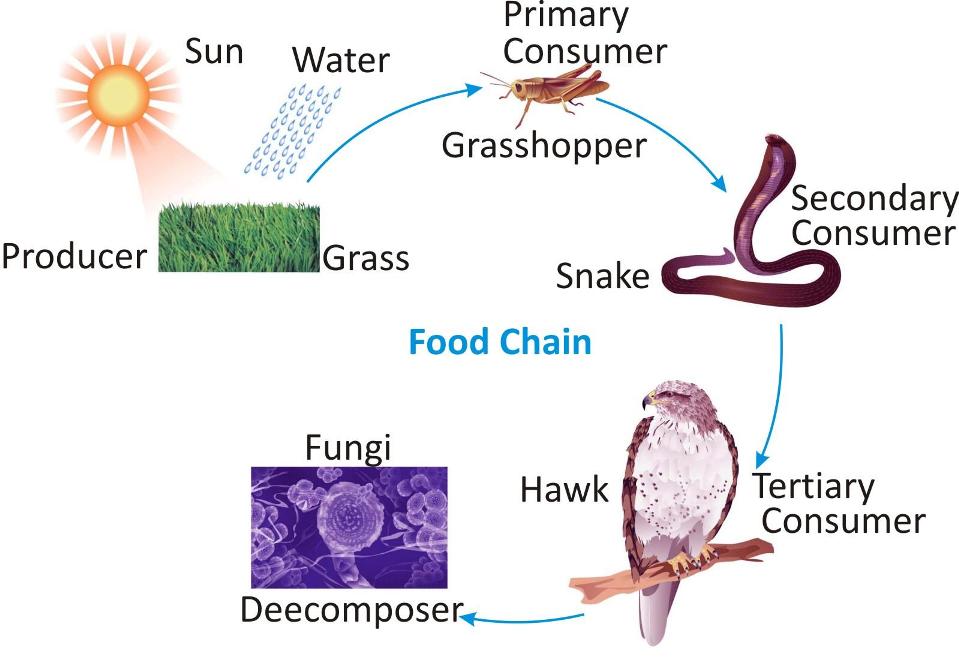
A typical food chain
-
Green plants are called the producers as they can produce their own food.
-
Animals are called consumers since they cannot produce their own food and depend on plants and other animals for food.
-
When animals die, their bodies break down (with the help of decomposers such as bacteria and fungi) and become a part of the soil.
-
This makes the soil fertile helping the growth of plants.
-
These plants again become food sources for the animals.
-
Thus, the food chain goes on and on.
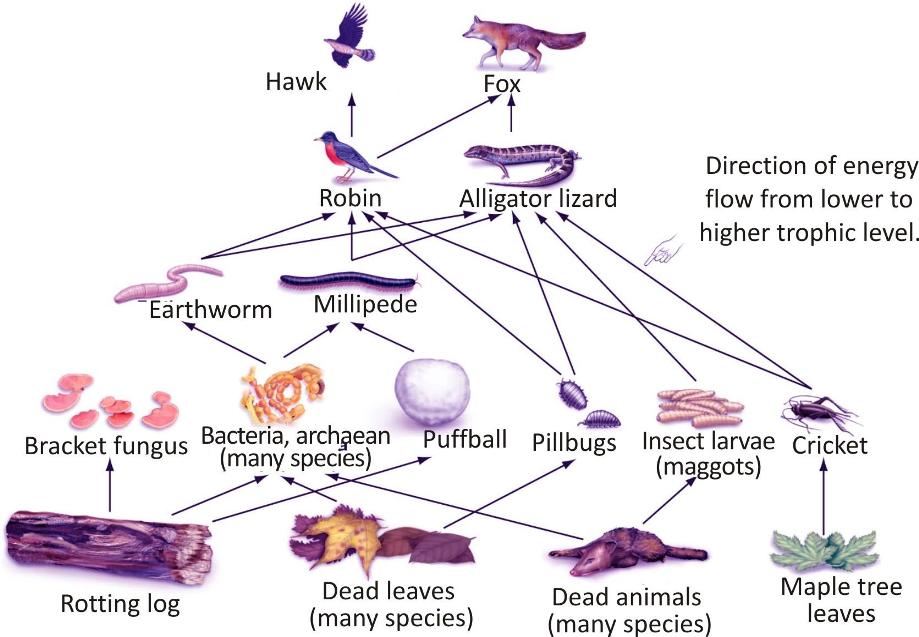
A typical food web
-
Food chains are simple representations of energy flow in nature.
-
They exist everywhere, be it in the pond or the ocean, the grassland, desert, or the mountain.
-
Several food chains that exist in nature are interconnected.
-
For example, a rat and a hen both eat grains. Both of them can be eaten by a cat.
-
A cat can be eaten by a bigger animal such as a wolf. But a wolf can also eat a hen and a rat directly.
-
There also exists a more complex representation of energy flow in nature.
-
We call such a representation a food web, as it appears like a web that a spider spins.
-
Few examples of interdependence of plants and forest and in nature are:
-
Trees in forests provide shelter to animals such as chimpanzees, monkeys, gorillas, snakes, chipmunks, birds, and squirrels.

Chipmunk
-
Trees absorb the harmful effects of natural elements such as wind, sunlight, and rainfall, thus protecting animals.
-
Several insects and birds become agents that bring about pollination of flowers, thereby assisting in fruit formation. Butterflies, bees, wasps, and humming birds are important pollinators.
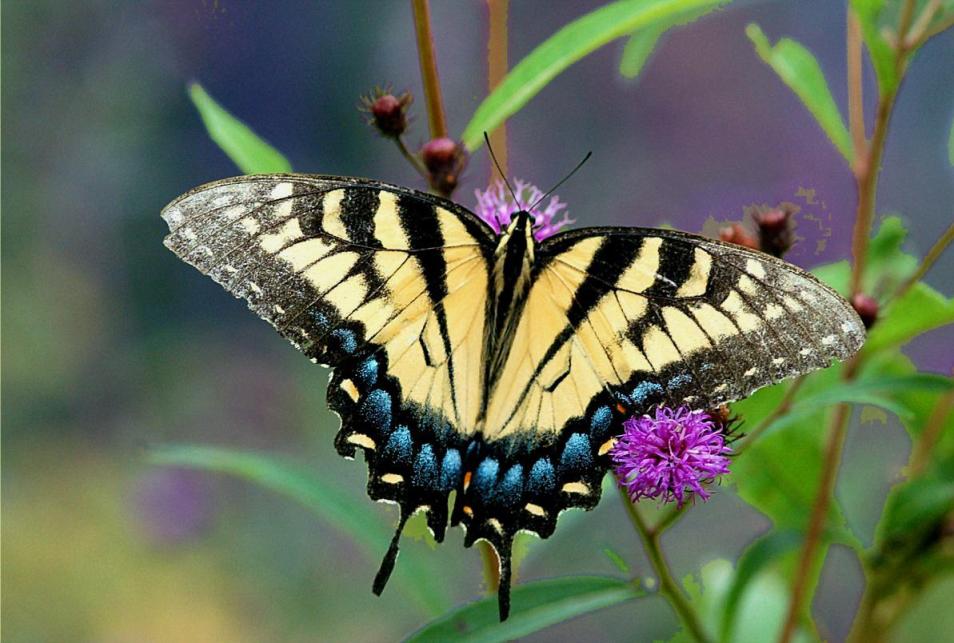

Butterfly acts as a pollinator
-
Seeds of several plants depend on animals for dispersal, which is important for survival of many varieties of plants.
-
Some seeds stick to the fur of animals and get transported to far-off places.
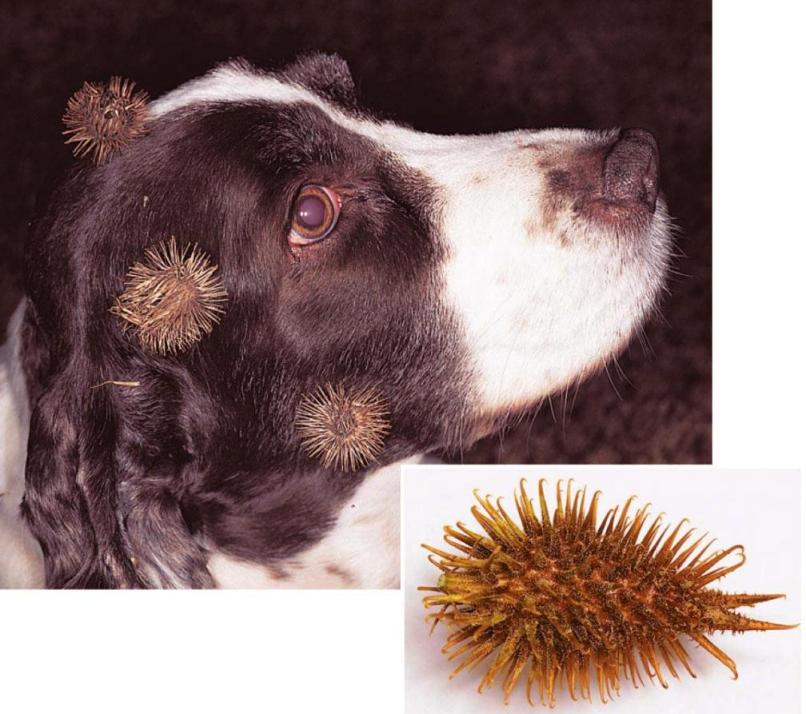

Cockleburr seeds stick to the animal
-
Animals such as monkeys, chimpanzees, and birds eat fruits along with the seeds.
-
These animals keep moving from one place to another.
-
The seeds of the fruits that they eat come out with the excreta and get scattered to distant places. Thus, animals help in dispersal of seeds.




