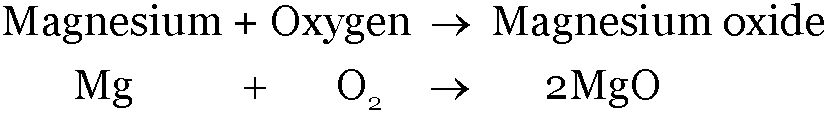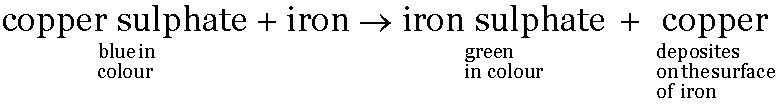CHEMICAL REACTIONS
-
Chemical reactions involve conversion of a chemical substance (elements/compounds) into some other chemical substance (elements/compounds).
-
The elements/compounds which combine to form a new substance are called reactants and the new substance formed is called Product.
-
A chemical equation is the shorthand notation used to represent a chemical reaction.
Writing a Chemical Equation:
-
Usually, chemical equations are written using formulae of elements or compounds.
For example:
The formation of magnesium oxide
-
The chemical equation for this reaction can be obtained by following the steps given below:
-
Identify the reactants and the products of the chemical reaction.
Reactants: Magnesium, Oxygen
Product: Magnesium oxide
-
Write the names of the reactants on the left hand side with a ' + ' sign between them.
-
Similarly, write the names of the products on the right hand side with a ' + ' sign between them.
-
Place an arrow (→) between the two sides, with the arrow-head pointing towards the products, i.e., between reactants and products.

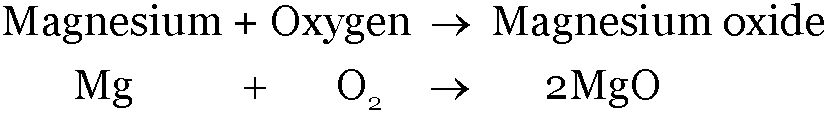
-
A chemical equation should also be balanced, i.e., the number of atoms of each element on both sides should be equal.
Advantages of chemical equations:
-
Chemical equations are important because they give us information about:
-
The number of atoms or molecules of the reactants taking part in these reactions, and the number of atoms or molecules of the products formed.
-
The substances or reactants that take part in chemical reaction, and the products formed.
Changes can be broadly divided into two types:
-
Physical changes
-
Chemical changes
Physical changes:
-
Physical changes are the changes in which no new substances are formed.
-
Like, formation of ice when water is kept in a freezer is a physical change because the chemical properties of water is not changes and also water can be obtained back by melting of ice.
-
Change of water to water vapour by boiling is also a physical change.
-
In most of the physical changes, properties such as colour, shape, size, or physical form of the substance may change.
-
Physical changes may or may not be reversible.
-
Change of colour of hack-saw blade when heated (becomes red) is also a physical change as its original colour can be regained on cooloig it.
Chemical changes:
-
A change in which one or more new substance is formed is called chemical change .A chemical change is also called chemical reaction. The properties of new substance are different from the ones which are undergoing the reaction.
-
A chemical change is permanent and such changes are occurring all around us, even within our body.
Reddish-brown Deposition on Iron Objects:
-
If we leave an iron object such as iron tools like spade, shovels or a bolt out in the rain, a reddish-brown layer is deposited on its surface after a few days.
-
This layer is called rust and the process is called rusting.

A rusted bolt
-
The layer of rust that forms falls off gradually, exposing fresh metal for further rusting.
-
As a result, with the passage of time iron objects become weak.
-
Iron reacts with oxygen of the air, in the presence of moisture, to form a substance called iron oxide which is called rust.
-
The chemical equation for this reaction can be represented as:
Iron → Oxygen + Water → Iron Oxide
-
Oxygen and water are two essential components for rusting of iron; absence of either one of them or both of them can prevent rusting.
-
Oiling trowels and other iron objects protects the surface from moisture and air, and hence prevents rusting.
-
This is a chemical change because it is permanent.
-
Galvanization is a process in which iron objects are coated with zinc to prevent them from rusting.
-
The water pipes used to carry water in our homes are made from galvanized iron.
Browning of Vegetable and Fruit Slices:
-
Cut surface of vegetables like potato, brinjal when exposed to air turns brown. This is due to a chemical reaction between certain compounds present in potato, brinjal and oxygen and moisture of the air.
-
The colour of slices of apple changes when cut and kept for some time.
Reason:
-
Cut slices of apples turn brown when exposed to air because it contains iron. So on being sliced; the oxygen in the air reacts with the iron to form the brown coloured compound which we see on the fruit’s sliced parts.
-
Soaking vegetables and fruits in water after cutting can reduce the level of browning by restricting the amount of oxygen in contact with their slices.
Reaction between Vinegar and Baking Soda:
-
The reaction can be represented as:
Vinegar + Baking Soda → Carbondioxide + Water + Other Compounds
-
Vinegar consists mainly of acetic acid (CH3COOH) and water.
-
Baking soda contains sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3).
-
The gas evolved can be tested by passing it through lime water which turns milky.
-
This reaction is also a chemical change and can be represented as:
Cabondioxide + Lime Water → Calcium Carbonate + Water

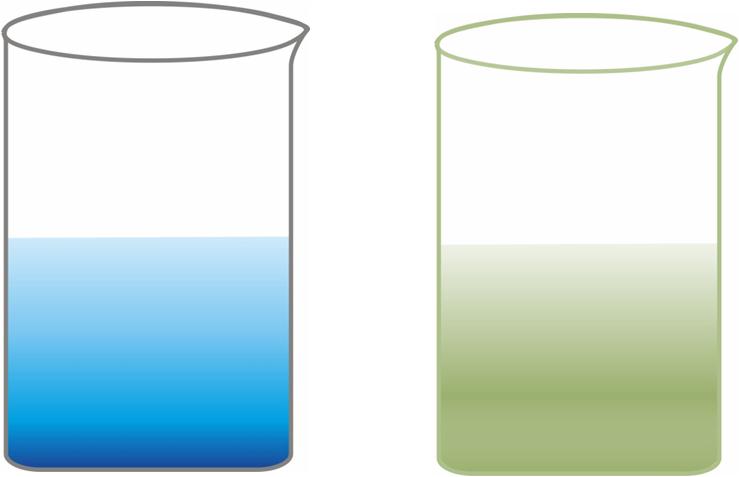
Reaction between copper sulphate solution and iron filings
-
Copper sulphate (CuSO4) solution is blue in colour and acquires sea-green colour when iron filings are dropped into it.
-
The iron filings acquire a brown colour which is because of the deposition of copper on the surface of iron filings.
-
The green colour of the solution is due to the formation of iron sulphate.
Reaction between copper sulphate solution and iron filings
-
This reaction can be represented as:
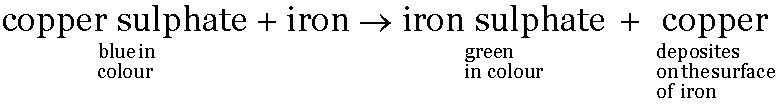
Crystallization:
-
Crystals are the purest solid form of a substance having a definite geometrical shape.
-
The process by which an impure compound is converted into its crystal is known as crystallization.
For example:
Table salt:
-
Chemically table salt is sodium chloride (NaCl).
-
Table salt is obtained by evaporating sea water.
-
The salt, thus obtained, contains certain undesirable substances such as magnesium chloride, sand, shells of sea animals etc.
-
These impurities are removed from table salt through the process of crystallization.
-
In this process, maximum amount of salt is dissolved in boiling water.
-
The salt solution formed is filtered to remove the insoluble impurities.
-
The filtered solution is left undisturbed for a few hours.
-
Sodium chloride will aggregate and form crystals with well defined shape leaving behind the undesirable impurities in the solution.