Respiration in Organisms Worksheet-2
At the start of the experiment, the indicator in each test-tube is red.
The indicator changes from red to yellow when exposed to increased levels of carbon dioxide.
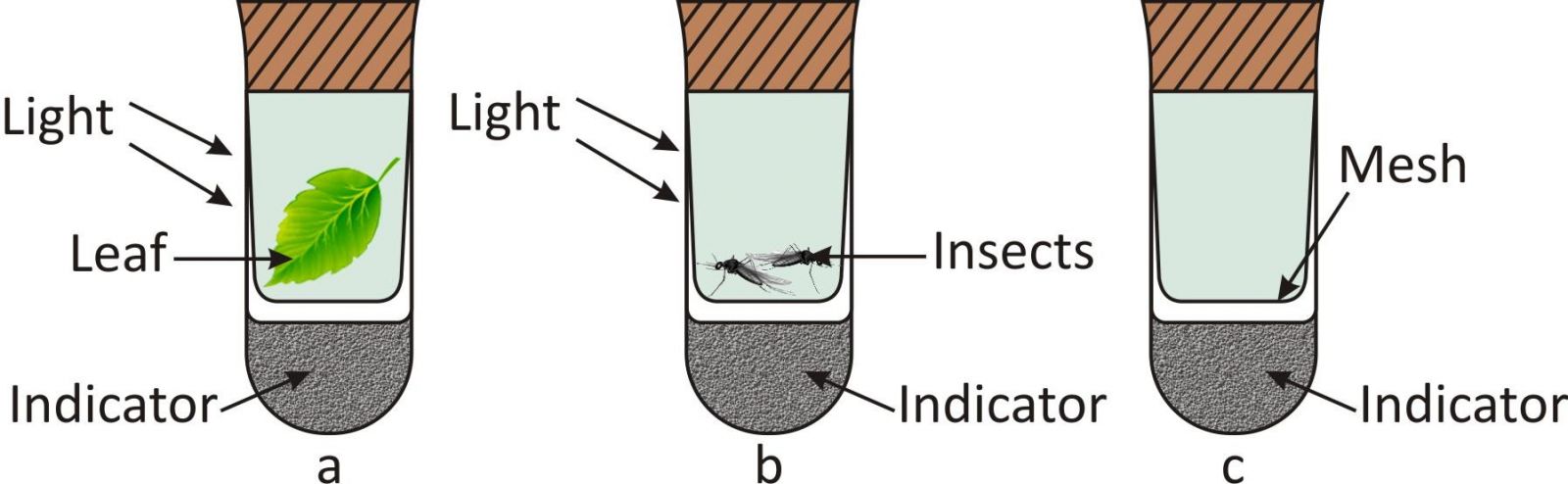
What will be the colour of the indicator in each test-tube after two hours?
(a) a → Red; b → red; c → yellow
(b) a → Red; b → yellow; c → red
(c) a → Yellow; b → red; c → red
(d) a → Yellow; b → yellow; c → yellow
Column I Column II
A. Earthworm 1. Pulmonary
B. Human 2. Branchial
C. Prawn 3. Tracheal
D. Insects 4. Cutaneous
(a) (A) → (1); (B) → (2); (C) → (3); (D) → (4)
(b) (A) → (4); (B) → (1); (C) → (2); (D) → (3)
(c) (A) → (3); (B) → (2); (C) → (4); (D) → (1)
(d) (A) → (4); (B) → (2); (C) → (1); (D) → (3)

(a) It helps in producing sound
(b) It helps in regulating air flow
(c) It helps in regulating passage of food
(d) It helps in filtering and air conditioning of air
(a) Intestine got twisted
(b) RBC became coagulated
(c) Stomach stopped digestion
(d) Diaphragm got punctured
(a) Increase in volume of thoracic cavity and fall in lung pressure
(b) Fall in pressure inside the lungs
(c) Increased volume of thoracic cavity
(d) Muscular expansion of lungs
(a) Bronchitis (b) Emphysema
(c) Lung cancer (d) Wheezing
(a) Move phlegm and germs upwards to the mouth so that they can be spit out
(b) Trap and kill germs inside the lungs
(c) Make the inside passages of the lungs smooth
(d) Secrete fluid which lubricates the lungs
(a) Alcohol and carbon dioxide
(b) Carbon dioxide and glucose
(c) Glucose and oxygen
(d) Oxygen and alcohol
(a) Diaphragm: Becomes flatter; Rib cage: downwards and inwards
(b) Diaphragm: Becomes flatter; Rib cage: outwards and upwards
(c) Diaphragm: Becomes more curved; Rib cage: downwards and inwards
(d) Diaphragm: Becomes more curved; Rib cage: outwards and upwards
(a) They get the gases they need from the water they float on
(b) They breathe through the flowers they produce
(c) They do not need any gas to live
(d) They can move their leaves above the water regularly for gaseous exchange.
Glucose + Oxygen → CO2 + H2 + Energy
(a) Photosynthesis (b) Combustion
(c) Respiration (d) Breathing
(a) Breathing is regulated by involuntary muscles
(b) The lungs operate automatically without any muscles
(c) Breathing is necessary for life
(d) All actions of the respiratory system are under one's control
(a) They lose energy
(b) They die
(c) They stop working until the oxygen supply is resumed
(d) Skin cells and lung cells can die, but other cells inside the body are not affected.
Answer Key: