FOSSIL FUELS AND ITS OVER EXPLOITATION
-
Fossil fuel is a general term for buried combustible geologic deposits of organic materials, formed from decayed plants and animals that have been converted to crude oil, coal, natural gas, or heavy oils by exposure to heat and pressure in the earth's crust over hundreds of millions of years.
-
Coal, oil and gas are called "fossil fuels" because they have been formed from the organic remains of prehistoric plants and animals.
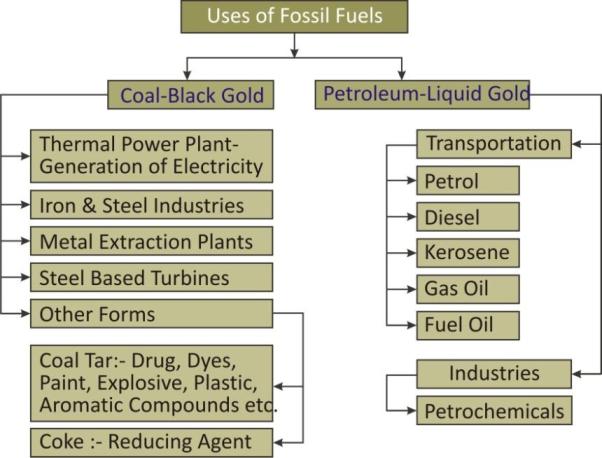
Uses of Coal and Petroleum:
Need for Conservation of Fossil Fuels:
-
The fossil fuels, coal and petroleum get exhausted and their combustion pollutes our environment, so a judicious use of these resources is necessary.
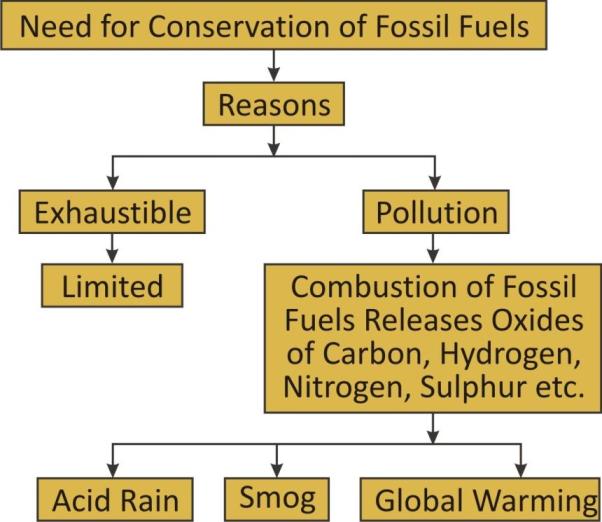
Exhaustible:
-
Fossil fuels are limited and are non renewable. They are used for many different purposes and it has been roughly estimated that if they will be used at same rate in future then petroleum will last for 40 years and coal will last for 200 years. This is because the rate of consumption is much higher than the rate of formation of fossil fuels. Thus sustainable management is required.
Pollution:
-
Combustion of fossil fuels results in the release of oxides of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and sulphur in atmosphere which results in Acid rain, Smog, Global warming which causes air pollution.
Conservation of Fossils Fuels:
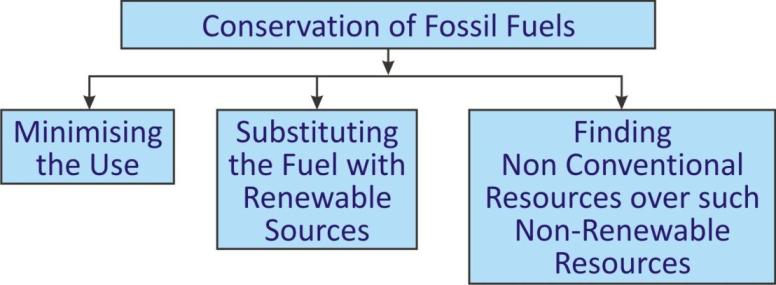
Minimization of Consumption of Fossil Fuels:
Example:
-
Use of stairs instead of lifts,
-
Prefer walking or cycling for short distances,
-
Use of public conveyance
Improvement in Existing Technologies:
-
So that hydrocarbon fuels are used more efficiently.
Example:
-
Use of vehicles having more efficient mileage and controlled exhaust smoke features.
-
Some technologies in cars now use alternate fuels in combination with petrol (alcohol mixed petroleum) or completely use biofuel.
-
Biogas can replace Liquid petroleum fuel (LPG) for cooking in rural areas.
Finding non-Conventional and Renewable Energy Sources:
-
Increase the use of non conventional sources of energy to reduce the dependence on hydrocarbon fuels.
Example:
-
Using Wind energy, hydro energy for generation of electricity,
-
Using steam turbines in industries,
-
Using solar energy based technologies (solar voltaic cells, solar panels are being used for areas such as for lighting, communications, solar heating etc.


