MIXTURES
-
A mixture is the combination of two or more substances (elements or compounds) which are not chemically combined with each other and may also be present in any proportion.
For example:
-
Sugar solution is a mixture of sugar and water
-
Steel is an alloy i.e. mixture of - iron, carbon (0.2 – 2.1%) by weight, some times other elements like manganese, chromium, tungsten, nickel may also be present.
-
Air is mixture of gases like oxygen, nitrogen, argon, carbon dioxide and water vapour.
-
Pure gold i.e. 24 carat gold is not useful in making coins or ornaments because it is very soft. It is generally mixed with a small amount of copper or silver and its purity is reduced. This is commonly used in making ornaments and coins etc.
TYPES OF MIXTURES:
-
Mixtures are of two types:
1. Homogeneous mixtures
2. Heterogeneous mixtures
Homogeneous mixtures:
-
A mixture is said to be homogenous if the different constituents or substances present in it are uniformly mixed and are indistinguishable from one another. The composition is uniform and every part of the solution has the same properties.

For example:
-
Solution of sodium chloride or sugar in water - Different constituents are uniformly mixed throughout. It is not possible to identify them.
-
Air is also a homogenous mixture of a number of gases like nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour, inert gases etc. All the gases present in air are uniformly mixed throughout. It is not possible to identify gases present in air.
-
Copper sulphate solution in water is also homogenous. The solution formed has the same intensity of blue colour throughout.
Heterogeneous mixtures:

-
A mixture is said to be heterogeneous if it does not have a uniform composition and also has visible boundaries of separation between the constituents.
-
In these types of mixtures substances remain separate and one substance is spread throughout the other substance as small particles, droplets or bubbles.


For example:
-
A mixture of sugar and sand is heterogeneous. The constituents have clear boundaries of separation. The particles of sugar and sand can be easily identified in the mixture.
-
All suspensions and colloids are heterogeneous mixtures.
-
For example- The suspension of flour in water, Clay in water, starch solution etc.

-
Mixture of oil and water.
Properties of a Mixture:
-
The constituents of a mixture can be separated by physical methods of separation
-
When iron filings and sulphur powder and mixed together, a grayish yellow mixture is obtained.
-
Iron filings can be separated from the mixture by using magnet.
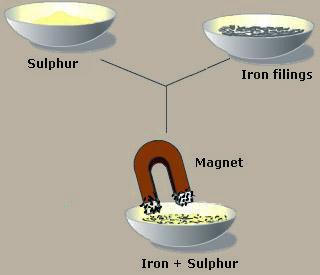

-
By dissolving mixture of iron and sulphur powder in an organic liquid known as carbon disulphide which dissolves sulphur but it does not dissolve iron in it. On filtration, iron is obtained as a residue and sulphur is recovered from the filtrate by evaporating carbon disulphide.
-
A mixture shows the properties of all the constituents present in it.
-
If dilute sulphuric acid is added to the mixture of iron filings and sulphur, iron reacts with sulphuric acid and hydrogen gas is produced where as sulphur remains unchanged.
-
This shows that a mixture of iron and sulphur shows the properties of iron.
-
If this mixture of iron and sulphur is treated with carbon disulphide, sulphur dissolves in it leaving the iron unchanged.
-
These two results, say that mixture of iron filings and sulphur shows the properties of its constituents, iron as well as sulphur.
-
The formation of a mixture is a physical process chemical reaction does not takes place between the constituents.
-
Heat is usually neither given out or absorbed in the process.
-
The composition of a mixture is variable; the constituents can be present in any proportion by mass.
-
A mixture does not have a definite melting point, boiling point, etc.
Difference between Mixtures and Compounds:
|
|
Mixtures
|
Compounds
|
|
1.
|
A mixture can be separated into its constituents by the physical process (like filtration, evaporation, sublimation, distillation, solvents, magnet, etc.).
|
A compound cannot be separated into its constituents by physical process (It can only be separated into its constituents by chemical process).
|
|
2.
|
A mixture shows the properties of its constituents.
|
The properties of a compound are entirely different from those of its constituents.
|
|
3.
|
Energy (in the form of heat, light, etc.) is usually neither given out nor absorbed in the preparation of a mixture.
|
Energy (in the form of heat, light, etc) is usually given out or absorbed during the preparation of a compound.
|
|
4.
|
The composition of a mixture is variable, the constituents can be present in any proportion by mass. A mixture does not have a definite formula.
|
The composition of a compound is fixed, the constituents are present in fixed proportion by mass. A compound has a definite formula.
|
|
5.
|
A mixture does not have a fixed melting point, boiling point, etc.
|
A compound has a fixed melting point, boiling point, etc.
|






