Geometry and Mensuration Worksheet-9
(a) Circumcentre (b) Incentre
(c) Orthocentre (d) None of these
(i) Circumcentre
(ii) Centroid
(iii) Orthocentre
(iv) Incentre
(a) (i), (ii) & (iii) (b) (i) and (ii)
(c) (i) and (iii) (d) All of these
(a) Collinear (b) Coincide
(c) Do not coincide (d) Done
(a) Perimeter (b) Hypotenuse
(c) Area (d) None
(a) The centroid of an obtuse angled triangle lies in the interior of the triangle.
(b) Orthocentre of an obtuse angled triangle lies in the exterior of the triangle.
(c) Circumcentre of an obtuse angled triangle lies in the exterior of the triangle.
(d) All of these
(a) Opposite sides (b) 2 : 1
(c) 3 : 1 (d) None
(a) The medians meet
(b) The altitudes meet
(c) The right bisectors of the sides of the triangle meet
(d) The bisectors of the angles of the triangle meet
(a) The medians meet
(b) The altitudes meet
(c) The right bisectors of the sides of the triangle meet
(d) The bisectors of the angles of the triangle meet
(a) The medians meet
(b) The altitudes meet
(c) The right bisectors of the sides of the triangle meet
(d) The bisectors of the angles of the triangle meet
(a) The medians meet
(b) The altitudes meet
(c) The right bisectors of the sides of the triangle meet
(d) The bisectors of the angles of the triangle meet
(a) An isosceles triangle
(b) An equilateral triangle
(c) A right angled triangle
(d) A right angled isosceles triangle
(a) If in a triangle, two angles are equal to 60º, then it is equilateral
(b) If the angles of a triangle are in the ratio 1 : 1 : 2 then it is a right angled isosceles triangle
(c) If the angles of a triangle are in the ratio 1 : 2 : 3 then it is a right angled triangle
(d) All of these
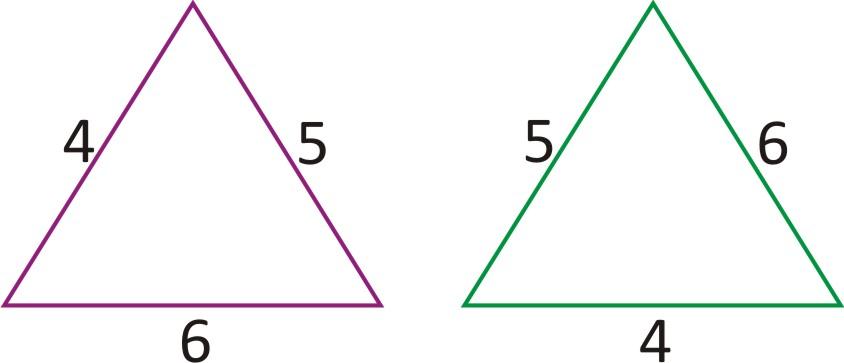
(a) SAS property (b) SSS property
(c) RHS property (d) ASA property
(a) SAS property (b) SSS property
(c) RHS property (d) ASA property
(a) SAS property (b) SSS property
(c) RHS property (d) ASA property
(a) SAS property (b) SSS property
(c) RHS property (d) ASA property
(a) 60º (b) 120º (c) 90º (d) None
(a) True (b) False
(c) Cannot be determined (d) None
R: two Δles are congruent if two sides and the included angle of the one must be equal to the corresponding two sides and included angle of the other then which of the following statement is correct
(a) A is false and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) A is true and R is the correct explanation of a A
(c) A is true and R is false
(d) None of these
(a) Two line segments having the same length are congruent
(b) Two squares having the same side length are congruent.
(c) Two circles having the same radius are congruent
(d) All of these
Answer Key:
(1)-(b); (2)-(c); (3)-(a); (4)-(b); (5)-(d); (6)-(a); (7)-(b); (8)-(a); (9)-(c); (10)-(d); (11)-(b); (12)-(d); (13)-(b); (14)-(c); (15)-(a); (16)-(d); (17)-(c); (18)-(b); (19)-(a); (20)-(d)