VACCINE
-
Vaccines are the medical preparations which are injected into the body so as to prevent us against diseases.
-
These vaccines are the dilute solutions containing weakened or dead microbes which are when introduced in a healthy body activate its immune system to prevent occurrence of disease.
-
These weakened microbes are not pathogenic, i.e., they cannot cause disease but can boost our immune system such that it can produce antibodies against it as well as keep it in memory for future response.
-
Thus immune system will remember the microbe without having disease so in future if similar natural pathogenic microbe invades our body the activated system will recognize and kill it and will not allow it to cause the disease.
-
In general if a disease causing organism, i.e., pathogen enters our body, our immune system gets activated and produces antibodies which neutralizes the effect of pathogen. Thus we are prevented against diseases.
-
Such response is also fed in memory of immune cells, thus if similar pathogen re-enters our body it respond immediately by producing antibodies.
-
Vaccines mimics with these natural invaders as they can expose the immune system to non pathogenic micro organisms without causing any disease and generating memory.
-
This is how vaccine works and protects us from the future attack of pathogenic bacteria.
-
Several diseases, including polio, tuberculosis, smallpox and hepatitis can be prevented by vaccination.
Discovery of vaccine:
-
The small pox vaccine was the first to be discovered successfully by Sir Edward Jenner in 1796. He realized that milkmaids who were exposed to cowpox virus did not catch small pox during epidemics. Cowpox is a viral disease found in cattle. Jenner injected the mild samples of cowpox virus in some of the people and found that they were now resistant to the disease small pox. This cowpox virus and smallpox virus belong to same category.
-
The word vaccine has come from the Latin word “vacca” and “vaccinia” which means cow and cowpox respectively. The process of injecting vaccine is known as vaccination.
Increasing Soil Fertility:
-
Some bacteria and blue green algae–cyanobacteria are able to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere to enrich soil with nitrogen and increase its fertility.
-
Examples of cyanobacteria are anabaena, nostoc, lyngbya etc.
Cyanobacteria: (Lyngbya sp.):

-
These microbes are commonly called biological nitrogen fixers.
-
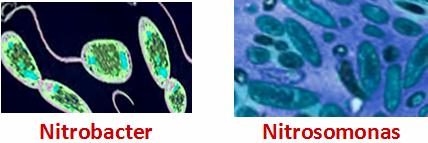
Other organisms increase fertility by forming the nitrates and nitrites or other usable forms of nitrogen. Examples of such bacteria are nitrosomonas, nitrobacter etc.
Cleaning the Environment:
-
Plant and animal waste when disposed in a pit gets decomposed by microorganisms and gets converted to manure.
-
These pits are known as compost pits and the manure produced is called as compost.

-
If composting is done by using worms then it is known as vermicompost.
-
The nutrients released in the process could be used by the plants again.
-
The microorganisms decompose dead organic waste of plants and animals converting them into simple substances.
-
These substances are again used by other plants and animals.
-
Microorganisms can be used to degrade the harmful and smelly substances and thereby clean up the environment.


