CHEMICAL SYMBOLS
-
The abbreviations used to represent elements are called chemical symbols.
-
A symbol is basically the short form of an element laid down by consensus so that it has universal recognition.
-
In earlier days, these symbols were pictorial in nature.
-
Later, Sir John Dalton, an English scientist created his own set of pictorial symbols for elements known in his time.
Some of the pictorial symbols of some elements:
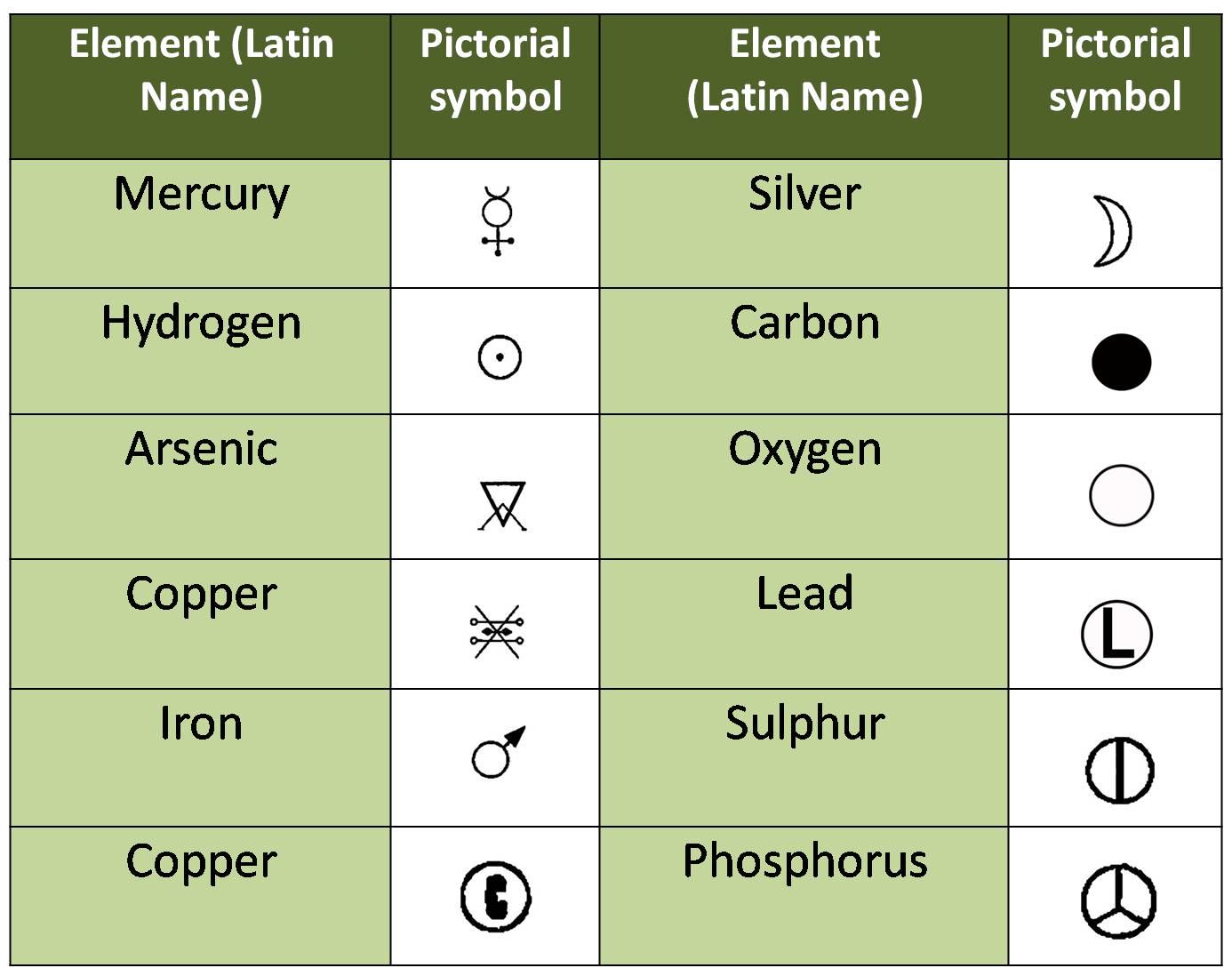
-
The modern system of representation was given by Berzelius.
-
Instead of pictures, he made use of letters of the English alphabet to represent various elements.
-
It is 1- or 2-letter internationally agreed code for an element usually derived from the name of the element in Latin.
-
The important features of this system are as follows:
-
The first letter appearing in the name of an element is used as its symbol. For example, the symbol for hydrogen is H, for carbon C, oxygen O, nitrogen N, etc.
-
When two or more elements have their names beginning with the same letter, then one more letter is added to the symbol.
-
For some elements, the second letter in their name is added, such as for calcium (Ca), cobalt (Co), xenon (Xe), helium (He), bromine (Br).
-
In some cases, another distinct letter is used, e.g., chlorine (CI), magnesium (Mg), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn).
Symbols of Some Other Common Elements:
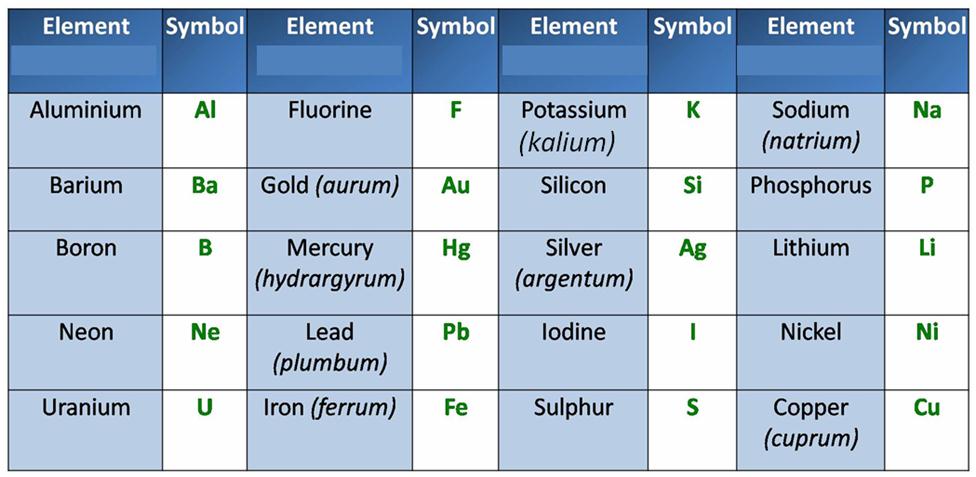
Note: Names given in the bracket are Latin names
Significance of a Symbol:
-
A symbol represents the following:
-
Abbreviation for a particular chemical element.
-
Single atom of that element.
For example:
-
CI is a symbol and it represents element chlorine and one atom of chlorine.

