WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT
-
A wastewater treatment plant is a facility that treats wastewater from industrial sources. There are basically three processes involved in treating wastewater: primary, secondary, and tertiary.
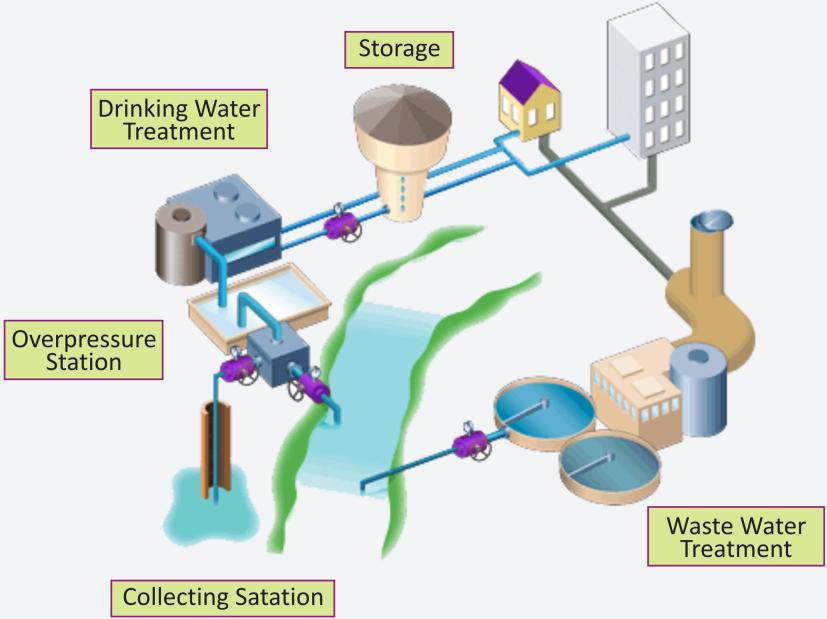
Wastewater Treatment Plant
Primary Process:
-
This is a mechanical process which involves screening and settling of large particles.

Vertical bars
-
First the sewage is passed through screens of vertical bars to remove larger impurities such as metal cans, plastic bags, cloth pieces, etc.

Grit chamber
-
The wastewater is then passed through a grit and sand removal tank called the grit chamber.
-
The speed of the incoming wastewater is reduced so that sand, grit, pebbles, etc., settle down.
-
The water is then passed through huge sedimentation tanks.
-
Here solid waste such as faeces is allowed to settle down and the light floatable waste such as soaps, oils, plastics, and grease rise.
-
The material that settles at the bottom is referred to as sludge and the material that rises to the top as scum.
-
The water that comes out of the sedimentation tanks is called clarified water.
Secondary Process:
-
This is a biological process in which the organic matter in the sludge is broken down with the help of bacteria.
-
This process is called digestion and as a result of this process biogas is produced.

Aeration tank
-
This biogas can be used either as a fuel or to produce electricity.
-
The treatment at this stage can be speeded up by allowing water to flow into large aeration tanks, where air is blown onto the sewage.
Tertiary Process:
-
This is basically a chemical process in which chemicals are used to remove phosphorus and nitrogen from the water.
-
Addition of chlorine and exposure to ultraviolet light kills any remaining bacteria and disinfects the water. The water is then discharged into water bodies.
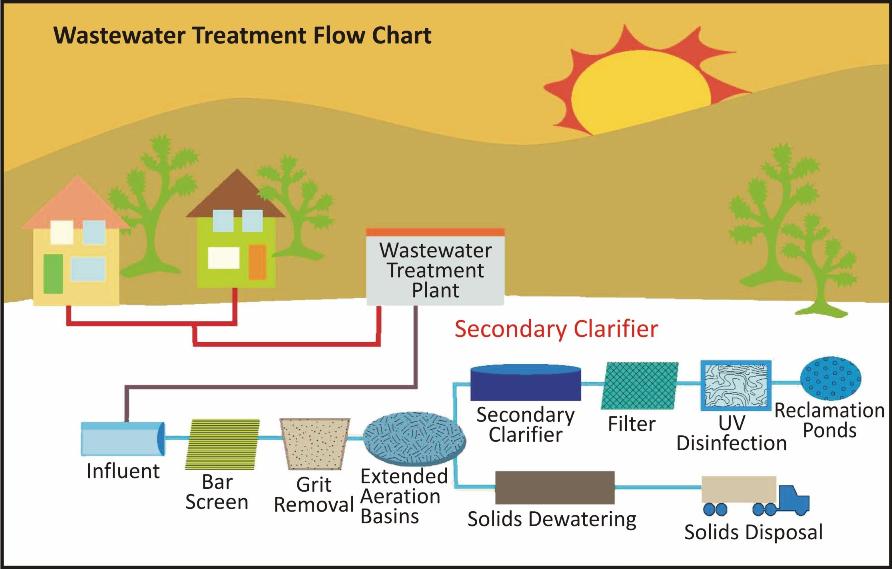
Wastewater treatment flowchart
What happens to the treated water:
-
The treated water is released into water bodies such as streams and rivers.
-
This water can be used again for number of purposes, such as supplying drinking water, spraying fertilizers on to the growing crops, for aquaculture etc.
What happens to the sludge:
-
Sludge consists of human faeces and other organic matter.
-
It also has large amounts of water and needs to be thickened so that it can be easily transported and used as compost in farmlands. There are three methods to do so.

Incinerating
-
Sludge may be incinerated, i.e., burnt into ashes. The ash is used as soil conditioner or as a construction material.

Dewatering
-
Sludge may be dewatered and then combined with other ingredients to make fertilizers.
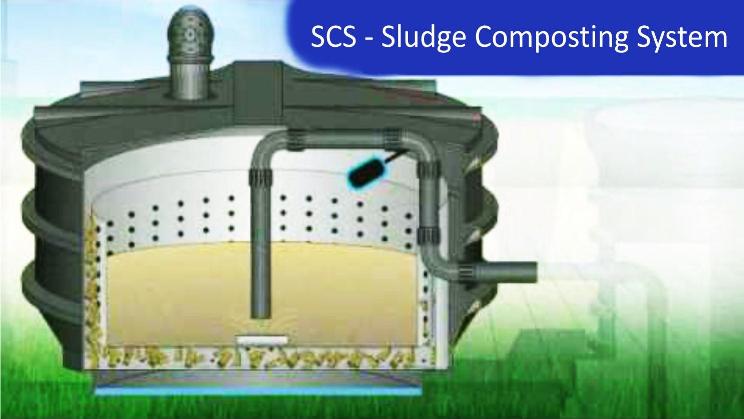
Solid composting
-
Sludge may be composted or processed to produce gases that can be used as fuel.







