SOURCES OF WATER
-
Precipitation in the form of rain or snow provides fresh water to our planet Earth.
-
Most of the fresh water returns to the oceans through rivers flowing across the globe.
-
A small portion of it is absorbed by the soil and is stored underground.
-
A still smaller portion is stored in natural (lakes and ponds) and man-made (tanks and reservoirs) water bodies.
-
Various sources of water can be divided into two main categories:
-
Surface water
-
Underground water or subsoil water
Surface Water:
-
Water present on the surface of the Earth is called surface water.
-
It can further be classified into three categories depending upon the 'purity' of water.
Rain water
River and Lake water
Sea and Ocean water
Rain water:
-
Rainwater is the purest form of water.
-
As water from the seas and rivers evaporate to form water vapour due to the heat of the sun, it leaves behind all the impurities.
-
When precipitation occurs, the first showers dissolve certain gases present in air and also bring suspended impurities along with it. Subsequent showers, however, contain pure water.
River and Lake Water:
-
The water in these water bodies comes either from rainfall or melting of snow (glaciers) on the mountains.
Sea and Ocean water:
-
Oceans are a huge store of water.
-
But the water is salty and is not fit for domestic or agricultural use.
Underground Water or Subsoil Water:
-
Groundwater is the water under the ground where the soil is completely filled or saturated with water.
-
Rainwater seeps through topsoil and layers of rocks like limestone, sand and gravel, and gets collected on top of non-porous layers.
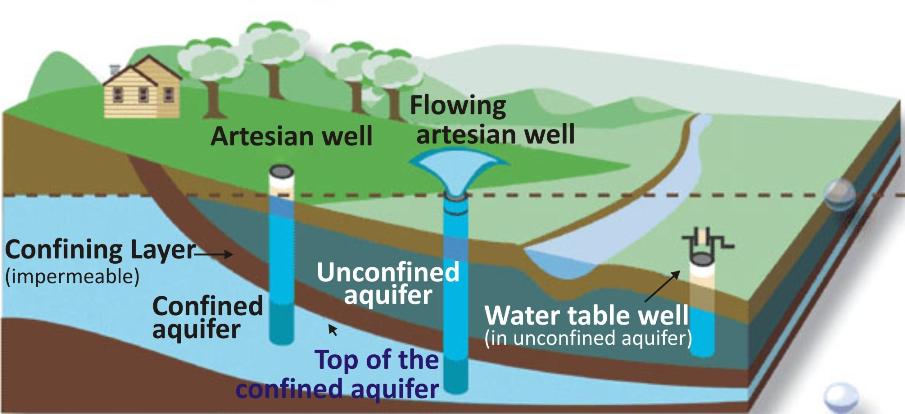
Aquifer
-
The top level of this underground water is called the water table.
-
Underground water is also called an aquifer.
-
The place where the water table meets the land surface, water may come out of the surface in the form of natural spring and flow into a lake, stream or an ocean.
-
Groundwater that meets the land surface also keeps rivers, streams, and lakes filled with water. Wells can also be drilled to take out the underground water.
