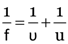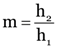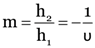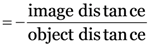Light reflection and refraction Worksheet-14
-
For what position of the object will a convex lens form a virtual and erect image?
-
For what position of an object, a real, inverted and diminished image is formed by a convex lens?
-
An object is placed between F and 2 F of a convex lens. What is the nature of the image formed ?
-
Where should an object be placed in order to use a convex lens as a magnifying glass ?
-
What is the difference between lens formula and mirror formula ?
-
When the image formed by a lens is always virtual, erect and diminished, what is the nature of the lens?
-
What kind of lens can form a
(i) Virtual, erect, diminished image ?
(ii) virtual, erect, magnified image ?
-
What is one dioptre ?
-
How is power of a lens related to its focal length ?
-
Which lens has greater power, a convex lens of focal length 10 cm or a convex lens of focal length 20 cm?
-
What is meant by number of lens ?
-
What is a spherical mirror ?
-
What is the basic difference between a concave mirror and a convex mirror?
-
In a concave mirror, is principal focus a real point? If yes, why?
-
The principal focus of a convex mirror lies at the back of the mirror. Explain.
-
How do you measure quickly the approximate focal length of a concave mirror ?
-
What is meant by linear magnification of a concave mirror?
-
State the expression for linear magnification of a concave mirror in terms of object distance and image distance.
-
What is the nature of image formed when an object is held at a distance of 10 cm from the pole of a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm ?
-
A concave mirror of focal length 20 cm is to be used as a shaving mirror. Which of the following is the suitable object distance from the mirror ?
(i) 10 cm (ii) 20 cm (iii) 30 cm.
Answer:
-
When the object is situated between optical centre and principal focus of the lens.
-
A convex lens forms a real, inverted and diminished image when the object is placed at a distance more than twice the focal length of the lens.
-
Real, inverted and magnified.
-
A convex lens acts as a magnifying glass, when it forms a virtual, erect and magnified image of an object. For this, the object is to be placed between principal focus and optical centre of the lens.
-
The lens formula is
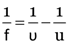 and the mirror formula is
and the mirror formula is 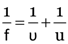
where the symbols have their usual meaning.
-
The lens must be concave.
-
(i) concave lens
(ii) convex lens.
-
One dioptre is the power of a lens of focal length one meter.
-
Power of a lens is reciprocal of the focal length of a lens.
-
A convex lens of smaller focal length has greater power.
-
Number of a lens represents power of the lens (in dioptres). It may be positive or negative.
-
A spherical mirror is that mirror whose reflecting surface is a part of a hollow sphere of glass. One side of the mirror is reflecting and the other side is opaque.
-
In a concave mirror, the reflecting surface is towards the centre of the sphere of which the mirror is a part. In a convex mirror, the reflecting surface is away from the centre of the sphere, of which the mirror is a part.
-
Yes, because the parallel rays reflected from the mirror actually pass through the principal focus of concave mirror.
-
Principal focus of a convex mirror is a virtual point. The parallel rays reflected from convex mirror only appear to come from the principal focus.
-
Hold the concave mirror facing some distant object like a tree.
Hold a cardboard screen in front of the mirror.
Try to adjust the position of the screen so that a sharp image of distant object is formed on the screen.
The distance of screen from the mirror gives the approximate focal length of the concave mirror.
-
Linear magnification (m) of a concave mirror is the ratio of the size of the image (h2) to the size of the object (h1) i.e.
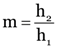
-
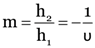
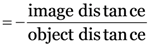
-
The object lies between pole and principal focus of concave mirror. Therefore, the image formed is virtual and erect.
-
For using a concave mirror as a shaving mirror, u < f. Therefore, object distance can only be 10 cm.
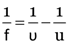 and the mirror formula is
and the mirror formula is