EXPERIMENTS/ACTIVITIES
(1) An Experiment to Show That Exhaled Air Has Carbon Dioxide:
Requirements:
-
Two disposable glasses with covers and a hole on top, two straws, and limewater
Procedure:
-
Fill both the glasses with limewater.
-
Put straws in both the glasses. Air enters in one of the glasses through the straw.
-
In the second, blow out some air (exhaled air).
Observation:
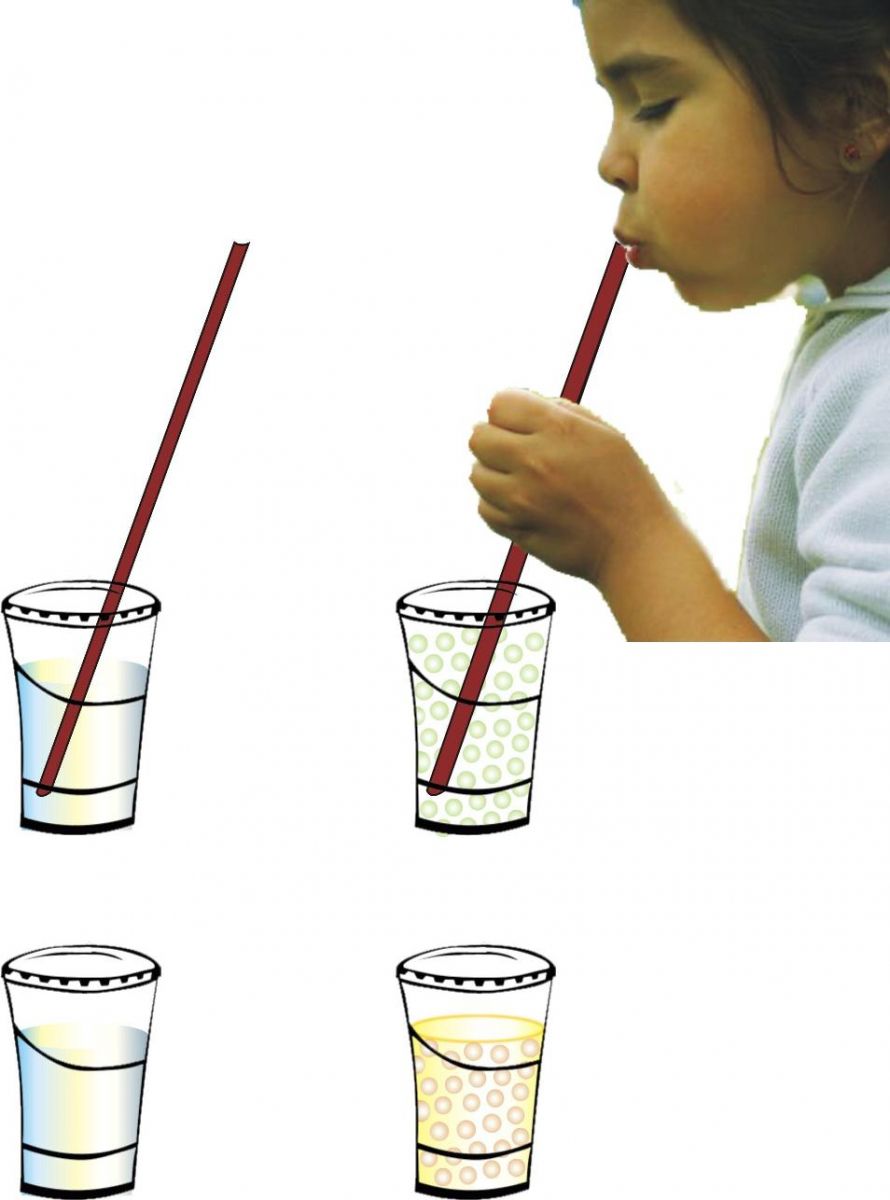

-
The limewater in glass one becomes only slightly milky, while in glass two becomes very milky.
Conclusion:
-
Carbon dioxide has the property of turning limewater milky. Hence, it is true that the exhaled air has more carbon dioxide.
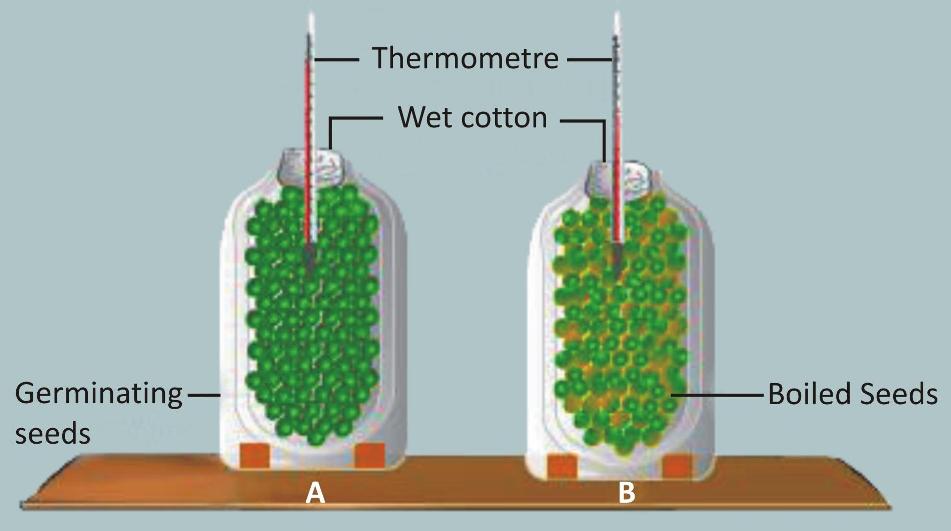
(2) An Experiment to Show That Heat Is Released During Respiration:
Requirements:
-
Two thermos flasks, seeds, formalin or carbolic acid, cotton wool, two thermometers
Procedure:
-
Take two thermos flasks and mark them (A) and (B).
-
Take a glassful of seeds and soak them in water for more than 24 hours.
-
Divide the seeds into two equal groups.
-
Boil one group of seeds and then wash them with dilute formalin or carbolic acid to prevent decay.
-
Put the live germinating seeds in Flask (A) and the killed ones in Flask (B).
-
Insert a thermometre in each flask and plug their mouths with cotton wool.
Observation:
-
After a few hours, the thermometre in Flask (A) shows a higher reading. The thermometre in Flask (B) does not show any rise in temperature.
Conclusion:
-
Germinating seeds give out heat since they are alive and are respiring.
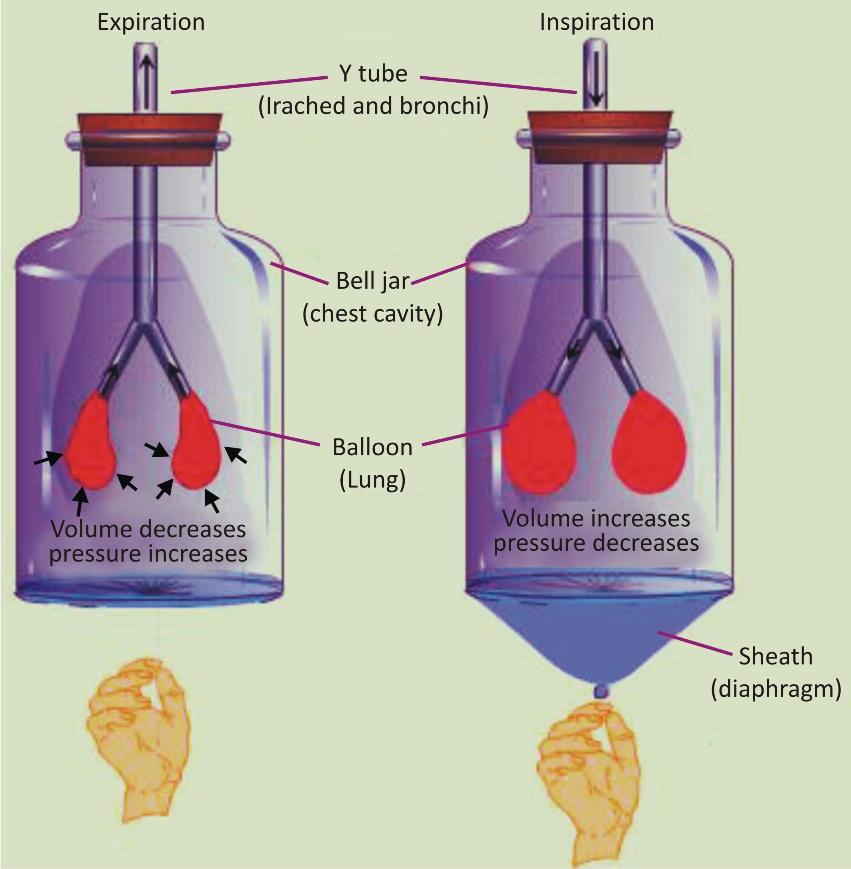
(3) An Experiment to Demonstrate How The Diaphragm Works During Breathing:
Requirements:
-
A bell jar with a cork, straws, a rubber sheet, thread for tying, a balloon
Procedure:
-
With the help of the thread, tie the rubber sheet to the bottom of the bell jar. This represents the diaphragm.
-
Now set up the arrangement with the straws and the balloon as shown in the figure such that the balloon depicts the lungs. Cork the bell jar.
-
Now pull the rubber sheet down. What happens to the balloon?
-
Then push the rubber sheet inside. Now observe what happens to the balloon?
Observation:
-
When the rubber sheet is pulled down, the balloon gets filled with air because the cavity increases and air rushes in. This is exactly what happens in inhalation. The diaphragm expands and the air rushes into the lungs.
-
When the rubber sheet is pushed up, the balloon collapses again. This is similar to exhalation. When the diaphragm contracts, the air rushes out of the lungs.
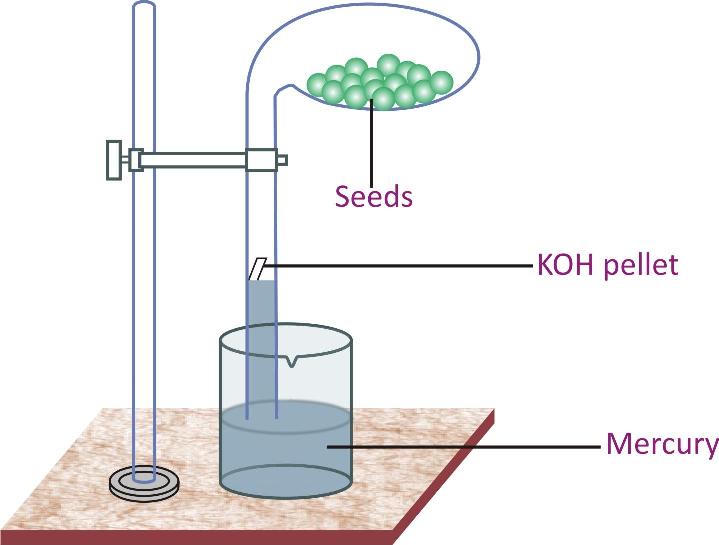
(4) An Experiment to Demonstrate That Oxygen Is Used Up During Aerobic Respiration:
Requirements:
-
Laboratory stand, a round-bottomed glass flask, KOH pellets, mercury, a glass tube, a beaker, some seeds
Procedure:
-
Take a few germinating seeds in the rounded flask and set up the apparatus as shown in the figure.
-
The glass tube is inverted into a beaker containing mercury.
-
KOH pellets are kept inside the set-up as shown. This helps to absorb the carbon dioxide so that it is not used up by the seeds.
-
Another similar set-up without KOH pellets is set up alongside to act as control.
Observation:
-
The mercury level gets raised in the set-up with KOH pellets after a day. No change occurs in the set-up without KOH pellets.
Conclusion:
-
When the oxygen in the apparatus is used up, it lowers the pressure inside the bulb, causing the level of mercury to rise up in the glass tube. This shows that oxygen is used up by the seeds for aerobic respiration.



